Abstract
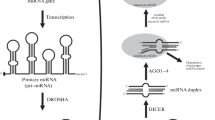
MiroRNAs (miRNAs) are double-stranded, noncoding RNA molecules (with an average size of 22bp) that serve as post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression in higher eukaryotes. miRNAs play an important role in development and other cellular processes by hybridizing with complementary target mRNA transcripts, preventing their translation and thereby destabilizing the target transcripts. Though hundreds of miRNAs have been discovered in a variety of organisms, little is known about their cellular function. They have been implicated in the regulation of developmental timing and pattern formation, restriction of differentiation potential, regulation of insulin secretion, resistance to viral infection, and in genomic rearrangements associated with carcinogenesis or other genetic disorders, such as fragile X syndrome. Recent evidence suggests that the number of unique miRNA genes in humans exceeds 1000, and may be as high as 20 000. It is estimated that 20–30% of all human mRNAs are miRNA targets.
During the last few years, special attention has been given to miRNAs as candidate drug targets for cancer, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and viral diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 2003; 113(6): 673–6
Bartel B, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: at the root of plant development? Plant Physiol 2003; 132(2): 709–17
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116(2): 281–97
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000; 408(6808): 86–9
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993; 75(5): 843–54
Lakatos L, Csorba T, Pantaleo V, et al. Small RNA binding is a common strategy to suppress RNA silencing by several viral suppressors. EMBO J 2006; 25(12): 2768–80
Yu B, Chapman EJ, Yang Z, et al. Transgenically expressed viral RNA silencing suppressors interfere with microRNA methylation in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett 2006; 580(13): 3117–20
Grey F, Antoniewicz A, Allen E, et al. Identification and characterization of human cytomegalovirus-encoded microRNAs. J Virol 2005; 79(18): 12095–9
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, et al. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 2002; 16(13): 1616–26
Lai EC, Tomancak P, Williams RW, et al. Computational identification of Drosophila microRNA genes. Genome Biol 2003; 4(7): R42
Lim LP, Lau NC, Weinstein EG, et al. The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev 2003; 17(8): 991–1008
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 2005; 37(7): 766–70
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, et al. Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell 2005; 120(1): 21–4
Tuccoli A, Poliseno L, Rainaldi G. miRNAs regulate miRNAs: coordinated transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation. Cell Cycle 2006; 5 (21): Epub ahead of print
Matzke M, Aufsatz W, Kanno T, et al. Genetic analysis of RNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004; 1677(1–3): 129–41
Jia S, Noma K, Grewal SI. RNAi-independent heterochromatin nucleation by the stress-activated ATF/CREB family proteins. Science 2004; 304(5679): 1971–6
Martienssen R, Lippman Z, May B, et al. Transposons, tandem repeats, and the silencing of imprinted genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 2004; 69: 371–9
Martienssen RA, Zaratiegui M, Goto DB. RNA interference and heterochromatin in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Trends Genet 2005 Aug; 21(8): 450–6
Mette MF, Matzke AJ, Matzke MA. Resistance of RNA-mediated TGS to HC-Pro, a viral suppressor of PTGS, suggests alternative pathways for dsRNA processing. Curr Biol 2001 Jul 24; 11(14): 1119–23
Sleutels F, Zwart R, Barlow DP. The non-coding Air RNA is required for silencing autosomal imprinted genes. Nature 2002 Feb 14; 415(6873): 810–3
Noma K, Sugiyama T, Cam H, et al. RITS acts in cis to promote RNA interference-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional silencing. Nat Genet 2004 Nov; 36(11): 1174–80
Robins H, Li Y, Padgett RW. Incorporating structure to predict microRNA targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102(11): 4006–9
Kim VN, Nam JW. Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet 2006; 22(3): 165–73
Hill AE, Hong JS, Wen H, et al. Micro-RNA-like effects of complete intronic sequences. Front Biosci 2006; 11: 1998–2006
