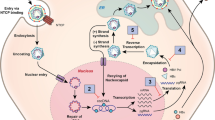
Abstract
Currently available anti-hepatitis C virus (HCV) therapy is effective in only half of infected patients and is limited by adverse effects that often necessitate discontinuation. Therefore, new treatments are being developed, including optimization of current standard treatment with peginterferon plus ribavirin, specifically targeted antiviral therapy for HCV, novel immunomodulatory agents and treatments aimed at reducing fibrosis. This review focuses on novel anti-HCV drugs that are currently in an advanced stage of clinical development. Albinterferon-α-2b, a fusion molecule of albumin and interferon-α-2b, has a longer half-life than peginterferon, which enables a bi-weekly administration interval. Preliminary data indicate similar response rates for albinterferon-α-2b plus ribavirin compared with peginterferon-α-2b plus ribavirin, but possible benefits with respect to quality of life. Telaprevir, a NS3/4 protease inhibitor, demonstrated a rapid and profound antiviral effect in phase I trials that was synergistic with that of peginterferon-α-2a. Recently completed phase II trials on triple combination treatment with telaprevir, peginterferon-α-2a and ribavirin given for 12–24 weeks reported sustained virological response in up to 68% of patients with treatment-naive HCV genotype 1 infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Hoofnagle JH, Mullen KD, Jones DB, et al. Treatment of chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis with recombinant human alpha interferon: a preliminary report. N Engl J Med 1986; 315(25): 1575–8
Lohmann V, Korner F, Koch J, et al. Replication of subgenomic hepatitis C virus RNAs in a hepatoma cell line. Science 1999; 285(5424): 110–3
Lindenbach BD, Evans MJ, Syder AJ, et al. Complete replication of hepatitis C virus in cell culture. Science 2005; 309(5734): 623–6
Lindenbach BD, Rice CM. Unravelling hepatitis C virus replication from genome to function. Nature 2005; 436(7053): 933–8
Appel N, Schaller T, Penin F, et al. From structure to function: new insights into hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J Biol Chem 2006; 281(15): 9833–6
Dubuisson J. Hepatitis C virus proteins. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(17): 2406–15
De Francesco R, Migliaccio G. Challenges and successes in developing new therapies for hepatitis C. Nature 2005; 436(7053): 953–60
McHutchison JG, Bartenschlager R, Patel K, et al. The face of future hepatitis C antiviral drug development: recent biological and virologic advances and their translation to drug development and clinical practice. J Hepatol 2006; 44(2): 411–21
Parfieniuk A, Jaroszewicz J, Flisiak R. Specifically targeted antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(43): 5673–81
Deutsch M, Hadziyannis SJ. Old and emerging therapies in chronic hepatitis C: an update. J Viral Hepat 2008; 15(1): 2–11
Tong M, Schiff E, Jensen DM, et al. Preliminary analysis of a phase II study of heptazyme (TM), a nuclease resistant ribozyme targeting hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA [abstract]. Hepatology 2002: 36 (4 Pt 2 Suppl. S): 788
McHutchison JG, Patel K, Pockros P, et al. A phase I trial of an antisense inhibitor of hepatitis C virus (ISIS 14803), administered to chronic hepatitis C patients. J Hepatol 2006; 44(1): 88–96
Volarevic M, Smolic R, Wu CH, et al. Potential role of RNAi in the treatment of HCV infection. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2007; 5(5): 823–31
Goudreau N, Llinas-Brunet M. The therapeutic potential of NS3 protease inhibitors in HCV infection. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2005; 14(9): 1129–44
Chen SH, Tan SL. Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of HCV NS3-4A protease as potential therapeutic agents against HCV infection. Curr Med Chem 2005; 12(20): 2317–42
Lamarre D, Anderson PC, Bailey M, et al. An NS3 protease inhibitor with antiviral effects in humans infected with hepatitis C virus. Nature 2003; 426(6963): 186–9
Hinrichsen H, Benhamou Y, Wedemeyer H, et al. Short-term antiviral efficacy of BILN 2061, a hepatitis C virus serine protease inhibitor, in hepatitis C genotype 1 patients. Gastroenterology 2004; 127(5): 1347–55
