Summary
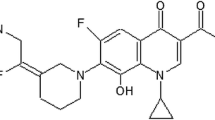
Lomefloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic with chemical and microbiological properties similar to most commercially available agents of this class. There are differences, however, between lomefloxacin and other quinolones in activity against specific micro-organisms, a situation that is typical of most antibiotic classes.
The pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin support once- or twice-daily dosage, depending on the pathogen or site of infection. This is a result of its relatively high serum concentrations and long half-life. The outstanding pharmacokinetic features of lomefloxacin are its high degree of tissue distribution, lack of significant metabolism (and, therefore, no competitive drug interactions with other metabolised drugs showing a common metabolic pathway), and good oral absorption. Like most fluoroquinolones, lomefloxacin can chelate with heavy metals. However, this interaction can be eliminated by administering lomefloxacin 2h before the cation-containing products. Dosage adjustments are required in patients with renal dysfunction. However, patients with liver disease do not require alterations in lomefloxacin dosage regimens.
The safety profile, lack of significant drug interactions and convenience of administration make lomefloxacin a useful agent in specific clinical settings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akahane K, Sekiguchi M, Une T, Osada Y. Structure-epilepto-genicity relationship of quinolones with special reference to their interaction with gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor sites. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 33: 1704–1708, 1989
Baldwin DR, Honeybourne D, Andrews JM, Ashby JP, Wise R. Concentrations of oral lomefloxacin in serum and bronchial mucosa. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 1017–1019, 1990
Bergogne-Bérézin E, Muller-Serieys C, Kafe H. Penetration of lomefloxacin into bronchial secretions following single and multiple oral administration. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 12S–14S, 1992
Blaser J, Stone BB, Groner MC, Zinner SH. Comparative study with enoxacin and netilmicin in a pharmacodynamic model to determine importance of ratio of antibiotic peak concentration to MIC for bactericidal activity and emergence of resistance. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 31: 1054–1060, 1987
Blum RA. Influence of renal function on the pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin compared with other fiuoroquinolones. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 18S–21S, 1992
Blum RA, Schultz RW, Schentag JJ. Pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin in renally compromised patients. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 2364–2368, 1990
Chamberland S, Bayer AS, Schollaardt T, Wong SA, Bryan LE. Characterisation of mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated in vitro and in vivo during experimental endocarditis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 33: 624–634, 1989
Chambers ST, Peddie BA, Robson RA, Begg EJ, Boswell DR. Antimicrobial effects of lomefloxacin in vitro. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 27: 481–489, 1991
Chin NX, Novelli A, Neu HC. In vitro activity of lomefloxacin (SC-47111; NY-198), a difluoroquinolone 3-carboxylic acid, compared with those of other quinolones. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 656–662, 1988
Christ W, Gindler K, Gruene S, Hecker W, Jacobson M, et al. Interactions of quinolones with opioids and fenbufen, a nonsteroidal antiinflamatory drug: involvement of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 11 (Suppl. 5): S1393–S1394, 1989
Chu DTW, Fernandes PB. Structure-activity relationships of the fiuoroquinolones. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 33: 131–135, 1989
Chu DTW, Fernandes PB, Claiborne AK, Pihuleac E, Nordeen CW, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel arylfluoroquinolone antibacterial agents. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 28: 1558–1564, 1985
Cohen SP, Hooper DC, Wolfson JS, Souza KS, McMurray LM, et al. Endogenous active efflux of norfloxacin in susceptible Escherichia coli. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 1187–1191, 1988
Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated 4-quinolone resistance: a real or apparent absence. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 681–684, 1990
Cowling P, Rogers S, McMullen CM, White LO, Lovering AM, et al. The pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin in elderly patients with urinary tract infection following daily dosing with 400mg. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 28: 101–107, 1991
