Summary
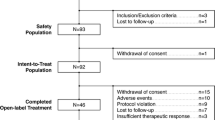
506 patients with schizophrenia, diagnosed according to Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-III) criteria, were included in a long term treatment programme with remoxipride, a selective dopamine (D2)-receptor antagonist. This overview includes pooled data from all patients who have been treated long term with remoxipride in clinical trials, focusing on patients treated for more than 6 months (n = 283).
Remoxipride was administered in daily doses of 75 to 600mg. The assessment tools were Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), Clinical Global Impression (CGI), Simpson and Angus scale, Abnormal Involuntary Movements Scale (AIMS) for abnormal involuntary movements, adverse events/symptoms using a 26-item checklist, clinical chemistry, and haematology and cardiovas-cular investigations.
The majority of patients had a long duration of illness (median 11 years). 67% of patients (340/506) withdrew from treatment before 12 months and 44% (223/506) stopped treatment before 6 months. The median BPRS total score decreased during the first 3 months from 23 to 12, and this level of improvement was maintained throughout the 12-month period. Treatment-emergent adverse events reported by more than 5% of the patients were insomnia, tiredness, drowsiness and tremor in the group treated for 6 to 12 months. No symptoms, including checklist extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), were reported by more than 5% of patients treated for 12 months. Low frequencies of EPS according to the Simpson and Angus scale were seen in patients treated for more than 6 months (n = 147). A small but statistically significant reduction of the mean total AIMS score from baseline to last rating was observed.
There were infrequent changes in heart rate, resting diastolic blood pressure and electrocardiogram (ECG). Clinical chemistry and haematology data showed no evidence of clinically significant changes over time during the 12 months of treatment. Among 506 patients, 7 suicides and 7 suicide attempts occurred during the study period. Other serious adverse events were abnormal liver function test (2 cases), gastrointestinal, urinary retention, status epilepticus (psychotic polydipsia), granulocytopenia (1 each) and myocardial infarction (5 cases).
Remoxipride is of potential value as a drug which is both effective and well tolerated in the long term management of patients with schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd ed., APA, Washington, D.C., 1980
Department of Health, Education and Welfare, Public Health Service Alcohol Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration National Institute of Mental Health. Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS). Early Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit Intercom 4: 3–6, 1975
Drake RE, Gates C, Whitaket A, Cotton PG. Suicide among schizophrenics: a review. Comprehensive Psychiatry 26: 90–100, 1985
Farde L, Bahr Distribution of remoxipride to the human brain and central D2-dopamine receptor binding examined in vivo PET. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 92–98, 1990
Farde L, Wiesel FA, Nordström AL, Sedvall G. D1 and D2-dopamine receptor occupancy during treatment with conventional and atypical neuroleptics. Psychopharmacology 99: 28–31, 1989
Kane JM. Prevention and treatment of neuroleptic noncompliance. Psychiatric Annals 16: 576–579, 1986
Kane JM. Treatment programme and long-term outcome in chronic schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 151–157, 1990
King DJ, Blomqvist M, Cooper SJ, Doherty MM, Mitchel MJ. A placebo controlled trial of remoxipride in the prevention of relapse in chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 107: 175–179, 1992
Köhler Hall H, Magnusson Lewander T, Gustafsson Biochemical pharmacology of the atypical neuroleptic remoxipride. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 26–36, 1990
Lewander T, Westerbergh SE, Morrison D. Clinical profile of remoxipride — combined analysis of a comparative double-blind multicenter trial programme. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 92–98, 1990
McCreadie RG, Todd M, Livingstone M, Ecclestone D, Watt JAG. A double-blind comparative study of remoxipride and thioridazine in the acute phase of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 136–138, 1990
Morrison D, Englund A, Lawrie V, Lewander T, Schlachet A. Safety evaluation in both short- and long-term treatment of schizophrenia with remoxipride. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 164–169, 1990
Ögren SO, Florvall L, Hall H, Magnusson O, Ängeby-Möller K. Neuropharmacological and behavioural properties of remoxipride in the rat. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 158–163, 1990
Ögren SO, Hall H, Köhler Magnusson Lindblom LO. Remoxipride, a new potential antipsychotic compound with selective antidopaminergic actions in the rat brain. European Journal of Pharmacology 102: 459–474, 1983
Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale, Psychological reports. In van Praag (Ed.) Handbook of Biological Psychiatry, Vol. IV, pp. 359–391, Dekker, New York, 1981
Simpson GM, Angus JWS. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 212: 11–19, 1970
Simpson GM, Pi EH, Sramek JJ. Adverse effects of antipsychotic agents. Drugs 21: 138–151, 1981
US Department of Health, Education and Welfare. ECDEU as-sessments manual, National Institute of Mental Health, Rockville, 1976
US Department of Health and Human Services. Food and Drug Administration, Federal Register 52: 37931–37936, 1987
Wålinder J, Holm AC. Experiences of long-term treatment with remoxiprixle: efficacy and tolerability. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 82(Suppl. 358): 158–163, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holm, AC., Edsman, I., Lundberg, T. et al. Tolerability of Remoxipride in the Long Term Treatment of Schizophrenia. Drug-Safety 8, 445–456 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199308060-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00002018-199308060-00005