Reiser M, Hinrichsen H, Benhamou Y, et al. Antiviral efficacy of NS3-serine protease inhibitor BILN-2061 in patients with chronic genotype 2 and 3 hepatitis C. Hepatology 2005; 41(4): 832–5
Vanwolleghem T, Meuleman P, Libbrecht L, et al. Ultra-rapid cardiotoxicity of the hepatitis C virus protease inhibitor BILN 2061 in the urokinase-type plasminogen activator mouse. Gastroenterology 2007; 133(4): 1144–55
Reesink HW, Zeuzem S, Weegink CJ, et al. Rapid decline of viral RNA in hepatitis C patients treated with VX-950: a phase Ib, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Gastroenterology 2006; 131(4): 997–1002
Lin C, Gates CA, Rao BG, et al. In vitro studies of cross-resistance mutations against two hepatitis C virus serine protease inhibitors, VX-950 and BILN 2061. J Biol Chem 2005; 280(44): 36784–91
Kieffer TL, Sarrazin C, Miller JS, et al. Telaprevir and pegylated interferon-alpha-2a inhibit wild-type and resistant genotype 1 hepatitis C virus replication in patients. Hepatology 2007; 46(3): 631–9
Forestier N, Reesink HW, Weegink CJ, et al. Antiviral activity of telaprevir (VX-950) and peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with hepatitis C. Hepatology 2007; 46(3): 640–8
McHutchison JG, Everson GT, Gordon SC, et al. Results of an interim analysis of a phase 2 study of telaprevir (VX-950) with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in previously untreated subjects with hepatitis C [abstract]. J Hepatol 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: S296
Hezode C, Ferenci P, Dusheiko GM, et al. PROVE2: phase II study of VX950 (telaprevir) in combination with peginterferon alfa2a with or without ribavirin in subjects with chronic hepatitis C, first interim analysis. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 268–9A
McHutchison JG, Everson GT, Gordon SC, et al. PROVE1: results from a phase 2 study of telaprevir with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in treatment-naive subjects with hepatitis C [abstract]. J Hepatol 2008; 48 (Suppl. 2): S4
Dusheiko GM, Hezode C, Pol S, et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with telaprevir (TVR) in combination with peginterferon-alfa-2a with or without ribavirin: further interim analysis results of the PROVE2 study [abstract]. J Hepatol 2008; 48 (Suppl. 2): S26
Sarrazin C, Rouzier R, Wagner F, et al. SCH 503034, a novel hepatitis C virus protease inhibitor, plus pegylated interferon alpha-2b for genotype 1 nonresponders. Gastroenterology 2007; 132(4): 1270–8
Kwo P, Lawitz E, McCone J, et al. Interim results from HCV SPRINT-1: RVR/EVR from phase 2 study of boceprevir plus Pegintron™ (peginterferon alfa-2b)/ribavirin in treatment-naive subjects with genotype-1 CHC [abstract]. J Hepatol 2008; 48 (Suppl. 2): S372
Pottage Jr JC, Lawitz E, Mazur D, et al. Short-term antiviral activity and safety of ACH-806 (GS-9132), an NS4A antagonist, in HCV genotype 1 infected individuals. J Hepatol 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: S294–5
Reesink H, Verloes R, Abou Farha K, et al. Safety of the HCV protease inhibitor TMC435350 in healthy volunteers and safety and activity in chronic hepatitis C infected individuals: a phase 1 study [abstract]. J Hepatol 2008; 48 (Suppl. 2): S28–9
Arrow Therapeutics. Hepatitis C [online]. Available from URL: http://www.arrowt.co.uk/product-HCV.asp [Accessed 2008 May 27]
Pierra C, Benzaria S, Amador A, et al. Nm 283, an efficient prodrug of the potent anti-HCV agent 2′-C-methylcytidine. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2005; 24(5–7): 767–70
Afdhal N, O'Brien C, Godofsky E, et al. Valopicitabine (NM283), alone or with peginterferon, compared to peginterferon/ribavirin (PEGIFN/RBV) retreatment in patients with HCV-1 infection and prior non-response to PEGIFN/ RBV: one-year results [abstract]. J Hepatol 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: S5
Lawitz E, Nguyen T, Younes Z, et al. Clearance of HCV RNA with valopicitabine (NM283) plus peginterferon in treatmentnaive patients with HCV-1 infection: results at 24 and 48 weeks [abstract]. J Hepatol 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: S9