Craig WA, Ebert SC. Killing and regrowth of bacteria in vitro: a review. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Disease (Suppl. 74): 63–70, 1991
Crome P, Morrison PJ. Pharmacokinetics of a single dose of lomefloxacin in healthy elderly volunteers. Drug Investigation 3: 183–187, 1991
Crumplin GC, Kenwright M, Hirst T. Investigations into the mechanism of action of the antibacterial agent norfloxacin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 13 (Suppl. B): 9–23, 1984
Crumplin GC, Smith JT. Nalidixic acid: an antibacterial paradox. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 8: 251–261, 1975
Cundy KV, Fasching CE, Willard KE, Peterson LR. Uptake of 3H-norfloxacin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 28: 491–497, 1991
Daikos GL, Lolans VT, Jackson GG. Alterations in outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with selective resistance to quinolones. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 785–787, 1988
Debbia EA, Pesce A. Schito GC. In vitro assessment of the postantibiotic effect of lomefloxacin against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 45S–47S, 1992
Domagala JM, Hanna LD, Heifetz CL, Hutt MP, Mich TF, et al. New structure-activity relationships of the quinolone antibac-terials using the target enzyme. Development and application of a DNA gyrase assay. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 29: 394–404, 1986
Drusano GL, Johnson DE, Rosen M, Lockatell V, Standiford HC. Pharmacodynamics of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic lomefloxacin. Abstract no. 1916. Program and Abstracts of the Seventeenth International Congress of Chemotherapy, Berlin, June 23–28, 1991b
Drusano GL, Johnson DE, Rosen M, Standiford HC. Pharmacodynamics of a fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent in a neutropenic rat model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 37: 483–490, 1992
Dudley MN. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of antibiotics with special reference to the fluoroquinolones. American Journal of Medicine 91 (Suppl. 6A): 45S–50S, 1991
Eagle H, Fleischman R, Musselman AD. Effect of schedule of administration on the therapeutic efficacy of penicillin. Americal Journal of Medicine 9: 280–299, 1950
Fasching CE, Tenover FC, Slama TG, Fisher LM, Sreedharan S, et al. gyrA Mutations in ciprofloxacin-resistant Stapylococcus aureus from Indiana, Minnesota, and Tennessee. Journal of Infectious Diseases 164: 976–979, 1991
Fernandes PB, Swanson RN. Correlation of in vitro activities of the fluoroquinolones to their in vivo efficacies. Drugs in Experimental Clinical Research 14: 375–378, 1988
Fisher LM, Lawrence JM, Josty IC, Hopewell R, Margerrison EEC, et al. Ciprofloxacin and the fluoroquinolones: new concepts on the mechanism of action and resistance. American Journal of Medicine 87 (Suppl. 5A): 2S–8S, 1989
Foster T, Blouin R. The effect of antacid timing on lomefloxacin bioavailability. Abstract no. 1277. Program and Abstracts of the Twenty-Ninth Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Houston, September 17–20, 1989
Furet YX, Pechere JC. Usual and unusual antibacterial effects of quinolones. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 26 (Suppl. B): 7–15, 1990
Griggs DJ, Wise R. A simple isocratic high-pressure liquid Chromatographic assay of quinolones in serum. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 24: 437–445, 1989
Gros I, Carbon C. Pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin in healthy volunteers: comparison of 400 milligrams once daily and 200 milligrams twice daily given orally for 5 days. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 150–152, 1990
Healy DP, Schoenle JR, Stotka J, Polk RE. Lack of an interaction between lomefloxacin and caffeine in normal volunteers. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 35: 660–664, 1991
Hirose T, Okezaki E, Kato H, Ito Y, Inoue M, et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of NY-198, a new difluorinated quinolone. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 31: 854–859, 1987
Hoffler D, Waetcke K, Koeppe P, Metz R, Sorgel F. Pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin in normal and impaired renal function. Acta Therapeutica 15: 321–336, 1989
Hooper DC, Wolfson JS, Souza KS, Ng EY, McHugh GL, et al. Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli: characterization of nfxB and cfxB, two mutant resistance loci decreasing norfloxacin accumulation. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 33: 283–290, 1989
