Abstract
-
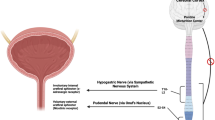
▲ Duloxetine is an orally administered, balanced, dual serotonin and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) reup-take inhibitor that increases neural input to the urethral sphincter, thereby relieving the symptoms of stress urinary incontinence (SUI).
-
▲ Duloxetine 40mg twice daily for 12 weeks reduced the median incontinence episode frequency (IEF) to a significantly greater extent than placebo in women with predominant symptoms of SUI. In most studies, Incontinence Quality of Life (I-QOL) questionnaire total scores were significantly improved compared with placebo.
-
▲ In a dose-escalation study in women with severe SUI scheduled for continence surgery, duloxetine 80–120 mg/day for 8 weeks significantly reduced IEF and increased I-QOL total scores compared with placebo, and caused 20% of recipients to reconsider their willingness to undergo surgery.
-
▲ Duloxetine or duloxetine plus pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) were more effective in reducing the median IEF than PFMT alone or no treatment in women with SUI. Mean I-QOL total scores suggested that combination therapy was more effective than either therapy alone.
-
▲ Nausea was the most frequent adverse event and was the main cause for discontinuing duloxetine therapy.li]

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Harrison GL, Memel DS. Urinary incontinence in women: its prevalence and its management in a health promotion clinic. Br J Gen Pract 1994 Apr; 44(381): 149–52
Brown JS, Grady D, Ouslander JG, et al. Prevalence of urinary incontinence and associated risk factors in postmenopausal women: Heart & Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study (HERS) Research Group. Obstet Gynecol 1999 Jul; 94(1): 66–70
Viktrup L. Female stress and urge incontinence in family practice: insight into the lower urinary tract. Int J Clin Pract 2002; 56(9): 694–700
Resnick NM, Griffiths DJ. Expanding treatment options for stress urinary incontinence in women. JAMA 2003 Jul 16; 290(3): 395–7
Culligan PJ, Heit M. Urinary incontinence in women: evaluation and management. Am Fam Physician 2000 Dec 1; 62(11): 2433–44, 2447, 2452
Chaliha C, Khullar V. Mixed incontinence. Urology 2004 Mar; 63 Suppl. 3A: 51–7
Siroky MB. Current treatment options for stress urinary incontinence. Adv Stud Med 2003; 3(8E): S834–8
Ostergard DR. New approaches to the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Adv Stud Med 2004; 4(2A): S88–94
Schuessler B, Baessler K. Pharmacologic treatment of stress urinary incontinence: expectations for outcome. Urology 2003 Oct; 62 Suppl. 4A: 31–8
Eli Lilly and Company. FDA approves Lilly’s Cymbalta® for the treatment of depression [media release]. 2004
European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use summary of opinion for Xeristar [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.eu.int [Accessed 2004 Oct 12]
European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use: summary of opinion for Cymbalta [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.eu.int/pdfs/human/opinion/4721604en.pdf [Accessed 2004 Oct 12]
Eli Lilly and Company. FDA approves antidepressant Cymbalta® for treatment of pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy, which affects up to 5 million Americans [media release]. 2004
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Mayle DA, et al. LY248686, a new inhibitor of serotonin and norepinephrine uptake. Neuropsychopharmacology 1993; 8(1): 23–33
Karpa KD, Cavanaugh JE, Lakoski JM. Duloxetine pharmacology: profile of a dual monoamine modulator. CNS Drug Rev 2002; 8(4): 361–76
Thor KB. Serotonin and norepinephrine involvement in efferent pathways to the urethral rhabdosphincter: implications for treating stress urinary incontinence. Urology 2003 Oct; 62 Suppl. 4A: 3–9
Thor KB, Katofiasc MA. Effects of duloxetine, a combined serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, on central neural control of lower urinary tract function in the chloralose-anesthetized female cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995; 274(2): 1014–24
Katofiasc MA, Nissen J, Audia JE, et al. Comparison of the effects of serotonin selective, norepinephrine selective, and dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors on lower urinary tract function in cats. Life Sci 2002; 71: 1227–36
