Abstract
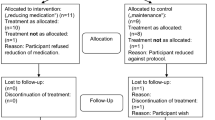
Sixty-two DSM III chronic schizophrenic inpatients were selected for a double-blind, placebo controlled, multi-centre, relapse prevention study of remoxipride, a selective dopamine (D2)-receptor antagonist. After a 1 month placebo washout, 23 patients had relapsed and were withdrawn. Of the remaining patients 19 were randomised to remoxipride (150–300 mg daily) and 20 to placebo. Their median age was 58 years, 26 were male, and the median duration of illness was 33 years. After 24 weeks a further total of 8 remoxipride and 17 placebo patients had been withdrawn. Excluding three patients withdrawn for reasons other than relapse, the comparative relapse rates were 37% and 75%, respectively (P=0.015). Efficacy analyses using clinical global impression (P=0.04) and change in BPRS scores (P=0.016) were in favour of remoxipride. Extrapyramidal symptoms were minimal in both groups. Treatment emergent adverse events were similar in the two groups. Remoxipride is therefore of potential value as a safe drug which is both effective and well tolerated in the long term management of chronic schizophrenic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1980) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd edn. APA, Washington, DC
Andreasen NC (1982) Negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:784–788
Andrews P, Hall JN, Snaith RP (1976) A controlled trial of phenothiazine withdrawal in chronic schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry 128:451–455
Baldessarini RJ, Davis JM (1980) Whatis the best maintenance dose of neuroleptics in schizophrenia? Psychiatry Res 3:115–122
Cooper SJ, Doherty MM (1989) Remoxipride in the treatment of coexistent schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease. Hum Psychopharmacol 4:145–147
Davis JM (1976) Comparative doses and costs of antipsychotic medication. Arch Gen Psychiatry 33:858–861
Fottrell E, Sheikh M, Kothari R, Sayed I (1976) Long-stay patients with long-stay drugs. A case for review: a cause for concern. Lancet i:81–82
Judah LN, Josephs ZM, Murphee OD (1961) Results of simultaneous withdrawal of ataraxics in 500 chronic psychotic patients. Am J Psychiatry 118:156–158
Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL (1980) The statistical analysis of failure time data. Wiley, New York, pp 16–19
King DJ, Devaney N, Cooper SJ, Blomqvist M, Mitchell MJ (1990) Pharmacokinetics and antipsychotic effect of remoxipride in chronic schizophrenic patients. J Psychopharmacol 4:83–89
Kolakowska T (1976) Brief psychiatric rating scale. Glossaries and rating instruction. Department of Psychiatry, Oxford University, Oxford, England
Letemendia FJJ, Harris AD (1967) Chlorpromazine and the untreated chronic schizophrenic: a long-term trial. Br J Psychiatry 113:950–958
Lewander T, Westerbergh S-E, Morrison D (1990) Clinical profile of remoxipride- a combined analysis of a comparative double-blind multicentre trial programme. Acta Psychiatr Scand 82 [Suppl 358]:92–98
Ögren SO, Hall H, Köhler C, Magnusson O, Lindblom LO, Ängeby K, Florwall L (1984) Remoxipride, a new potential antipsychotic compound with selective antidopaminergic actions in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 102:459–474
Olson GW, Peterson DB (1960) Sudden removal of tranquilizing drugs from chronic psychiatric patients. J Nerv Ment Dis 131:252–255
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Prien RF, Cole JO, Belkin NF (1968) Relapse in chronic schizophrenics following abrupt withdrawal of tranquillizing medication. Br J Psychiatry 115:679–686
SAS Institute Inc (1985a) SAS User's Guide: Basics, version 5th edn. SAS Institute, Cary NC, pp 1290
SAS Institute Inc (1985b) SAS User's Guide: Statistics, version 5th edn. SAS Institute, Cary NC, pp 956
Simpson GM, Angus JWS (1970) A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 45 [Suppl 212]:11–12
Suy E, Woestenborghs R, Heykants J (1982) Bioavailability and clinical effect of two different concentrations of haloperidol decanoate. Curr Ther Res 31:982–991
Wing JK (1961) A simple and reliable sub-classification of chronic schizophrenia. J Ment Sci 107:862–875
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, D.J., Blomqvist, M., Cooper, S.J. et al. A placebo controlled trial of remoxipride in the prevention of relapse in chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 107, 175–179 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245134
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245134