Hooper WD, Dickinson RG, Eadie MJ. Effect of food on absorption of lomefloxacin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 1797–1799, 1990
Hori S, Shimada J, Saito A, Matsuda M, Miyahara T. Comparison of the inhibitory effects of new quinolones on gamma-aminobytyric acid receptor binding in the presence of antiinflammatory drugs. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 11 (Suppl. 5): S1397–S1398, 1988
Hunt TL, Adams MA. Pharmacokinetics and safety of lomefloxacin following multiple doses. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 12: 181–187, 1989
Jaber LA, Bailey EM, Rybak M. Enoxacin: a new fluoroquinolone. Clinical Pharmacy 8: 97–107, 1989
Kaatz GW, Barriere SL, Schaberg DR, Fekety R. The emergence of resistance to ciprofloxacin during treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 20: 753–758, 1987
Kaatz GW, Seo SM, Ruble CA. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Infectious Diseases 163: 1080–1086, 1991
Kavi J, Stone J, Andrews JM, Ashby JP, Wise R. Tissue penetration and pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin following multiple doses. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Disease 8: 168–170, 1989
Koga J, Itch A, Marimba S, Cease S, Irikura T. Structure-activity relationships of antibacterial 6,7- and 7,8-disubstituted 1-alkyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acids. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 23: 1358–1363, 1980
Kotilainen P, Nikoskelainen J, Huovinen P. Emergence of ciprofloxacin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococcal skin flora in immunocompromised patients receiving ciprofloxacin. Journal of Infectious Diseases 161: 41–44, 1990
Kovarik JM, de Hond JAPM, Hoepelman IM, Boon T, Verhoef J. Intraprostatic distribution of lomefloxacin following multiple-dose administration. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 2398–2401, 1990
Kovarik JM, Hoepelman AIM, Smit JM, Sips PA, Rozenberg-Arska M, et al. Steady-state pharmacokinetics and sputum penetration of lomefloxacin in patients with chronic pulmonary disease and acute respiratory tract infections. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 36: 2458–2461, 1992
Kresken M, Wiedemann B. Development of resistance to nalidixic acid and the fluoroquinolones after the introduction of norfloxacin and ofloxacin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 1285–1288, 1988
Krueger JH, Walker GC. groEL and dnaK genes of Escherichia coli are induced by UV irradiation and nalidixic acid in an htpR+-dependent fashion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 81: 1499–1503, 1984
Kurkemeyer J, Lima J, Adams M, Hunt T. Lomefloxacin pharmacokinetics: binding to plasma proteins and the effect of food on absorption. Abstract no. 1274. Program and Abstracts of the Twenty-Ninth Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Houston, September 17–20, 1989
Kuzuya T, Takagi K, Apichartpichean R, Muraoka I, Nadai M, et al. Kinetic interaction between theophylline and a newly developed quinolone NY-198. Journal of Pharmacobio-Dynamics 12: 405–409, 1989
Lebel M, Vallee F, Marcotte N, St-Laurent M. Tissue penetration of lomefloxacin in young and elderly healthy volunteers. Abstract no. 84E. Pharmacotherapy 9: 185, 1989
Lebel M, Vallee F, St-Laurent M. Influence of lomefloxacin on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 1254–1256, 1990
Lebrec D, Gaudin C, Benhamou JP. Pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin in patients with cirrhosis. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 41S–44S, 1992
Leggett JE, Ebert S, Fantin B, Craig WA. Comparative dose-effect relations at several dosing intervals for beta-lactam, aminoglycoside and quinolone antibiotics against Gram-negative bacilli in murine thigh-infection and pneumonitis models. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Disease (Suppl. 74): 179–184, 1991
Leigh DA, Harris C, Tait S, Walsh B, Hancock P. Pharmacokinetic study of lomefloxacin and its effect on the faecal flora of volunteers. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 27: 655–662, 1991
Leroy A, Fillastre JP, Humbert G. Lomefloxacin pharmacokinetics in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 17–20, 1990
Leroy A, Humbert G, Fillastre J-P, Grise P. Penetration of lomefloxacin into human prostatic tissue. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 12S–14S, 1992
Mant TGK. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin: rationale for once-a-day dosing. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 26S–32S, 1992
Mayer KH, Ellal JA. Lomefloxacin: microbiological assessment and unique properties. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 58S–62S, 1992
