Abstract
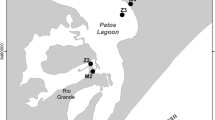
Voltammetric methods using direct insertion of a gold-amalgam microelectrode with a sensitive, computercontrolled voltammeter detected soluble iron(II) sulfide, [FeS]aq, in the porewaters of anoxic, sulfidic, fine-grained sediments from the Loughor Estuary, Wales. The voltammetric results are reproducible. Studies of cores stored in sealed, refrigerated containers for up to 21 d reveal no measurable oxidation. [FeS]aq forms in this estuarine environment as a result of the dissolution of amorphous FeS, and appears to be involved in the formation of pyrite. [FeS]aq makes no significant contribution to the total sulfide and iron contents of the sediment but could constitute an important component of the dissolved Fe(II) and S(−II) contents of the porewater. Mass balance calculations show pyrite forms in this system by the addition of sulfur to FeS rather than by the loss of iron from FeS. The overall process appears to involve [FeS]aq as an intermediary. Although the porewaters of the Loughor Estuary sediments are iron-rich relative to seawater, the iron sulfide-forming process is iron-limited rather than sulfide-limited. Reactive iron is bound to sulfide rapidly in the sediment. After the reactive iron is bound to sulfide, additional sulfide produced is fixed as pyrite.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Berner, R. A. 1970. Sedimentary pyrite formation.American Journal of Science 268:1–23.
Bottrell, S. H., P. K. K. Louie, R. C. Timpe, andS. B. Hawthorne. 1994. The use of stable isotope ratio analysis to assess selectivity of chemical analyses and extractions of forms of sulphur in coal.Fuel 73:1578–1582.
Brendel, P. J. andG. W. Luther, III. 1995. Development of a gold amalgam voltammetric microelectrode for the determination of dissolved Fe, Mn, O2 and S(-II) porewaters of marine and freshwater sediments.Environmental Science and Technology 29:751–761.
Buffle, J., R. De Vitre, D. Perrett, andG. G. Leppard. 1988. Combining field measurements for speciation in non-perturbable water samples, p. 99–124.In J. R. Kramer and H. E. Allen (eds.), Metal Speciation: Theory, Analysis and Application. Lewis Publishers Inc., Boca Raton, Florida.
Chadwell, S. J., D. Rickard, and G. W. Luther, III. In press. Electrochemical evidence for pentasulfide complexes with Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+.Aquatic Geochemistry.
Cotton, F. A. andG. Wilkinson. 1988. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Cramp, A., J. Thomas, and P. J. Brabham. 1995. Hydrodynamics and sedimentation in the Loughor Estuary (Burry Inlet)— Observations from the present and recent past, p. 51–66.In J. Atkins (ed.), Burry Inlet and Loughor Estuary Symposium, State of the Estuary Report, Part 2. Proceedings of the Conference on the Burry Inlet and Loughor Estuary. Swansea City Council, Swansea.
Davison, W., J. Buffle, andR. De Vitre. 1988. Direct polarographic determination of O2, Fe(II), Mn(II), S(-II) and related species in anoxic waters.Pure and Applied Chemistry 60: 1535–1548.
Davison, W., J. Buffle, and R. De Vitre. In press. Voltammetric characterization of a dissolved iron sulphide species by laboratory and field studies.Analytica Chimica Acta.
Davison, W., N. Phillips, andB. J. Tabner. 1998. Soluble iron sulfide species in natural waters: Reappraisal of their stoichiometry and stability constants.Aquatic Science 377:193–203.
Helz, G. R., J. M. Charnock, D. J. Vaughan, andC. D. Garner. 1993. Multinuclearity of aqueous copper and zinc bisulfide complexes: An EXAFS investigation.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 54:15–25.
Huettel, M., W. Ziebis, S. Forster, andG. W. Luther, III. 1998. Advective transport affecting metal and nutrient distributions and interfacial fluxes in permeable sediments.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 62:613–631.
Luther, III,G. W. andT. G. Ferdelman. 1993. Voltammetric characterization of iron(II) sulfide complexes in laboratory solutions and in marine waters and porewaters.Environmental Science and Technology 27:1154–1162.
Luther, III,G. W., D. Rickard, S. M. Theberge, andA. Oldroyd. 1996. Determination of metal (bisulfide) stability constants of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn by voltammetric methods.Environmental Science and Technology 30:671–679.
Meites, L. 1965. Polarographic Techniques, 2nd edition. Wiley Interscience, New York.
Rickard, D. 1975. Kinetics and mechanism of pyrite formation at low temperatures.American Journal of Science 275:636–652.
Rickard, D. 1995. Kinetics of FeS precipitation: 1. Competing reaction mechanisms.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 59:4367–4380.
Rickard, D. andG. W. Luther, III. 1997. Kinetics of pyrite formation by the H2S oxidation of iron (II) monosulfide in aqueous solutions between 25°C and 125°C: The mechanism.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 61:135–147.
Rickard, D., M. A. A. Schoonen, andG. W. Luther, III. 1995. The chemistry of iron sulfides in sedimentary environments, p. 168–193.In V. Vairavamurthy and M. A. A. Schoonen (eds.), Geochemical Transformations of Sedimentary Sulfur. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Schoonen, M. A. A. andH. L. Barnes. 1991. Reactions forming pyrite and marcasite from solution: I. Nucleation of FeS2 below 100°C.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 55:1495–1504.
Theberge, S. andG. W. Luther, III. 1997. Determination of the electrochemical properties of a soluble aqueous FeS species present in sulfidic solutions.Aquatic Geochemistry 3:191–211.
Wilkins, R. T. andH. L. Barnes. 1996. Pyrite formation by reactions of iron monosulfides with dissolved inorganic and organic sulfur species.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 60:4167–4179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rickard, D., Oldroyd, A. & Cramp, A. Voltammetric evidence for soluble FeS complexes in anoxic estuarine muds. Estuaries 22, 693–701 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2307/1353056
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1353056