Coelmont L, Paeshuyse J, Windisch MP, et al. Ribavirin antagonizes the in vitro anti-hepatitis C virus activity of 2′-C-methylcytidine, the active component of valopicitabine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006; 50(10): 3444–6
Roberts S, Cooksley G, Dore G, et al. Results of a phase 1b, multiple dose study of R1626, a novel nucleoside analog targeting HCV polymerase in chronic HCV genotype 1 patients [abstract]. Hepatology 2006; 44 Suppl. 1: 692A
Pockros P, Nelson D, Godofsky E, et al. Robust synergistic antiviral effect of R1626 in combination with peginterferon alfa-2a (40kD), with or without ribavirin: interim analysis results of a phase 2a study [abstract]. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 311A
Nelson D, Pockros PJ, Godofsky E, et al. High end-of-treatment response (84%) after 4 weeks of R1626, peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin followed by a further 44 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin [abstract]. J Hepatol 2008; 48 (Suppl. 2): S371
Reddy R, Rodriguez-Torres M, Gane E, et al. Antiviral activity, pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of R7128, a novel nucleoside HCV RNA polymerase inhibitor, following multiple, ascending, oral doses in patients with HCV genotype 1 infection who have failed prior interferon therapy [abstract]. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 862–3A
Lalezari J, Gane E, Rodriguez-Torres M, et al. Potent antiviral activity of the HCV nucleoside polymerase inhibitor R7128 with PEG-IFN and ribavirin: interim results of R7128 500 mg BID for 28 days [abstract]. J Hepatol 2008; 48 (Suppl. 2): S29
Villano SA, Raible D, Harper D, et al. Antiviral activity of the non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitor, HCV-796, in combination with pegylated interferon alfa-2b in treatment-naive patients with chronic HCV [abstract]. J Hepatol 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: S24
ViroPharma. ViroPharma announces discontinuation of HCV-796 development [online]. Available from URL: http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=92320&=irol-newsArticle&ID=1131055&highlight [Accessed 2008 May 27]
Erhardt A, Wedemeyer H, Benhamou Y, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and antiviral effect of BILB1941, a novel HCV RNA polymerase inhibitor, after 5 days oral treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C [abstract]. J Hepatol 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: S222
Bavisotto L, Wang CC, Jacobson IM, et al. Antiviral, pharmacokinetic and safety data for GS-9190, a non-nucleoside HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor, in a phase-1 trial in HCV genotype 1 infected subjects [abstract]. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 255A
Flisiak R, Dumont JM, Crabbe R. Cyclophilin inhibitors in hepatitis C viral infection. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2007; 16(9): 1345–54
Ma S, Boerner JE, TiongYip C, et al. NIM811, a cyclophilin inhibitor, exhibits potent in vitro activity against hepatitis C virus alone or in combination with alpha interferon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006; 50(9): 2976–82
Flisiak R, Horban A, Kierkus J, et al. The cyclophilin inhibitor DEBIO-025 has a potent dual anti-HIV and anti-HCV activity in treatment-naive HIV/HCV co-infected subjects [abstract]. Hepatology 2006; 44 Suppl. 1: 609A
Le Pogam S, Kang H, Harris SF, et al. Selection and characterization of replicon variants dually resistant to thumb- and palm-binding nonnucleoside polymerase inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus. J Virol 2006; 80(12): 6146–54
Sarrazin C, Kieffer TL, Bartels D, et al. Dynamic hepatitis C virus genotypic and phenotypic changes in patients treated with the protease inhibitor telaprevir. Gastroenterology 2007; 132(5): 1767–77
Lu L, Pilot-Matias TJ, Stewart KD, et al. Mutations conferring resistance to a potent hepatitis C virus serine protease inhibitor in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004 Jun; 48(6): 2260–6
Yi M, Tong X, Skelton A, et al. Mutations conferring resistance to SCH6, a novel hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitor: reduced RNA replication fitness and partial rescue by second-site mutations. J Biol Chem 2006; 281(12): 8205–15