Mayersohn M. Special pharmacokinetic considerations in the elderly. In Evans et al. (Eds) Applied pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed., pp. 229–293, Applied Therapeutics, Inc., Washington, 1987
Meng X, Nightingale CH, Sweeney KR, Quintiliani R. Loss of bactericidal activity of quinolones (Q) in the presence of postantibiotic effect (PAE) induced by rifampin (R). Abstract no. 539. Program and Abstracts of the Thirty-Second Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Anaheim, October 11–14, 1992
Metz R, Hoffler D, Waetcke K, Keoppe P, Seibel M, et al. Altered pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin (LFX) in patients with impaired renal function. Abstract no. 1271. Program and Abstracts of the Twenty-Ninth Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Houston, September 17–20, 1989
Minguez F, Ramos C, Barrientos S, Loscos A, Prieto J. Postantibiotic effect of ciprofloxacin compared with that of five other quinolones. Chemotherapy 37: 420–425, 1991
Molinari G, Bandelloni R, Paglia P, Debbia E, Schito GC. In vitro antimicrobial activity and postantibiotic effect of lomefloxacin, a new difluoroquinolone. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 12 (Suppl. 3): 53S–56S, 1989
Morrison PJ, Mant TGK, Norman GT, Robinson J, Kunka RL. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of lomefloxacin after sequentially increasing oral doses. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 1503–1507, 1988
Morse IS. Pharmacokinetics and safety of single oral doses of lomefloxacin. Biopharmaceutics and Drug Disposition 11: 543–551, 1990
Nagata O, Yamada T, Yamaguchi T, Hasegawa H, Okezaki E. Disposition and metabolism of NY-198 V. Metabolism of 14C-NY-198 in rats and dogs. Chemotherapy 36 (Suppl. 2): 174–187, 1988
Neu HC. The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 257: 1064–1073, 1992
Nilsen OG, Saltvedt E, Walstad RA, Marstein S. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin in patients with normal and impaired renal function. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 38S–40S, 1992
Nix DE, Norman A, Schentag JJ. Effect of lomefloxacin on theophylline pharmacokinetics. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 33: 1006–1008, 1989
Nix D, Schentag J. Lomefloxacin (L) absorption kinetics when administered with ranitidine (R) and sucralfate (S). Abstract no. 1276. Program and Abstracts of the Twenty-Ninth Inter-science Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Houston, September 17–20, 1989
On A, Nightingale CH, Quintiliani R, Sweeney KR, Pasternak HS, et al. Lomefloxacin concentrations in bone after a single oral dose. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 41): 155–175, 1992
Pascual A, Garcia I, Perea EJ. Fluometric measurement of ofloxacin uptake by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 33: 653–656, 1989
Percival A. Impact of chemical structure on quinolone potency, spectrum and side effects. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 28 (Suppl. C): 1–8, 1991
Perea EJ, Garcia I, Pascual A. Comparative penetration of lomefloxacin and other quinolones into human phagocytes. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 48S–51S, 1992
Piddock LJV, Hall MC, Wise R. Mechanism of action of lomefloxacin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 1088–1093, 1990
Pruul H, McDonald PJ. Lomefloxacin-induced modification of the kinetics of growth of Gram-negative bacteria and susceptibility of phagocytic killing by human neutrophils. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 25: 91–101, 1990
Reeves DS, Bywater MJ, Holt HA, White LO. In-vitro studies with ciprofloxacin, a new 4-quinolone compound. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 13: 333–346, 1984
Robillard NJ, Scarpa AL. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 535–539, 1988
Robson RA. The effects of quinolones on xanthine pharmacokinetics. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 22S–25S, 1992
Robson RA, Begg EJ, Atkinson HC, Saunders DA, Frampton CM. Comparative effects of ciprofloxacin and lomefloxacin on the oxidative metabolism of theophylline. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 29: 491–493, 1990
Rustige C, Wiedemann B. Antibacterial activity of lomefloxacin in a pharmacokinetic in vitro model. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 1107–1111, 1990
Sanders CC, Sanders WE, Goering RV, Werner V. Selection of multiple antibiotic resistance by quinolones, beta-lactams, and aminoglycosides with special reference to cross-resistance between unrelated drug classes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 26: 797–801, 1984
