Abstract
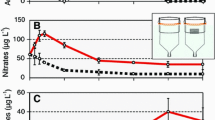
Mussel populations (Mytilus edulis) in the Dutch Wadden Sea (intertidal mussel beds, subtidal beds and culture plots), the culture methods, the extent of mussel culture, and the ecology of the mussel are described. Mussels filter suspended matter from the water column and deposit it as feces and pseudofeces. Mussel beds consume large amounts of phytoplankton and speed up the cycle of production and breakdown of organic matter. There are indications that the consumption of phytoplankton can lead to food shortage for several animal groups. Mussels serve as an important food source for a wide range of organisms (e.g., starfish, eider ducks, and oystercatchers). Because mussel culture increased the mussel biomass in the Dutch Wadden Sea, the impact also increased. The most obvious impact of the culture is the dredging of seed mussels. Overexploitation of intertidal mussel and cockle beds and bad spatfall of both mussels and cockles since 1988 had a negative impact on bird populations. The extent of positive and negative aspects of mussel culture depends on natural and human influences. The negative aspects may (partly) be overcome by appropriate measures. *** DIRECT SUPPORT *** A01BY069 00007
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Asmus, H. 1987. Secondary production of an intertidal mussel bed community related to its storage and turnover compartments.Marine Ecology Progress Series 39:251–266.
Asmus, H. 1988. Experimente zur Nährstoffbilanz der Nordseegewässer. Arbeitsbericht. BAH, Litoralstation List/Sylt. Re 424/6-1. Sylt.
Asmus, H., R. Asmus, andK. Reise. 1990. Exchange processes in an intertidal mussel bed: A Sylt flume study in the Wadden Sea.Bericht der Biolgischen Anstalt Helgoland 6:1–79.
Asmus, R. M. andH. Asmus. 1991. Mussel beds: Limiting of promoting phytoplankton?Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 148:215–232.
Bayne, B. L. andR. C. Newell. 1983. Physiological energetics of marine molluscs, p. 407.In K. M. Wilbur (ed.), The Mollusca, Vol. III. Academic Press, New York.
Bayne, B. L. andC. M. Worrel. 1980. Growth and production of mussels (Mytilus edulis) from two populations.Marine Ecology Progress Series 3:317–328.
Baretta, J. W. and P. Ruardij. 1990. Carbon flows in the Wadden Sea: Model calculations.In J. Ros (ed.), Topics in Marine Biology,Scientia Marina 53:523–528.
Beurkema, J. J. 1976. Biomass and species richness of the macrobenthic animals living on the tidal flats of the Dutch Wadden Sea.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 10:236–261.
Beukema, J. J. 1982. Annual variation in reproductive success and biomass of the major macrozoobenthic species living in a tidal flat area of the Wadden Sea.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 16:37–45.
Beukema, J. J., W. de Bruin, andJ. J. M. Jansen. 1978. Biomass and species richmess of the macrobenthic animals living in the tidal flats of the Dutch Wadden Sea: Long-term changes during a period with mild winters.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 12:58–77.
Blok, J. W. De andHannie J. F. M. Geelen. 1958. The substratum required for the settling of mussels (Mytilus edulis L.).Archives Neerlandaises Zoologie, Tome XIII. I. Suppl. 1958; 446–460.
Cadée, G. C. 1980. Reappraisal of the production and import of organic carbon in the western Wadden Sea.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 14:305–322.
Cadée, G. C. 1982. Tidal and seasonal variation in particulate and dissolved carbon in the western Dutch Wadden Sea and Marsdiep tidal inlet.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 16:228–249.
Cadée, G. C. andJ. J. Hegeman. 1974. Primary production of phytoplankton in the Dutch Wadden Sea.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 8:240–259.
Common Wadden Sea Secretariat. 1992. Mussel fishery in the Wadden Sea. Working Document 1991–2, revised version 1992. Wilhelmshaven. 56 p.
Coosen, J. andA. C. Smaal. 1985. Jaargemiddelde biomassa en activiteit van de dominante bodemdieren in de Oosterschelde. Balansrapport 1985–12. Deltadients, Middelburg. 81 p.
Dame, R. andN. Dankers. 1988. Uptake and release of materials by a Wadden Sea mussel bed.Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 118:207–216.
Dame, R., N. Dankers, T. Prins, H. Jongsma, andA. Smaal. 1991. The influence of mussel beds on nutrients in the western Wadden Sea and eastern Scheldt estuaries.Estuaries 14: 130–138.
Dankers, N. andK. Koelemaij. 1989. Variations in the mussel population of the Dutch Wadden Sea in relation to monitoring.Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 43:529–535.
Dankers, N. andJ. de Vlas. 1992. Multifunctioneel beheer in de Waddenzee-Integratie van natuurbeheer en schelpdiervisserij. RIN-rapport 92/15. DLO-Instiuut voor Bos-en Natuurbeheer. Texel, The Netherlands.
