Summary
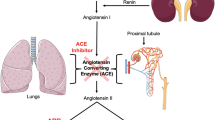
ACE inhibitors are used widely in the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure, but there is only limited information on adverse interactions between ACE inhibitors and other cardiovascular or noncardiovascular drugs. The present article provides an overview of this issue, with emphasis on those interactions having the greatest clinical implications.
In patients who have been sodium and/or volume depleted by thiazide or loop diuretics, the additional use of ACE inhibitors can lead to an excessive reduction in blood pressure and symptomatic hypotension. An increase in serum potassium levels may occur after coadministration of potassium-sparing diuretics and ACE inhibitors, resulting in hyperkalaemia especially in patients with renal insufficiency. The incidence of acute renal failure may be associated with ACE inhibitor therapy when these drugs are combined with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and given to patients whose renal function becomes increasingly dependent on angiotensin II and prostaglandins. There is some evidence, albeit scant, linking ACE inhibitors with the induction of lithium toxicity in patients maintained on lithium, and with the occurrence of severe hypersensitivity reactions in patients undergoing haemodialysis, venom immunisation or concomitant allopurinol therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The 1988 Joint National Committee. The 1988 report of the Joint National Committee on detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure. Arch Intern Med 1988; 148: 1023–38
The CONSENSUS Trial Study Group. Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. Results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS). N Engl J Med 1987; 316: 1429–35
SOLVD Investigators. Effect of enalapril on survival in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fractions and congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 293–302
Unger Th, Gohlke P. Converting enzyme inhibitors in cardiovascular therapy: current status and future potential. Cardiovasc Res 1994; 28: 146–58
Ryan N, Higgins G. Surprise results from ISIS-4 and GISSI-3. New Ethicals 1994; 31: 75–7
Shionoiri H. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions with ACE inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet 1993; 25: 20–58
Ondetti MA. Structural relationships of angiotensin converting-enzyme inhibitors to pharmacologic activity. Circulation 1988; 77 Suppl. 1: 174–18
Gohlke P, Lamberty V, Kuwer I, et al. Long-term low-dose angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition treatment increases vascular cyclic guanosine 3’,5’-monophosphate. Hypertension 1993; 22: 682–7
Gohlke P, Linz W, Schölkens BA, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition improves cardiac function. Role of bradykinin. Hypertension 1994; 23: 411–8
Stauss HM, Zhu Y-C, Redlich Th, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in infarct-induced heart failure in rats: bradykinin versus angiotensin II. J Cardiovasc Risk 1994; 1: 255–62
Linz W, Wiemer G, Gohlke P, et al. Contribution of kinins to the cardiovascular actions of ACE inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev. In press
Todd PA, Goa KL. Enalapril. A reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in hypertension. Drugs 1992; 43: 346–81
Di Bianco R. Adverse reactions with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Med Toxicol 1986; 1: 122–41
Clealand JGF, Dargie HJ, Ball SG, et al. Effects of enalapril in heart failure: a double blind study on exercise performance, renal function, hormones and metabolic state. Br Heart J 1985; 54: 305–12
Packer M, Lee WH, Kessler PD. Functional renal insufficiency during long-term therapy with captopril and enalapril in severe chronic heart failure. Ann Intern Med 1987; 106: 346–54
Packer M, Lee WH, Kessler PD. Preservation of glomerular filtration rate in human heart failure by activation of the renin-angiotensin system. Circulation 1986; 74: 766–74
Zanella MT, Mattei Jr E, Draible SA, et al. Inadequate aldosterone response to hyperkalaemia during angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in chronic renal failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1985; 38: 613–7
Weber MA. Safety issues during antihypertensive treatment with angiotensin converting inhibitors. Am J Med 1988; 84 Suppl. 4A: 16–23
Balfour JA, Goa KL. Benazepril. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Drugs 1991; 42: 511–39
Wood SM, Mann RD, Rawlins MD. Angio-oedema and urticaria associated with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. BMJ 1987; 294: 91–2
Warner NJ, Rush JE. Safety profiles of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Drugs 1988; 35 Suppl. 5: 89–97