Ying SY, Lin SL. Intronic microRNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 326(3): 515–20
Ying SY, Lin SL. Intron-derived microRNAs: fine tuning of gene functions. Gene 2004; 342(1): 25–8
Ying SY, Lin SL. Current perspectives in intronic micro RNAs (miRNAs). J Biomed Sci 2006; 13(1): 5–15
Stole V, Samanta MP, Tongprasit W, et al. Identification of transcribed sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana by using high-resolution genome tiling arrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102(12): 4453–8
Robins H, Press WH. Human microRNAs target a functionally distinct population of genes with AT-rich 3′ UTRs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102(43): 15557–62
Xie X, Lu J, Kulbokas EJ, et al. Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 3′ UTRs by comparison of several mammals. Nature 2005; 434(7031): 338–45
Jing Q, Huang S, Guth S, et al. Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA instability. Cell 2005; 120(5): 623–34
Ambros V, Lee RC, Lavanway A, et al. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr Biol 2003; 13(10): 807–18
Tijsterman M, Plasterk RH. Dicers at RISC: the mechanism of RNAi. Cell 2004; 117(1): 1–3
Yang WJ, Yang DD, Na S, et al. Dicer is required for embryonic angiogenesis during mouse development. J Biol Chem 2005; 280(10): 9330–5
Lee YS, Nakahara K, Pham JW, et al. Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell 2004; 117(1): 69–81
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005; 120(1): 15–20
Vella MC, Reinert K, Slack FJ. Architecture of a validated microRNA::target interaction. Chem Biol 2004; 11(12): 1619–23
Cullen BR. Transcription and processing of human microRNA precursors. Mol Cell 2004; 16(6): 861–5
Cai X, Hagedorn CH, Cullen BR. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA 2004; 10(12): 1957–66
Doench JG, Petersen CP, Sharp PA. siRNAs can function as miRNAs. Genes Dev 2003; 17(4): 438–42
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, et al. Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev Biol 2006; 289(1): 3–16
Meyers BC, Souret FF, Lu C, et al. Sweating the small stuff: microRNA discovery in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2006; 17(2): 139–46
Carrington JC, Ambros V. Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 2003; 301(5631): 336–8
Ambros V. microRNAs: tiny regulators with great potential. Cell 2001; 107(7): 823–6
Pasquinelli AE, Ruvkun G. Control of developmental timing by micrornas and their targets. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2002; 18: 495–513
Finnegan EJ, Matzke MA. The small RNA world. J Cell Sci 2003; 116 (Pt 23): 4689–93
Ruvkun GB. The tiny RNA world. Harvey Lect 2003; 99: 1–21
Ideker T, Thorsson V, Ranish JA, et al. Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of a systematically perturbed metabolic network. Science 2001; 292(5518): 929–34
Hobert O. Common logic of transcription factor and microRNA action. Trends Biochem Sci 2004; 29(9): 462–8
Dieterich C, Grossmann S, Tanzer A, et al. Comparative promoter region analysis powered by CORG. BMC Genomics 2005; 6(1): 24
Scitz H, Royo H, Lin SP, et al. Imprinted small RNA genes. Biol Chem 2004; 385(10): 905–11
Ronemus M, Martienssen R. RNA interference: methylation mystery. Nature 2005;433(7025): 472–3
Gyory I, Minarovits J. Epigenetic regulation of lymphoid specific gene sets. Biochem Cell Biol 2005; 83(3): 286–95
Bentwich I. A postulated role for microRNA in cellular differentiation. Faseb J 2005; 19(8): 875–9
Cheng LC, Tavazoie M, Doetsch F. Stem cells: from epigenetics to microRNAs. Neuron 2005; 46(3): 363–7
Cawley S, Bekiranov S, Ng HH, et al. Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of noncoding RNAs. Cell 2004 Feb 20; 116(4): 499–509
Kampa D, Cheng J, Kapranov P, et al. Novel RNAs identified from an in-depth analysis of the transcriptome of human chromosomes 21 and 22. Genome Res 2004 Mar; 14(3): 331–42
Lall S, Grun D, Krek A, et al. A genome-wide map of conserved microRNA targets in C. elegans. Curr Biol 2006; 16(5): 460–71
Rajewsky N. microRNA target predictions in animals. Nat Genet 2006; 38Suppl. 1 (6s): S8–S13
Calin GA, Croce CM. Genomics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia microRNAs as new players with clinical significance. Semin Oncol 2006; 33(2): 167–73