Dankers, N., K. Koelemij, andJ. Zegers. 1989a. De rol van de mossel en de mosselcultuur in het ecosysteem van de Waddenzee. RIN-rapport 89/9. Rijksintituut voor Natuurbeheer, Texel, The Netherlands.
Dankers, N., R. Dame, and K. Kersting. 1989b. The oxygen consumption of mussel beds in the Dutch Wadden Sea.In J. Ros (ed.), Topics in Marine Biology.Scientia Marina 53:473–476.
Dare, P. J. 1976. Settlement, growth and production of the musselMytilus edulis L. in Morecambe Bay, England.Fishery Investigation, London (Ser. 2) 28:1–25.
Dare, P. J. andD. B. Edwards. 1975. Seasonal changes in flesh weight and biochemical composition of mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) in the Conwy estuary, North Wales.Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 18:89–97.
Dekker, R. 1987. The importance of the subtidal macrobenthos as a food source for the Wadden Sea ecosystem. Proceedings of the 5th International Wadden Sea Symposium, Esbjerg.Biologiske Meddelser 37:27–36.
Dekker, R. 1989. The macro-benthos of the subtidal western Dutch Wadden Sea: 1. Biomass and species richness.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 23:57–68.
Dijkema, K. S., G. van Tienen, andJ. G. van Beek. 1989. Habitats of the Netherlands, German and Danish Wadden Sea 1:sn100,000. Veth Foundation/Research Institute for Nature Management. Texel, The Netherlands.
Dittmann, S. 1990. Mussel beds—Amensalism or amelioration for intertidal fauna.Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 44:335–352.
Frechette, M. andE. Bourget. 1985a. Food limited growth ofMytilus edulis L. in relation to the benthic boundary layer.Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 42:1166–1170.
Frechette, M. andE. Bourget. 1985b. Energy flow between the pelagic and benthic zones: Factors controlling particulate organic matter available to an intertidal mussel bed.Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 42:1158–1165.
Heral, M., J. M. Deslous Paoli, andJ. Prou. 1986. Dynamiques de production et des biomasses des huîtres creuses cultivées (Crassostrea angulata etCrassostrea gigas) dans le bassin de Marennes Oléron depuis un siecle. ICES CM 1986/F: 41. Mariculture Committee, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Hulscher, J. B. 1980. Oystercatcher (Haematopus ostralegus L.).In C. J. Smit and W. J. Wolff (eds.), Birds of the Wadden Sea. Balkema, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
Kamps, L. F. 1962. Mud distribution and land reclamation in the eastern Wadden shallows.Rijkswaterstaat Communications Rijkswaterstaat. Den Haag, The Netherlands.
Kesteloo-Hendrikse, J. J. andM. R. van Stralen. 1992. Het kokkelbestand in de Oosterschelde, de Westerschelde en de Waddenzee in 1992. RIVO-rapport AQ 92-06. Rijksinstituut voor Visserijonderzoek. Ijmuiden.
Korringa, V. 1956. Oyster culture and biological productivity.Rapports et Proces-verbaux des Réunions Conseil Permanent International pour l'Exploration de la Mer. 140:30/31, 59–61.
Kuenen, D. J. 1942. On the distribution of mussels on the intertidal sand flats near Den Helder.Archives Neerlandaises Zoologie 6:117–160.
Kuip, C. van de 1991. Wanbeleid in de Waddenzee kost duizenden vogels het leven.Vogels 66:230–235.
Lasiewski, R. C. andW. R. Dawson. 1976. A re-examination of the relation between standard metabolic rate and the body weight in birds.Condor 69:13–23.
Maas-Geesteranus, R. A. 1942. On the formation of banks byMytilus edulis L.Archives Neerlandaises Zoologie 6:283–326.
McGrorty, S., R. T. Clark, C. J. Reading, andJ. D. Goss-Custard. 1990. Population dynamics of the musselMytilus edulis. Density changes and regulations of the population in the Exe estuary, Devon.Marine Ecology Progress Series 67:157–169.
Möbius, K. 1877. Die Auster und die Austernwirtschaft. Wiegund Hempel and Parey, Berlin.
Obert, B. andH. Michaelis. 1991. History and ecology of the mussel beds (Mytilus edulis L.) in the catchment area of a Wadden Sea tidal inlet, p. 185–194.In M. Elliot and J. P. Ducrotoy (eds.), Estuaries and Coasts: Spatial and Temporal Intercomparisons. Olsen and Olsen, Fredensburg, Denmark.
Peterson, C. H. andR. Black. 1987. Resource depletion by active suspension feeders on tidal flats: Influence of local density and tidal evaluation.Limnology and Oceanography 32:143–166.