Wadworth AN, Brodgen RN. Quinapril. A review of its pharmacological properties, and therapeutic efficacy in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1991; 41: 378–99
Plosker GI, Sorkin EM. Quinapril. A reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1994; 48: 227–52
Todd PA, Fitton A. Perindopril. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1991; 42: 90–114
Weinberger MH. Comparison of captopril and hydrochlorothiazide alone and in combination in mild to moderate essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1982; 14: 127S-31S
Lancaster SG, Todd PA. Lisinopril. A preliminary review of its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, and therapeutic use in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Drugs 1988; 35: 646–69
Todd PA, Benfield P. Ramipril. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1990; 39: 110–35
Wiseman LR, McTavish D. Trandolapril. A review of its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, and therapeutic use in essential hypertension. Drugs 1994; 48: 71–90
Deget F, Brodgen RN. Cilazapril. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1991; 41: 799–820
Kaiser G, Dresse A, Ackermann R, et al. Interaction between benazepril hydrochloride and hydrochlorothiazide in healthy volunteers [abstract]. Eur Heart J 1989; 10 (Suppl.): 118
Horvath AM, Ferry JJ, Sedman AJ, et al. Lack of a quinapril-hydrochlorothiazide pharmacokinetic drug interaction in healthy volunteers [abstract]. J Clin Pharmacol 1987; 27: 720
Nilsen OG, Sellevold OFM, Romfo OS, et al. Pharmaeokinetics and effects on renal function following cilazapril and hydrochlorothiazide alone and in combination in healthy subjects and hypertensive patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1989; 27: 323S-8S
Todd PA, Heel RC. Enalapril. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Drugs 1986; 31: 198–248
Gomez HJ, Vincent JC, Moncloa F. The clinical pharmacology of lisinopril. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1987; 9 Suppl. 3: S27–S34
Brown CL, Backhouse CI, Grippat JC, et al. The effect of perindopril and hydrochlorothiazide alone and in combination on blood pressure and on the renin-angiotensin system in hypertensive subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1990; 39: 327–32
Duchin KL, McKinstry DN, Cohen AI, et al. Pharmacokinetics of captopril in healthy subjects and in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Clin Pharmacokinet 1988; 14: 241–59
Beermann B. Pharmacokinetics of lisinopril. Am J Med 1988; 85 Suppl. 3B: 25–30
Van Hecken AM, Verbesselt R, Buntnix A, et al. Absence of a pharmacokinetic interaction between enalapril and furosemide. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1987; 23: 84–7
De Lepeleire I, Van Hecken A, Verbesselt R, et al. Interaction between furosemide and the converting enzyme inhibitor benazepril in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1988; 34: 465–8
Meyer BH, Muller FO, Luus HG, et al. Pharmacokinetic interaction study between trandolapril, a new ACE inhibitor, and furosemide [abstract]. J Hypertens 1992; 10 Suppl. 4: 274
Johnston GD, Passmore AP. The effects of cilazapril alone and in combination with frusemide in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1989; 27 Suppl. 2: 235–42
Niarchos AP, Pickering TG, Case DB, et al. Role of renin-angiotensin system in blood pressure regulation. The cardiovascular effects of converting enzyme inhibition in normotensive subjects. Circ Res 1979; 45: 829–57
MacGregor GA, Markandu ND, Singer DRJ, et al. Moderate sodium restriction with angiotensin converting inhibitor: a double blind study. BMJ 1987; 294: 531–4
Vidt DG (for the Multiclinic Study Group).A controlled multi-clinic study to compare the antihypertensive effects of MK-421, hydrochlorothiazide, and MK-421 combined with hydrochlorothiazide in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. J Hypertens 1984; 2 Suppl. 2: 81–8
Pethica BD. Safety and tolerability of benazepril in the treatment of hypertension — an overview. In: Brunner HR, Salvetti A, Sever PS, editors. Benazepril: profile of a new ACE inhibitor. Royal Society of Medicine Services International Congress and Symposium Series No. 166. Royal Society of Medicine Services, 1990: 161–7
Carretero OA, Scicli AG. The renal kallikrein-kinin system in human and in experimental hypertension. Am J Physiol 1980; 238: F247–55
McLay JS, McMurray JJ, Bridges AB, et al. Acute effects of captopril on the renal actions of furosemide in patients with chronic heart failure. Am Heart J 1993; 126: 879–86
Toussaint C, Masselink A, Gentges A, et al. Interference of different ACE-inhibitors with the diuretic action of furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide. Klin Wochenschr 1989; 67: 1138–46
