Abstract
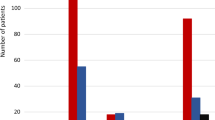
Olanzapine/fluoxetine (Symbyax®) is an oral once-daily fixed-dose combination of the atypical antipsychotic olanzapine and the SSRI fluoxetine that is approved in the US for the treatment of depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder in adults. Combination therapy with olanzapine plus fluoxetine is effective in the treatment of patients with acute bipolar depression. The combination improves depressive symptoms and symptom severity in this patient population, with an efficacy greater than that of olanzapine alone or lamotrigine. Furthermore, olanzapine plus fluoxetine is generally well tolerated. Although associated with weight gain and potential elevations in glucose, lipid and prolactin levels, the combination does not increase the risk of treatment-emergent mania. Additional placebo- and active comparator-controlled studies are required in order to confirm the efficacy of olanzapine/fluoxetine in the treatment of bipolar depression and to definitively position olanzapine/fluoxetine with respect to other agents. In the meantime, fixed-dose olanzapine/fluoxetine offers an effective and generally well tolerated first-line option for the treatment of acute bipolar depression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deeks ED, Keating GM. Olanzapine/fluoxetine: a review of its use in the treatment of acute bipolar depression. Drugs 2008; 68(8): 1115–37
Bhana N, Perry CM. Olanzapine: a review of its use in the treatment of bipolar I disorder. CNS Drugs 2001; 15(11): 871–904
Yatham LN, Goldstein JM, Vieta E, et al. Atypical antipsychotics in bipolar depression: potential mechanisms of action. J Clin Psychiatry 2005; 66Suppl. 5: 40–8
Eli Lilly and Company. Symbyax® (olanzapine and fluoxetine HCL capsules): US prescribing information [online]. Available from URL: http://pi.lilly.com/us/symbyax-pi.pdf [Accessed 2007 Oct 17]
Hurst M, Lamb HM. Fluoxetine: a review of its use in anxiety disorders and mixed anxiety and depression. CNS Drugs 2000; 14(1): 51–80
Benfield P, Heel RC, Lewis SP. Fluoxetine: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in depressive illness. Drugs 1986; 32: 481–508
Koch S, Perry KW, Bymaster FP. Brain region and dose effects of an olanzapine/fluoxetine combination on extracellular monoamine concentrations in the rat. Neuropharmacology 2004 Feb; 46(2): 232–42
Zhang W, Perry KW, Wong DT, et al. Synergistic effects of olanzapine and other antipsychotic agents in combination with fluoxetine on norepinephrine and dopamine release in rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000 Sep; 23(3): 250–62
Maragnoli ME, Fumagalli F, Gennarelli M, et al. Fluoxetine and olanzapine have synergistic effects in the modulation of fibroblast growth factor 2 expression within the rat brain. Biol Psychiatry 2004 Jun 1; 55(11): 1095–102
Gossen D, de Suray J-M, Vandenhende F, et al. Influence of fluoxetine on olanzapine pharmacokinetics. AAPS PharmSci 2002; 4(2): E11
Bergemann N, Frick A, Parzer P, et al. Olanzapine plasma concentration, average daily dose, and interaction with co-medication in schizophrenic patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 2004 Mar; 37(2): 63–8
Brown EB, McElroy SL, Keck Jr PE, et al. A 7-week, randomized, double-blind trial of olanzapine/fluoxetine combination versus lamotrigine in the treatment of bipolar I depression. J Clin Psychiatry 2006 Jul; 67(7): 1025–33
Tohen M, Vieta E, Calabrese J, et al. Efficacy of olanzapine and olanzapine-fluoxetine combination in the treatment of bipolar I depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003 Nov; 60(11): 1079–88
Shi L, Namjoshi MA, Swindle R, et al. Effects of olanzapine alone and olanzapine/fluoxetine combination on health-related quality of life in patients with bipolar depression: secondary analyses of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Clin Ther 2004 Jan; 26(1): 125–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Adapted and reproduced from Drugs 2008; 68 (8): 1115–1137. The full text article[1] was reviewed by: R. Bottlender, Newham Centre for Mental Health, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK; J. Cookson, The Royal London Hospital, London, UK; T. Denko, Department of Psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA; H.C.R. Grunze, School of Neurology, Neurobiology and Psychiatry, University of Newcastle, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK; S. Kasper, Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria. The manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the original article during the peer review process. Changes based on any comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit. The preparation of the original article and this spotlight was not supported by any external funding
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deeks, E.D., Keating, G.M. Spotlight on Olanzapine/Fluoxetine in Acute Bipolar Depression. CNS Drugs 22, 793–795 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-200822090-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-200822090-00006