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNAs and chromosomal abnormalities in cancer cells. Oncogene 2006; 25(46): 6202–10
Jannot G, Simard MJ. Tumour-related microRNAs functions in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oncogene 2006; 25(46): 6197–201
Kent OA, Mendell JT. A small piece in the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes. Oncogene 2006; 25(46): 6188–96
Jovanovic M, Hengartner MO. miRNAs and apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene 2006; 25(46): 6176–87
Dalmay T, Edwards DR. MicroRNAs and the hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene 2006; 25(46): 6170–5
Hutvagner G. MicroRNAs and cancer: issue summary. Oncogene 2006; 25(46): 6154–5
Osada H, Takahashi T. MicroRNAs in biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2007 Jan; 28(1): 2–12
Zhang L, Coukos G. MicroRNAs: a new insight into cancer genome. Cell Cycle 2006 Oct; 5(19): 2216–9
Saito Y, Jones PA. Epigenetic activation of tumor suppressor microRNAs in human cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2006 Oct; 5(19): 2220–2
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102(39): 13944–9
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, et al. MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004; 101(32): 11755–60
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, et al. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2005; 353(17): 1793–801
Sevignani C, Calin GA, Siracusa LD, et al. Mammalian microRNAs: a small world for fine-tuning gene expression. Mamm Genome 2006; 17(3): 189–202
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, et al. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 2006; 25(17): 2537–45
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, et al. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 2007 Mar; 120(5): 1046–54
Hossain A, Kuo MT, Saunders GF. Mir-17-5p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting translation of AIB1 mRNA. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26(21): 8191–201
Sun Y, Koo S, White N, et al. Development of a micro-array to detect human and mouse microRNAs and characterization of expression in human organs. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32(22): el88
Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, et al. MicroRNA-143 regulates adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279(50): 52361–5
Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J, et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 2004; 432(7014): 226–30
Krutzfeldt J, Stoffel M. MicroRNAs: a new class of regulatory genes affecting metabolism. Cell Metab 2006; 4(1): 9–12
Zhao Y, Samal E, Srivastava D. Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature 2005; 436(7048): 214–20
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Liu N, et al. A signature pattern of stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006; 103(48): 18255–60
Cao X, Yeo G, Muotri AR, et al. Noncoding RNAs in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 2006; 29: 77–103
Bilen J, Liu N, Burnett BG, et al. MicroRNA pathways modulate polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration. Mol Cell 2006; 24(1): 157–63
Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, et al. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific microRNA. Science 2005 Sep 2; 309(5740): 1577–81
Zhang J, Yamada O, Sakamoto T, et al. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication by pol Ill-directed overexpression of RNA decoys corresponding to stem-loop structures in the NS5B coding region. Virology 2005; 342(2): 276–85
Bennasser Y, Le SY, Yeung ML, et al. MicroRNAs in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. Methods Mol Biol 2006; 342: 241–53
Cullen BR. Is RNA interference involved in intrinsic antiviral immunity in mammals? Nat Immunol 2006; 7(6): 563–7
Berezikov E, Thuemmler F, van Laake LW, et al. Diversity of microRNAs in human and chimpanzee brain. Nat Genet 2006; 38(12): 1375–7
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation (grant EIA-0205061) to Dr Ray and a grant from the Memorial Health Medical Center to Dr Perera.
The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perera, R.J., Ray, A. MicroRNAs in the Search for Understanding Human Diseases. BioDrugs 21, 97–104 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200721020-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200721020-00004