Waeber B, Gavras I, Brunner HR, et al. Safety and efficacy of chronic therapy with captopril in hypertensive patients I. An update. J Clin Pharmacol 1981; 21: 508–16
Ponce SP, Jennings AE, Madias NE, et al. Drug-induced hyperkalemia. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985; 64: 357–70
Speirs CJ, Dollery CT, Inman WHW, et al. Postmarketing surveillance of enalapril. II: Investigation of the potential role of enalapril in deaths with renal failure. BMJ 1988; 297: 830–2
Singer DRJ, Markandu ND, Shore AC, et al. Captopril and nifedipine in combination for moderate to severe essential hypertension. Hypertension 1987; 9: 629–33
Brouwer RML, Bolli P, Erné P, et al. Antihypertensive treatment using calcium antagonists in combination with captopril rather than diuretics. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1985; 7: S88–S91
Guazzi MD, DeCesare N, Galli C, et al. Calcium channel blockade with nifedipine and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition with captopril in the therapy of patients with severe primary hypertension. Circulation 1984; 70: 279–84
MacGregor GA, Markandu ND, Smith SJ, et al. Captopril: contrasting effects of adding hydrochlorothiazide, propranolol, or nifedipine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1985; 7 Suppl. 1: S82–7
Pieri R, Nardeccia A, Pirelli A. Combined nifedipine and captopril treatment in moderately severe primary hypertension. Am J Nephrol 1986; 6 Suppl. 1: 111–4
Salvetti A, Innocenti PF, Iardella M, et al. Captopril and nifedipine interactions in the treatment of essential hypertensives: a crossover study. J Hypertens 1987; 5 Suppl. 4: S139–42
DeQuattro V. Benazepril compared with other antihypertensive agents, singly and in combination — a review. In: Brunner HR, Salvetti A, Sever PS, editors. Benazepril: profile of a new ACE inhibitor. Royal Society of Medicine Services International Congress and Symposium Series No.166. Royal Society of Medicine Services, 1990: 91–8
Loock ME, Rossouw DS, Venter CP. Benazepril and nifedipine alone and in combination for the treatment of essential hypertension in Black patients [abstract]. Chest 1990; 98 Suppl.: 17S
Kloke HJ, Huysmans FThM, Wetzels JFM, et al. Antihypertensive effects of nitrendipine and cilazapril alone, and in combination in hypertensive patients with chronic renal failure. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1989; 27: 289S-99S
Donnelly R, Elliot HL, Reid JL. Nicardipine combined with enalapril in patients with essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1986; 22: 283S-7S
Sun JX, Cipriano A, Chan K, et al. Pharmacokinetic interaction study between benazepril and amlodipine in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1994; 47: 285–9
Bainbridge AD, MacFadyen RJ, Lees KR, et al. A study of the acute pharmacodynamic interaction of ramipril and felodipine in normotensive subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1991; 31: 148–53
Tremblay D, Patat A, Rey E, et al. Absence of interaction between trandolapril and nifedipine [abstract]. J Hypertens 1992; 10 Suppl. 4: 342
Douglas WW. Polypeptides — angiotensin, plasma kinins, and others. In: Goodman Gilman A, Goodman LS, Rall TW, et al, editors. The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. New York: MacMillan, 1985: 639–59
Kondowe GB, Copeland S, Passmore AP, et al. The effect of chronic captopril therapy on adrenergic receptors, plasma noradrenaline and the vascular responses to infused noradrenaline. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1987; 32: 229–35
Pickering TG. The use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in combination with other antihypertensive agents. Am J Hypertens 1991; 4: 73S-8S
Unger Th, Gohlke P, Gruber MG. Converting enzyme inhibitors. In: Ganten D, Mulrow PJ, editors. Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Vol 93. Berlin: Springer Verlag, 1990: 377–481
Pickering TG, Case DB, Sullivan PA, et al. Comparison of antihypertensive and hormonal effects of captopril and propranolol at rest and during exercise. Am J Cardiol 1982; 49: 1566–8
Gengo FM, Brady E. The pharmacokinetics of benazepril relative to other ACE inhibitors. Clin Cardiol 1991; 14 Suppl. IV: 44–50
Belz GG, Breithaupt K, Erb K, et al. Influence of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor cilazapril, the β-blocker propranolol and their combination on haemodynamics in hypertension. J Hypertens 1989; 7: 817–24
Wing LMH, Chalmers JP, West MJ, et al. Enalapril and atenolol in essential hypertension: attenuation of hypotensive effects in combination. Clin Exp Hypertens 1988; 10 Part A: 119–33
Franz IW, Behr V, Ketelhur R. Resting and exercise blood pressure with atenolol, enalapril and a low dose combination. J Hypertens 1987; 5 Suppl. 3: 537–41