Lin C, Lin K, Luong YP, et al. In vitro resistance studies of hepatitis C virus serine protease inhibitors, VX-950 and BILN 2061: structural analysis indicates different resistance mechanisms. J Biol Chem 2004; 279(17): 17508–14
Tong X, Chase R, Skelton A, et al. Identification and analysis of fitness of resistance mutations against the HCV protease inhibitor SCH 503034. Antiviral Res 2006; 70(2): 28–38
Mo H, Lu L, Pilot-Matias T, et al. Mutations conferring resistance to a hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor alone or in combination with an HCV serine protease inhibitor in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005; 49(10): 4305–14
Villano S, Howe A, Raible D, et al. Analysis of HCV NS5B genetic variants following monotherapy with HCV-796, a non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitor, in treatment-naive HCV-infected patients [abstract]. Hepatology 2006; 44 Suppl. 1: 607–8A
Le Pogam S, Jiang WR, Leveque V, et al. In vitro selected Con1 subgenomic replicons resistant to 2′-C-methyl-cytidine or to R1479 show lack of cross resistance. Virology 2006; 351(2): 349–59
Carroll SS, Davies ME, Handt L, et al. Robust suppression of viral replication by a nucleoside polymerase inhibitor in chimpanzees infected with hepatitis C virus [abstract]. Hepatology 2006; 44 Suppl. 1: 535A
Tomei L, Altamura S, Bartholomew L, et al. Mechanism of action and antiviral activity of benzimidazole-based allosteric inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol 2003; 77(24): 13225–31
Migliaccio G, Tomassini JE, Carroll SS, et al. Characterization of resistance to non-obligate chain-terminating ribonucleoside analogs that inhibit hepatitis C virus replication in vitro. J Biol Chem 2003; 278(49): 49164–70
Ludmerer SW, Graham DJ, Boots E, et al. Replication fitness and NS5B drug sensitivity of diverse hepatitis C virus isolates characterized by using a transient replication assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005; 49(5): 2059–69
Trozzi C, Bartholomew L, Ceccacci A, et al. In vitro selection and characterization of hepatitis C virus serine protease variants resistant to an active-site peptide inhibitor. J Virol 2003; 77(6): 3669–79
Rehermann B. Interaction between the hepatitis C virus and the immune system. Semin Liver Dis 2000; 20(2): 127–41
Wedemeyer H, He XS, Nascimbeni M, et al. Impaired effector function of hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Immunol 2002 Sep 15; 169(6): 3447–58
Neumann-Haefelin C, Blum HE, Chisari FV, et al. T cell response in hepatitis C virus infection. J Clin Virol 2005 Feb; 32(2): 75–85
Osborn BL, Olsen HS, Nardelli B, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of a human serum albumin-interferon-alpha fusion protein in cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2002; 303(2): 540–8
Subramanian GM, Fiscella M, Lamouse-Smith A, et al. Albinterferon alpha-2b: a genetic fusion protein for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Nat Biotechnol 2007; 25(12): 1411–9
Balan V, Nelson DR, Sulkowski MS, et al. A phase I/II study evaluating escalating doses of recombinant human albumin-interferon-alpha fusion protein in chronic hepatitis C patients who have failed previous interferon-alpha-based therapy. Antivir Ther 2006; 11(1): 35–45
Bain VG, Kaita KD, Yoshida EM, et al. A phase 2 study to evaluate the antiviral activity, safety, and pharmacokinetics of recombinant human albumin-interferon alfa fusion protein in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C patients. J Hepatol 2006; 44(4): 671–8
Nelson D, Rustgi V, Balan V, et al. Sustained virologic response with albinterferon alfa-2b/ribavirin treatment in prior interferon therapy non-responders [abstract]. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 256A
Zeuzem S, Yoshida EM, Benhamou Y, et al. Sustained virologic response rates with albinterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin treatment in IFN-naive, chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 patients [abstract]. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 317–8A
Novozhenov V, Zakharova N, Vinogradova E, et al. Phase 2 study of omega interferon alone or in combination with ribavirin in subjects with chronic hepatitis C genotype-1 infection [abstract]. J Hepatol 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: S8