Prins, T. C. andA. C. Smaal. 1990. Benthic-pelagic coupling: The release of inorganic nutrients by an intertidal bed ofMytilus edulis, p. 89–103.In M. Barnes and R. M. Gibson (eds.), Trophic Relationships in the Marine Environment. Proceedings of the 24th European Marine Biology Symposium Aberdeen University Press, Scotland.
Reise, K. 1982. Long-term changes in the macrobenthic invertebrate fauna of the Wadden Sea: Are polychaetes about to take over?Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 16:29–36.
Reise, K., E. Herre, andM. Sturm. 1989. Historical changes in the benthos of the Wadden Sea around the island of Sylt in the North Sea.Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 43:417–433.
Riesen, W. andK. Reise. 1982. Macrobenthos of the subtidal Wadden Sea: Revisited after 55 years.Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 35:409–423.
Rijksinstituut voor Natuurbeheer. 1987. Effecten van kokkelvisserij in de Waddenzee. RIN-rapport 87/18.
Rodhouse, P. G., C. M. Roden, G. M. Burnell, M. P. Hensey, T. McMahon, B. Ottway, andT. H. Ryan. 1984. Food resource, gametogenesis, and growth ofMytilus edulis on the shore and in suspended culture: Killary Harbour, Ireland.Journal of Marine Biology Assessment UK 64:513–529.
Seed, R. 1993. Invertebrate predators and their role in structuring coastal and estuarine populations of filter feeding bivalves, p. 149–195.In R. F. Dame (ed.), Bivalve Filter Feeders in Coastal and Estuarine Ecosystem Processes. Springer, Berlin.
Smaal, A. C. 1991. The ecology and cultivation of mussels: New advances.Aquaculture 94:245–261.
Smaal, A. C. andM. R. van Stralen. 1990. Average annual growth and condition of mussels as a function of food supply.Hydrobiologia 195:179–188.
Smit, C. J. 1980. Production of biomass by invertebrates and consumption by birds in the Dutch Wadden Sea, p. 290–301.In C. J. Smit and W. J. Wolff (eds.), Birds of the Wadden Sea. Balkema, Rotterdam.
Straaten, L. M. J. U. van. 1965. De bodem der Waddenzee. Het Waddenboek. Thieme, Zutphen.
Stralen, M. van. 1990. Het kokkelbestand in de Oosterschelde en de Waddenzee in 1990. RIVO-rapport AQ90-03. Rijksinstituut voor Visserijonderzoek. IJmuiden.
Stralen, M. R. van, andR. Dijkema. 1993. Mussel culture in a changing environment: The effects of a coastal engineering project on mussel culture in the Oosterschelde, p. 359–379.In P. Nienhuis and R. C. Smaal (eds.), The Oosterschelde Estuary (The Netherlands): Case Study of a Changing Ecosystem. Kluwer, Dordrecht.
Stralen, M. van andJ. Kesteloo-Hendrikse 1992. Het kok-kelbestand en de broedval van kokkels in de Oosterschelde en de Waddenzee in 1991. RIVO-rapport AQ 92-05. Rijksinstituut voor Visserijonderzoek, IJmuiden.
Swennen, C. 1976. Population structure and food of the eiderSomateria mollissima in the Dutch Wadden Sea.Ardea 64:311–371.
Swennen, C., G. Nehls, andK. Laursen. 1989. Numbers and distribution of eidersSomateria mollissima in the Wadden Sea,Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 24:83–92.
Verhagen, J. 1983. A distribution and population model of mussels (Mytilus edulis) in Lake Grevelingen, p. 373–383.In G. V. Skogerbol and M. Flug (eds), Analysis of Ecological Systems: State of the Art in Ecological Modelling. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Verwey, J. 1952. On the ecology and distribution, of cockle and mussel in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Their role in sedimentation and the source of their food supply. With a short review of the feeding behaviour of bivalve molluscs.Archives Neerlandaises Zoologie 10:171–239.
Vries, I. de andC. F. Hopstaken. 1984. Nutrient cycling and ecosystem behaviour in a salt-marsh lake.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 18:221–245.
Zimmerman, J. T. F. 1976. Mixing and flushing of tidal embayments in the western Dutch Wadden Sea. Part. I. Distribution of salinity and calculation of mixing timescales.Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 10:149–191.
Zuidema, D. 1988. De rol van de mossel (Mytilus edulis) in het ecosysteem van de westelijke Wadden Sea. Intern rapport. Netherlands Institute for Sea Research, Texel, The Netherlands.
Zwarts, L. 1991. Mosselbanken: Wadvogels op een kluitje.Vogels 66:8–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dankers, N., Zuidema, D.R. The role of the mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) and mussel culture in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Estuaries 18, 71–80 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2307/1352283
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1352283