Clealand JGF, Dargie HJ, Pettigrew A, et al. The effects of captopril on serum digoxin and urinary urea and digoxin clearance in patients with congestive heart failure. Am Heart J 1986; 112: 130–5
Magelli C, Bassein L, Ribani MA, et al. Lack of effect of captopril on serum digoxin in congestive heart failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1989; 22: 752–3
Miyakawa T, Kobayashi L, Shionoiri H. The effect of captopril on serum digoxin concentration in patients with mild congestive heart failure [abstract]. Circulation 1987; 76: IV–86
Douste-Blazy Ph, Blanc M, Montastruc JL, et al. Is there any interaction between digoxin and enalapril? Br J Clin Pharmacol 1986; 22: 752–3
Vandenburg MJ, Kelly JG, Wiseman WT, et al. The effect of lisinopril on digoxin pharmacokinetics in patients with congestive heart failure [abstract]. Proceedings of the British Pharmacological Society, 1988 Jan 6–8; London. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1988; 25: 656P-7P
Vandenburg MJ, Stephens JD, Dews IM, et al. Lack of pharmacokinetic interaction between digoxin and perindopril after chronic treatment of patients with congestive heart failure [abstract]. J Clin Pharmacol 1990; 30: 858
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, Francis RJ, et al. Clinical pharmacology of cilazapril. Drugs 1991; 41 Suppl. 1: 3–10
Vandenburg MJ, Morris F, Marks C, et al. A study of the potential pharmacokinetic interaction of lisinopril and digoxin in healthy volunteers. Xenobiotica 1988; 18: 1179–84
Ferry JJ, Sedman AJ, Hengy H, et al. Concomitant multiple dose quinapril administration does not alter the steady-state pharmacokinetics of digoxin [abstract]. Pharm Res 1987; 4 Suppl.: 98
Kromer EP, Elsner D, Riegger GAJ. Digoxin, converting-enzyme inhibition (quinapril), and the combination in patients with congestive heart failure function class II and sinus rhythm. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1990; 16: 9–14
Doering W, Maass L, Irmisch R, et al. Pharmacokinetic interaction study with ramipril and digoxin in healthy volunteers. Am J Cardiol 1987: 59: 60D-4D
Johnson BF, Wilson J, Johnson J, et al. Digoxin pharmacokinetics and spirapril, a new ACE inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol 1991; 31: 527–30
Swartz SL, Williams GH. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and prostaglandins. Am J Cardiol 1982; 49: 1405–9
Salvetti A, Pedrinelli R, Magagna A, et al. Differential effects of selective and non-selective prostaglandin-synthesis inhibition on the pharmacological responses to captopril in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Sci 1982; 63: 261S-3S
Salvetti A, Abdel-Haq B, Magagna A, et al. Indomethacin reduces the antihypertensive action of enalapril. Clin Exp Hypertens 1987; A9: 559–67
Lucarini AR, Abdel-Haq B, Arrighi P, et al. Are prostaglandins involved in the systemic and renal haemodynamic actions of lisinopril? [abstract]. Am J Hypertens 1989; 2: 113A
Abdel-Haq B, Magagana A, Favilla S, et al. Hemodynamic and humoral interactions between perindopril and indomethacin in essential hypertensive subjects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1991; 18 Suppl. 7: S33–6
Kirch W, Stroemer K, Hoogkamer JFW, et al. The influence of prostaglandin inhibition by indomethacin on blood pressure and renal function in hypertensive patients treated with cilazapril. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1989; 27 Suppl. 2: 297–301
Belz GG, Kirch W, Kleinbloesem CH. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Relationship between pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 1988; 15: 295–318
Hall D, Zeitler H, Rudolph W. Counteraction of the vasodilator effects of enalapril by aspirin in severe heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992; 20: 1549–55
Van Wijngaarden J, Smit AJ, de Graeff PA, et al. Effects of acetylsalicylic acid on peripheral hemodynamics in patients with chronic heart failure treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1994; 23: 240–5
Heeg JE, de Jong PE, Vriesendorp R, et al. Additive anti-proteinuric effect of the NSAID indomethacin and the ACE inhibitor lisinopril. Am J Nephrol 1990; 10 Suppl. 1: 94–7
Heeg JE, de Jong PE, de Zeeuw D. Additive anti-proteinuric effect of angiotensin converting-enzyme inhibition and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy: a clue to the mechanism of action. Clin Sci 1991; 81: 367–72
Packer M. Interaction of prostaglandins and angiotensin II in the modulation of renal function in congestive heart failure. Circulation 1988; 77 Suppl. 1: I64–I73
Dietz R, Nagel F, Osterziel K-J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and renal function in heart failure. Am J Cardiol 1992; 70: 119C-25C