Schaefler S. Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to quinolones. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 27: 335–336, 1989
Schentag JJ, Goss TF. Quinolone pharmacokinetics in the elderly. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 33S–37S, 1992
Searle Laboratories. Maxaquin package insert. Skookie, March 1992
Shah PM, Muller S, Kipp J, Stille W. In vitro activity of lomefloxacin (NY-198 or SC 47111). Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 12 (Suppl. 3): 97S–101S, 1989
Shen LL, Pernet AG. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by analogues of nalidixic acid: the target of the drugs is DNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 82: 307–311, 1985
Shibl AM, Tawfik AKF, El-Houfy S, Al-Shammary FJ. Determination of lomefloxacin in biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography and a microbiological method. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 16: 353–359, 1991
Shimada J, Shiba K, Oguma T, Miwa H, Yoshimura Y, et al. Effect of antacid on absorption of the quinolone lomefloxacin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 36: 1219–1224, 1992
Smith JT. The mode of action of 4-quinolones and possible mechanisms of resistance. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 18 (Suppl. D): 21–29, 1986
Sorgel F, Jaehde U, Naber K, Stephan U. Pharmacokinetic disposition of quinolones in human body fluids and tissues. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 16 (Suppl. 1): 5–24, 1989
Staib AH, Harder S, Fuhr U, Wack C. Interaction of quinolones with the theophylline metabolism in man: investigations with lomefloxacin and pipemidic acid. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Therapy and Toxicology 27: 289–293, 1989
Stein GE. Drug interactions with fluoroquinolones. American Journal of Medicine 91 (Suppl. 6A): 81S–86S, 1991
Stevens PJE. Bactericidal effect against Escherichia coli of nalidixic acid and four structurally related compounds. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 6: 535–542, 1980
Stone JW, Andrews JM, Ashby JP, Griggs D, Wise R. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of orally administered lomefloxacin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 1508–1510, 1988
Stratum CW, Weeks LS. Bactericidal activity of lomefloxacin SC 47111 (NY-198) and ciprofloxacin against selected pathogens. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 12 (Suppl. 3): 29S–34S, 1989
Tsuji A, Sato H, Kume Y, Tamai I, Okezaki E, et al. Inhibitory effects of quinolone antibacterial agents on γ-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in rat brain membranes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 190–194, 1988
Van der Auwera P, Grenier P, Glupczynski Y, Pierard D. In-vitro activity of lomefloxacin in comparison with pefloxacin and ofloxacin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 23: 209–219, 1989
Wijnands GJA, Cornel JH, Martea M, Vree TB. The effect of multiple-dose oral lomefloxacin on theophylline metabolism in man. Chest 98: 1440–1444, 1990
Wise R, Andrews JM, Ashby JP, Matthews RS. In vitro activity of lomefloxacin, a new quinolone antimicrobial agent, in comparison with those of other agents. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 617–622, 1988
Wise R, Andrews JM, Edwards LJ. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinolone derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 23: 559–564, 1983
Wise R, Baldwin DR, Andrews JM, Honeybourne D. Comparative pharmacokinetic disposition of fluoroquinolones in the lung. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 28 (Suppl. C): 65–71, 1991
Wolfson JS, Hooper DC. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 28: 581–586, 1985
Woodworth J, Fitzsimmons S. Lomefloxacin pharmacokinetics in young and elderly subjects. Abstract no. 1268. Program and Abstracts of the Twenty-Ninth Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Houston, September 17–20, 1989
Yoshida H, Bogaki M, Nakamura M, Nakamura S. Quinolone resistance-determining region in the DNA gyrase gyrA gene of Escherichia coli. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 1271–1272, 1990
Zweerink MM, Edison A. Inhibition of Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase by norfloxacin and 10 other quinolone carboxylic acids. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 29: 598–601, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freeman, C.D., Nicolau, D.P., Belliveau, P.P. et al. Lomefloxacin Clinical Pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 25, 6–19 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199325010-00002
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199325010-00002