De Leede LG, Humphries JE, Bechet AC, et al. Novel controlled-release Lemna-derived IFN-alpha2b (Locteron): pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability in a phase I clinical trial. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2008; 28(2): 113–22
Dzyublyk I, Yegorova T, Moroz L, et al. Phase 2a study to evaluate the safety and tolerability and anti-viral of 4 doses of a novel, controlled-release interferon-alfa 2b (Locteron) given every 2 weeks for 12 weeks in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C (genotype 1) [abstract]. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 863A
Gish RG. Treating HCV with ribavirin analogues and ribavirinlike molecules. J Antimicrob Chemother 2006; 57(1): 8–13
Gish RG, Arora S, Rajender Reddy K, et al. Virological response and safety outcomes in therapy-naive patients treated for chronic hepatitis C with taribavirin or ribavirin in combination with pegylated interferon alfa-2a: a randomized, phase 2 study. J Hepatol 2007; 47(1): 51–9
Benhamou Y, Pockros P, Rodriguez-Torres M, et al. The safety and efficacy of Viramidine plus pegylated interferon alpha-2b versus ribavirin plus pegylated interferon alpha-2b in therapynaive patients infected with HCV: phase 3 results [abstract]. J Hepatol 2006; 44 Suppl. 2: S273
Valeant Pharmaceuticals. Valeant Pharmaceuticals initiates taribavirin phase 2b clinical study [online]. Available from URL: http://www.valeant.com/mediaCenter/newsArticle/newsArticle.jspf?objectId=4192 [Accessed 2008 May 27]
Marcellin P, Horsmans Y, Nevens F, et al. Phase 2 study of the combination of merimepodib with peginterferon-alpha2b, and ribavirin in nonresponders to previous therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 2007; 47(4): 476–83
McHutchison JG, Shiffman ML, Cheung RC, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-escalation trial of merimepodib (VX-497) and interferon-alpha in previously untreated patients with chronic hepatitis C. Antivir Ther 2005; 10(5): 635–43
Pappas SC. Good science behind hepatitis C virus antiviral drug development: necessary but not sufficient. Hepatology 2007; 46(5): 1317–8
Pockros PJ, Guyader D, Patton H, et al. Oral resiquimod in chronic HCV infection: safety and efficacy in 2 placebocontrolled, double-blind phase IIa studies. J Hepatol 2007 Aug; 47(2): 174–82
Horsmans Y, Berg T, Desager JP, et al. Isatoribine, an agonist of TLR7, reduces plasma virus concentration in chronic hepatitis C infection. Hepatology 2005 Sep; 42(3): 724–31
McHutchison JG, Bacon BR, Gordon SC, et al. Phase 1B, randomized, double-blind, dose-escalation trial of CPG 10101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 2007; 46(5): 1341–9
Pockros PJ, Patel K, O'Brien C, et al. A multicenter study of recombinant human interleukin 12 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in patients nonresponsive to previous therapy. Hepatology 2003; 37(6): 1368–74
Zein NN. Etanercept as an adjuvant to interferon and ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Hepatol 2005; 42(3): 315–22
Di Bisceglie A, Shiffman M, Everson GT, et al. Prolonged antiviral therapy with peginterferon to prevent complications of advanced liver disease associated with hepatitis C: results of the hepatitis C antiviral long-term treatment against cirrhosis (HALT-C) trial [abstract]. Hepatology 2007; 46 Suppl. 1: 290A
Pockros PJ, Jeffers L, Afdhal N, et al. Final results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the antifibrotic efficacy of interferon-gammalb in chronic hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007; 45(3): 569–78
Pockros PJ, Schiff ER, Shiffman ML, et al. Oral IDN-6556, an antiapoptotic caspase inhibitor, may lower aminotransferase activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2007; 46(2): 324–9
Acknowledgements
No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this review. The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stauber, R.E., Kessler, H.H. Drugs in Development for Hepatitis C. Drugs 68, 1347–1359 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200868100-00002
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200868100-00002