Abstract
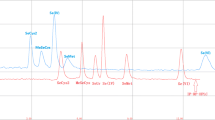
Pumpkins were treated by spraying the leaves in the flowering period with a water solution containing 1.5 mg Se per liter in the form of Na2SeO4. The average total selenium content of seeds was found to be 0.19 μg g-1 in nontreated pumpkins and 1.1 μg g-1 in exposed ones. For speciation analysis, enzymatic hydrolysis with different amounts of Protease XIV was carried out. Under optimal conditions of enzymatic hydrolysis, 90% of the total selenium was found in soluble forms. Separation of species was performed using HPLC on anion and cation exchange columns and for detection UV-HG-AFS was applied. In enzymatic hydrolysis extracts, the main fraction of selenium was bound as selenomethionine (SeMet), representing on average of 81 ± 8% of the total Se content in the sample.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Seppanen, M. Turakainen, and H. Hartikainen, Plant Sci., 2003, 755, 311.
E. Valkama, M. Kivimaenpaa, H. Hartikainen, and A. Wulff, Agric. For. Meteorol., 2003, 120, 267.
K. Pyrzynska, Mikrochim. Acta, 2002, 140, 55.
M. Stadlober, M. Sager, and K. J. Irgolic, Food Chem., 2001, 73, 357.
S. McSheehy, F. Pannier, J. Szpunar, M. Potin-Gautier, and R. Lobinski, Analyst, 2002, 727, 223.
C. Ip, M. Birringer, E. Block, M. Kotrebai, J. F. Tyson, P. C. Uden, and D. J. Lisk, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2000, 48, 2062.
E. T. Bodo, Z. Stefanka, I. Ipolyi, C. Soros, M. Dernovics, and P. Fodor, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2003, 377, 32.
S. S. Kannamkumarath, K. Wrobel, K. Wrobel, A. Vonderheide, and J. A. Caruso, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2002, 373, 454.
V. Stibilj, I. Kreft, P. Smrkolj, and J. Osvald, Eur. Food Res. Technol, 2004, 279, 142.
C. Casiot, J. Szpunar, R. Lobinski, and M. Potin-Gautier, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1999, 14, 645.
C. B’Hymer and J. A. Caruso, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2000, 15, 1531.
G. A. Pedersen and E. H. Larsen, Fresenius J. Anal. Chem., 1997, 358, 591.
J. Auger, W. Yang, I. Arnault, F. Pannier, and M. Potin-Gautier, J. Chromatogr., 2004, 1032, 103.
K. Wrobel, K. Wrobel, S. S. Kannamkumarath, J. A. Caruso, I. A. Wysocka, E. Bulska, J. Swiatek, and M. Wierzbicka, Food Chem., 2004, 86, 617.
P. D. Whanger, C. Ip, C. E. Polan, P. C. Uden, and G. Welbaum, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2000, 48, 5723.
Y. Zhang and W. T. Frankenberger, Sci. Total Environ., 2001, 269, 39.
M. Vilano and R. Rubio, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2000, 111.
Zs. Stefanka, I. Ipolyi, M. Dernovics, and P. Fodor, Talanta, 2001, 55, 437.
M. Dernovics, Zs. Stefanka, and P. Fodor, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2002, 372, 473.
K. Pyrzynska, Analyst, 1996, 727, 77.
P. Smrkolj and V. Stibilj, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2004, 572, 11.
D. Mazej, I. Falnoga, and V. Stibilj, Acta Chim. Slov., 2003, 50, 185.
M. Dermelj, A. R. Byrne, M. Franko, B. Smodis, and P. Stegnar, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. Lett., 1986, 106, 91.
V. Stibilj, M. Dermelj, and A. R. Byrne, Mikrochim. Acta, 1996, 123, 311.
D. Mazej, I. Falnoga, M. Veber, and V. Stibilj, Talanta, 2005, in press.
H. Hartikainen, in “Proceedings of the World Congress of Soil Science”, ed. J. Kheoruenromme, 2002, Bangkok, Thailand, 1693.
P. Moreno, M. A. Quijano, A. M. Gutierrez, M. C. Perez-Conde, and C. Camara, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2002, 374, 466.
E. Dumont, K. De Cremer, M. Van Hulle, C. C. Chery, F. Vanhaecke, and R. Cornells, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2004, 19, 167.
W. R. Wolf and R. J. Goldschmidt, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2004, 378, 1175.
A. P. Vonderheide, K. Wrobel, S. S. Kannamkumarath, C. B’Hymer, M. Montes-Bayon, C. P. De Leon, and J. A. Caruso, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2002, 50, 5722.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smrkolj, P., Stibilj, V., Kreft, I. et al. Selenium Species Determination in Selenium-Enriched Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) Seeds by HPLC-UV-HG-AFS. ANAL. SCI. 21, 1501–1504 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.1501
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21.1501