Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis
The aim of our study was to evaluate the effect of a combination of innovative pelvic floor muscle training (iPFMT) and duloxetine compared with the use of duloxetine alone on women with stress urinary incontinence (SUI) after 12 weeks of treatment.
Methods
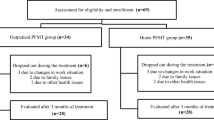
We conducted a parallel multicentre study with randomized intervention in 45 national urological outpatient clinics. Patients with an enrolment ratio of 1:1 were divided into the experimental and control groups. The following were used for evaluation: incontinence episode frequency (IEF)/week, the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire (ICIQ-SF), the Urinary Incontinence Quality of Life Scale (I-QoL) and the Patient Global Impression of Improvement (PGI-I). The experimental group received oral treatment with duloxetine (a daily dose of 40 mg BID) and innovative pelvic floor muscle training (iPFMT). The control group received only oral treatment with duloxetine at a daily dose of 40 mg BID.
Results
The number of women who were evaluated was 158. The control group comprised 79 women with an average age of 56.8 ± 13.8 years and the experimental group comprised 79 women with an average age of 53.4 ± 11.9 years. There were no significant differences in pre-treatment parameters. For the intent-to-treat analysis after 12 weeks’ treatment, significant differences were observed between the experimental vs. control group (p < 0.001) for the following variables: IEF/week decrease (66.7% vs. 50.0%); ICIQ-UI SF decrease (8.3 ± 3.8 vs. 9.7 ± 4.2); PGI-I (70.8% vs. 65.6%); I-QoL score increase (19.3% vs. 6.6%).
Conclusion
The addition of iPFMT to duloxetine treatment improves SUI syndrome in women compared with duloxetine treatment alone.
Registration
Clinical Trials.gov NCT04140253.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haylen BT, de Ridder D, Freeman RM, Swift SE, Berghmans B, Lee J, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Int Urogynecol J. 2010;21(1):5–26.
Abrams P, Andersson KE, Apostolidis A, Birder L, Bliss D, Brubaker L, et al. 6th International Consultation on Incontinence. Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE, PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018;37(7):2271–2.
Bernards ATM, Berghmans B, Slieker-ten Hove MCP, Staal JB, de Bie RA, Hendriks EJM. Dutch guidelines for physiotherapy in patients with stress urinary incontinence: an update. Int Urogynecol J. 2014;25(2):171–9.
Bo K, Frawley HC, Haylen BT, Abramov Y, Almeida FG, Berghmans B, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for the conservative and nonpharmacological management of female pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017;36(2):221–44.
Bo K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, Van Kampen M. Evidence-based physical therapy for the pelvic floor- 2nd edition. Churchill Livingstone, 2015; 446 p. ISBN 9780702060731.
Ghoniem GM, Van Leeuwen JS, Elser DM, Freeman RM, Zhao YD, Yalcin I, et al. A randomized controlled trial of duloxetine alone, pelvic floor muscle training alone, combined treatment and no active treatment in women with stress urinary incontinence. Duloxetine/pelvic floor muscle training clinical trial group. J Urol. 2005;173(5):1647–53.
Kim EY, Kim SY, Oh DW. Pelvic floor muscle exercises utilizing trunk stabilization for treating postpartum urinary incontinence: randomized controlled pilot trial of supervised versus unsupervised training. Clin Rehabil 2012; 26(2):132–141.
Klarskov N, Cerneus D, Sawyer W, Newgreen D, Van till O, Lose G. The effect of single oral doses of duloxetine, reboxetine, and midodrine on the urethral pressure in healthy female subjects, using urethral pressure reflectometry. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018;37(1):244–9.
Maund E, Guski LS, Gøtzsche PC. Considering benefits and harms of duloxetine for treatment of stress urinary incontinence: a meta-analysis of clinical study reports. CMAJ. 2017;189(5):E194–203.
Avery K, Donovan J, Peters TJ, Shaw C, Gotoh M, Abrams P. ICIQ: a brief and robust measure for evaluating the symptoms and impact of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2004;23:322–30.
Klovning A, Avery K, Sandvik H, Hunskaar S. Comparison of two questionnaires for assessing the severity of urinary incontinence: the ICIQ-UI SF versus the incontinence severity index. Neurourol Urodyn. 2009;28(5):411–5.
Coyne K, Revicki D, Hunt T, Corey R, Stewart W, Bentkover J, et al. Psychometric validation of an overactive bladder symptom and health-related quality of life questionnaire: the OAB-q. Qual Life Res. 2002;11(6):563–74.
Coyne KS, Payne C, Bhattacharyya SK, Revicki DA, Thompson C, Corey R, et al. The impact of urinary urgency and frequency on health related quality of life in overactive bladder: results from a national community survey. Value Health. 2004;7:455–63.
Cardozo L, Staskin D, Currie B, Wiklund I, Globe D, Signori M, et.al. Validation of a bladder symptom screening tool in women with incontinence due to overactive bladder. Int Urogynecol J 2014; 25(12): 1655–1663.
Bushnell DM, Martin ML, Summers KH, Svihra J, Lionis C, Patrick DL. Quality of life of women with urinary incontinence: cross-cultural performance of 15 language versions of the I-QOL. Qual Life Res. 2005;14:1901–13.
Patrick DL, Martin ML, Bushnell DM, Yalcin I, Wagner TH, Buesching DP. Quality of life of women with urinary incontinence: further development of the incontinence quality of life instrument (I-QOL). Urology. 1999;53(1):71–6.
Schurch B, Denys P, Kozma CM, Reese PR, Slaton T, Barron R. Reliability and validity of the incontinence quality of life questionnaire in patients with neurogenic urinary incontinence. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(5):646–52.
Yalcin I, Bump RC. Validation of two global impression questionnaires for incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189(1):98–101.
Acknowledgements
We thank the physians for their cooperation in the study.
List of physians from out-patient clinics in Slovakia: Barbora Spodniaková, Ľubomír Uherčík, Eva Šulcová, Juraj Barta, Daniel Fajtl, Milan Chalachan, Tomáš Danys, Vladimír Starovecký, Kamil Duranka, Dzmitry Lapatko, Lukáš Čmarada, Richard Ľuník, Miloš Pisák, Cyril Fedor, Oto Šoltés.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS was responsible for the study design and methodology. MH was responsible for writing the article and preparing educational materials for the exercises. JS, MH, JB, JD and MV were responsible for coordinating centre and data management. MH, JS, JB, JD and MV read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagovska, M., Svihra, J., Breza, J. et al. A randomized, intervention parallel multicentre study to evaluate duloxetine and innovative pelvic floor muscle training in women with uncomplicated stress urinary incontinence—the DULOXING study. Int Urogynecol J 32, 193–201 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-020-04516-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-020-04516-w