Abstract
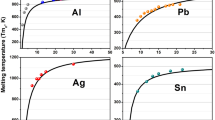
The size dependence of the nanocrystal melting temperature has been investigated based on a nonequilibrium thermodynamics approach. An expression has been derived for the melting temperature that, contrary to the classical Tomson formula, takes into account the metastable character of the crystal nucleus-melt shell equilibrium. Quantitative estimations have been carried out for small spherical particles of aluminum, tin, and lead.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Pawlov: “Uber die Abhangigkeit des Schmelzpunctes von der Oberflachenenergie eines festen Korpers”, Z. Phys. Chem., Bd. 65, (1909), Vol. 1, pp. 1–35, Vol. 5, pp.545–548.
Yu.I. Petrov: Physics of small particles, Nauka, Pub., Moskow, 1982 (in Russian).
V.P. Skripov and V.P. Koverda: Spontaneous crystallization of liquids, Nauka. Pub., Moskow, 1984 (in Russian).
L.M. Shcherbakov, V.M. Samsonov, V.A. Lavrov and O.A. Rybalchenko: “Principles of similarity in thermodynamics of microgeterogenious systems”, Colloid Journal, Vol. 61, (1999), pp. 1–6.
B. Wunderlich: Macromolecular Physics, Vol. 2, Academic Press, New York, San Francisco, London A Subsidiary of Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers, 1974.
M. Schmidt, R. Kusche, H. Haberland and B. von Issendorff “Irregular variation in the melting point of size-selected atomic clusters”, Nature, Vol. 393, (1998), pp. 238–240.
K.F. Peters, J.B. Cohen and Ch. Yip-Wah.: “Melting of Pb nanocrystals.”, Phys. Rev. B., Vol. 57, (1998), pp. 13430–13438.
A. Adamson: Physical chemistry of third edition, 2nd Ed., John Willey and sons, New York, London, Sidney, Toronto, 1967, pp. 113–116.
Yu.V. Naidich, V.M. Perevertailo and N.F. Grigorenco: Capillary fenomena in processes of crystal growth and melting, Naukova dumka, Kiev, 1983.
R. Good: “Contact Angles and Surface Free Energy of Solid”, Surface and Coloid Science, Vol. 11, (1979), pp. 1–30.
N. Eustatopolous: “Energetics of solid/liquid interfaces of metals and alloys”, International Metals Reviews, Vol. 28(4), (1983), pp. 189–210.
G. Kaptay: “A Model for the Solid Liquid Interfacial Energies of Pure Metals” Transactions Toining and Welding Research Institute, Vol. 30, (2001), pp. 245–250.
Ph. Buffat and J.P. Borel: “Size effect on the melting temperature of gold particles” Phys. Rev., Vol. 13(6), (1976), pp. 2287–2298.
R. Haase: Thermodinamik der Irreversiblen Pozesse, Dr. Dietrich Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt, 1963.
Gyarmati: Non-equilibrium thermodynamics spinger, Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York, 1970.
I. Prigogine: Introduction to thermodynamics of irreversible processes, Charles C. Thomas, Springfild, Illinois, 1955.
P. Chambadal: Evolution et applications du concept d'entropie, Dunod, Paris, 1963.
A.I. Rusanov: Phasengleichgewichte und Grenzflaechen erscheinungen, Academie-Verlag, Berlin, 1978.
C.R.W. Wronski: “The size dependence of the melting point of small particles of tin”, Brit. J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 18(12), (1967), pp. 1731–1737.
A.A. Dic, V.N. Skokov and V.P. Koverda: Size dependence of the melting temperature of aluminium island films. Thermodinamic properties of metastable systems and kinetics of phase transitions, Ural scientific center, Sverdlovsk, 1985, pp. 27–29.
V.P. Koverda, V.N. Skokov and V.P. Skripov: “Influence of fluctuations and nonequilibrium facing on the melting of small metallic crystals”, Physics of metals and metal sience, Vol. 51, (1981), pp. 1238–1244. (in Russian).
A.R. Regel and V.M. Glasov: Periodic low and physical properties of electronic melts, Nauka. Pub., Moskow, 1978 (in Russian).
S.I. Popel: Surface Phenomena in Melts, Ural'sk State Technical University, 1994.
Ch. Kittel: Introduction to solid state physics, 4th Ed., John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, London, Sydney, Toronto, 1972.
Kh.B. Khokonov: “The measurement methods of the surface energy and tension of metals and alloys in the solid state”, Surface phenomena in melts and solid phases, Shtiintsa, Kishinev, (1974), pp. 190–261.
V.M. Samsonov: “Conditions for applicability of a thermodynamic description of highly disperse and microheterogeneous systems”, Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry, Vol. 76, (2002), pp. 1863–1867.
A.N. Basulev, V.M. Samsonov, N.Yu. Sdobnyakov: “Thermodynamic perturbation theory calculations of interpose tension in small objects”, Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry, Vol. 76, (2002), pp. 1872–1876.
V.M. Samsonov, A.N. Basulev, N.Yu. Sdobnyakov: “On applicability of the Gibbs thermodynamic to nanoparticles”, Central European Journal of Physics, (2003), (in print).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Samsonov, V.M., Malkov, O.A. Thermodynamic model of crystallization and melting of small particles. centr.eur.j.phys. 2, 90–103 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2478/BF02476274
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/BF02476274
Keywords
- Theoretical methods
- nonequilibrium thermodynamics
- melting temperature
- surface free energy
- interfacial tension
- nanocrystals
- aluminum
- tin and lead particles