Skinner MH, Kuan HY, Skerjanec A, et al. Effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of duloxetine in women. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2004 Jan; 57(1): 54–61
Lantz RJ, Gillespie TA, Rash TJ, et al. Metabolism, excretion, and pharmacokinetics of duloxetine in healthy human subjects. Drug Metab Dispos 2003 Sep; 31(9): 1142–50
Granier LA, Vandenhende F, de Suray JM, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of duloxetine, a potential new antidepressant with serotonin and norepinephrine uptake inhibition [abstract no. P.1.043]. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1999 Sep; 9 Suppl. 5: S222
Sharma A, Goldberg MJ, Cerimele BJ. Pharmacokinetics and safety of duloxetine, a dual-serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol 2000; 40(2): 161–7
DeLong AF, Johnson JT, Oldham SW, et al. Disposition of 14C duloxetine after oral administration in man [abstract no. 4005]. FASEB J 1995 Mar 10; 9 (4 Pt II): 691
Skinner MH, Skerjanec A, Seger M, et al. The effect of food and bedtime administration on duloxetine pharmacokinetics [abstract no. PII-59]. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2000 Feb; 67(2): 129
Ishigooka J, Nagata E, Takahashi A, et al. Simultaneous monitoring of inhibition of serotonin uptake by platelets and plasma drug concentrations following administration of duloxetine, a new antidepressant candidate, to healthy volunteers. Curr Ther Res 1997 Oct; 58(10): 679–92
Eli Lilly Nederland BV. Yentreve®: summary of product characteristics [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.eu.int/humandocs/Humans/EPAR/yentreve/yentreve.htm [Accessed 2004 Oct 11]
van Kerrebroeck P, Abrams P, Lange R, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of European and Canadian women with stress urinary incontinence: Duloxetine Urinary Incontinence Study Group. BJOG 2004 Mar; 111(3): 249–57
Millard RJ, Moore K, Rencken R, et al. Duloxetine vs placebo in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence: a four-continent randomized clinical trial. Duloxetine UI Study Group. BJU Int 2004 Feb; 93(3): 311–8
Dmochowski RR, Miklos JR, Norton PA, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo for the treatment of North American women with stress urinary incontinence: Duloxetine Urinary Incontinence Study Group. J Urol 2003 Oct; 170 (4 Pt 1): 1259–63
Norton PA, Zinner NR, Yalcin I, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence: Duloxetine Urinary Incontinence Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002 Jul; 187(1): 40–8
Cardozo L, Drutz HP, Baygani SK, et al. Pharmacological treatment of women awaiting surgery for stress urinary incontinence: Duloxetine Severe UI Study Group. Obstet Gynecol 2004 Sep; 104(3): 511–9
Ghoniem GM, Elser DM, Freeman R, et al. Controlled trial of duloxetine alone, pelvic floor muscle training alone, combined treatment, and no treatment in women with stress urinary incontinence [abstract no. 1239]. J Urol 2004 Apr; 171 Suppl. 4: 326
Yalcin I, Versi E, Benson JT, et al. Validation of a clinical algorithm to diagnose stress urinary incontinence for large studies. J Urol 2004 Jun; 171 (6 Pt 1): 2321–5
Bump RC, Norton PA, Zinner NR, et al. Mixed urinary incontinence symptoms: urodynamic findings, incontinence severity, and treatment response: Duloxetine Urinary Incontinence Study Group. Obstet Gynecol 2003 Jul; 102(1): 76–83
Eli Lilly and Company, Boehringer Ingelheim. Yentreve™ receives approval across the European Union for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women [media release]. 2004
Boehringer Ingelheim. Yentreve®/Ariclaim® now approved throughout the European Union for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women [media release]. 2004
Eli Lilly and Company. FDA issues approvable letter for duloxetine for stress urinary incontinence (SUI); Lilly expects regulatory update on Cymbalta later this year [media release]. 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCormack, P.L., Keating, G.M. Duloxetine. Drugs 64, 2567–2573 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200464220-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200464220-00005