Seelig CB, Maloley PA, Campbell JR. Nephrotoxicity associated with concomitant ACE inhibitor and NSAID therapy. South Med J 1990; 83: 1144–8
Cinotti GA. Clinical assessment of the renal toxicity of anti-rheumatic drugs. Arch Toxicol 1984; 7 (Suppl.): 338–49
Murray MD, Brater DG. Renal toxicity of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1993; 32: 435–65
Nicolls MG, Gilchrist NL. Sulindac and cough induced by converting enzyme inhibitors. Lancet 1987; 1: 872
Gilchrist NL, Richards AM, March R, et al. Effect of sulindac on angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor-induced cough: randomised placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study. J Hum Hypertens 1989; 3: 451–5
Choudry N, McEwan JR, Fuller RW. The effects of sulindac on the cough associated with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor therapy [abstract]. Proceedings of the British Pharmacological Society, 1988 Dec 19–21; London. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1988; 27: 657P-8P
Murray BM, Venuto RC, Kohli R, et al. Enalapril-associated acute renal failure in renal transplants: possible role of cyclosporine. Am J Kidney Dis 1990; 16: 66–9
Pulik M, Lida H. Interaction lithium-inhibiteurs de l’enzyme de conversion. Presse Médicale 1988; 17: 755
Douste-Blazy Ph, Rostin M, Livaek B, et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and lithium treatment. Lancet 1986; 1: 1448
Correa FJ, Eiser AR. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and lithium toxicity. Am J Med 1992; 93: 108–9
Baldwin CM, Safferman AZ. A case of lisinopril-induced lithium toxicity. DICP 1990; 24: 946–7
Navis GJ, de Jong PE, de Zeeuw D. Volume homeostasis, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition, and lithium therapy. Am J Med 1989; 86: 621
Fernere M, Lachkar H, Richard JL, et al. Captopril and insulin sensitivity. Ann Intern Med 1985; 102: 134–5
Helgeland A, Strommen R, Hagelund C, et al. Enalapril, atenolol, and hydrochlorothiazide in mild to moderate hypertension. Lancet 1986; 1: 872–5
Pollare T, Lithel H, Berne C. A comparison of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide and captopril on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with hypertension. N Engl J Med 1989; 321: 868–73
Rett K, Wicklmayr M, Dietze GJ. Hypoglycemia in hypertensive diabetic patients treated with sulfonylureas, biguanides, and captopril. N Engl J Med 1988; 319: 1609
Arauz-Pacheco C, Ramirez LC, Rios JM, et al. Hypoglycemia induced by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes receiving sulfonylurea therapy. Am J Med 1990; 89: 811–3
Shionoiri H, Iino S, Inoue S. Glucose metabolism during captopril mono- and combination-therapy in diabetic hypertensive patients. Clin Exp Hypertens 1987; 9 Part A: 675–9
Goldner MG, Knatterud GL, Prout TE. Effects of hypoglycaemic agents on vascular complications in patients with adult-onset diabetes. III. Clinical implications of UGDP results. JAMA 1971; 218: 1400–10
United Kingdom prospective diabetes study. II. Reduction in HbA1c with basal insulin supplement, sulphonylurea or biguanide therapy. Diabetes 1985; 34: 793–8
Pennell DJ, Nunan TO, O’Doherty MJ, et al. Fatal Stevens-Johnson syndrome in a patient on captopril and allopurinol. Lancet 1984; 1: 463
Samanta A, Burden AC. Fever, myalgia, and arthralgia in a patient on captopril and allopurinol. Lancet 1984; 1: 679
Tielemans C, Madhoun P, Lenaers M, et al. Anaphylactoid reactions during hemodialysis on AN69 membranes in patients receiving ACE inhibitors. Kidney Int 1990; 38: 982–4
Verresen L, Waer M, Vanrenterghem Y, et al. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and anaphylactoid reactions to high-flux membrane dialysis. Lancet 1990; 2: 1360–2
Alvarez-Lara MA, Martin-Malo A, Espinosa M, et al. ACE inhibitors and anaphylactoid reactions to high-flux membrane dialysis [letter]. Lancet 1991; 1: 370
Jadoul M, Struyven J, Stragier A, et al. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and anaphylactoid reactions to high-flux membrane dialysis [letter]. Lancet 1991; 1: 112
Van Es A, Henny FC, Lobatto S. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and anaphylactoid reactions to high-flux membrane dialysis [letter]. Lancet 1991; 1: 112–3
Parnes EL, Shapiro WB. Anaphylactoid reactions in hemodialysis patients treated with the AN69 dialyzer. Kidney Int 1991; 40: 1148–52
Tunon-de-Lara JM, Villanueva P, Marcos M, et al. ACE inhibitors and anaphylactoid reactions during venom immunotherapy. Lancet 1992; 1: 908
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mignat, C., Unger, T. ACE Inhibitors. Drug-Safety 12, 334–347 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199512050-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199512050-00005