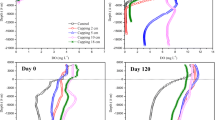
Abstract
Sulfate pollution of lakes and rivers is recognized as a serious problem in many regions of Central Europe, thus we evaluated the role of rewetted fens in mitigating sulfate pollution and tested if high sulfate concentrations in fen-feeding water counteract the re-establishment of their function as sinks for phosphorus (P). A long-term incubation experiment was conducted with highly decomposed peat from upper soil layers of fens that have been rewetted for 1 to 15 years. Periodic sulfate pulses to inundated peat mesocosms, equating to an annual loading of 50 g S m−2, induced significant changes of sulfate consumption and phosphorus mobilization. Sulfate consumption of highly decomposed peat from all sampling sites was related to sulfate concentrations in overlying water (linear regression, p<0.01). Sulfate additions also led to significant increases of P concentrations or P mobilization in peat porewater (t test, p<0.05) and P concentrations in the overlying water were 2–3 times higher than in non-treated controls. In conclusion, rewetting of fens is an important tool to mitigate sulfate pollution of adjacent lakes and rivers. However, an elevated sulfate concentration in waters feeding the fen impairs P retention and increases P losses to adjacent surface waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aherne, J., T. Larssen, B. J. Cosby, and P. J. Dillon. 2006. Climate variability and forecasting surface water recovery from acidification: modeling drought-induced sulphate release from wetlands. Science of the Total Environment 365:186–99.
Beltman, B., T. G. Rouwenhorst, M. B. van Kerkhov, T. van der Krift, and J. T. A. Verhoeven. 2000. Internal eutrophication in peat soils through competition between chloride and sulphate with phosphate for binding sites. Biogeochemistry 50:183–94.
Berg, P., N. Risgaard-Petersen, and S. Rysgaard. 1998. Interpretation of measured concentration profiles in sediment pore water. Limnology and Oceanography 43:1500–10.
Boström, B., J. M. Anderson, S. Fleischer, and M. Jansson. 1988. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. Hydrobiologia 170:229–44.
Bull, K. R., et al. (20 authors). 2001. Coordinated effects monitoring and modelling for developing and supporting international air pollution control agreements. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 130:119–30.
Caraco, N. F., J. J. Cole, and G. E. Likens. 1993. Sulfate control of phosphorus availability in lakes — A test and re-evaluation of Hasler and Einsele’s Model. Hydrobiologia 253:275–80.
DIN 38406-32. German standard methods for the examination of water, waste water and sludge — cations (group E) — Part 32: Determination of iron by atomic absorption spectrometry (E 32), 49. Lieferung 2001.
EN ISO 10304-1. Water quality — Determination of dissolved fluoride, chloride, nitrite, orthophosphate, bromide, nitrate and sulfate ions, using liquid chromatography of ions — Part 1: Method for water with low contamination, 33. Lieferung 1995.
EN ISO 14911. Water quality — Determination of dissolved Li+, Na+, NH4 +, K+, Mn2 +, Ca2 +, Mg2 +, Sr2 + and Ba2 + using ion chromatography — Method for water and waste water, 48. Lieferung 2000.
Evans, H. E., P. J. Dillon, and L. A. Molot. 1997. The use of mass balance investigations in the study of the biogeochemical cycle of sulphur. Hydrological Processes 11:765–82.
Furrer, G. and B. Wehrli. 1996. Microbial reactions, chemical speciation, and multicomponent diffusion in porewaters of a eutrophic lake. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 60:2333–46.
Gauci, V., D. Fowler, S. J. Chapman, and N. B. Dise. 2004. Sulfate deposition and temperature controls on methane emission and sulphur forms in peat. Biogeochemistry 71:141–62.
Gelbrecht, J., H.-J. Exner, S. Conradt, M. Rehfeld-Klein, and F. Sensel. 2002. Water chemistry. p. 74–85.In J. Köhler, J. Gelbrecht, and M. Pusch (eds.) Die Spree — Zustand, Probleme und Entwicklungsmöglichkeiten. Limnologie aktuell, Bd. 10, Schweizerbath, Stuttgart.
Geurts, J. J. M., A. J. P Smolders, J. T. A. Verhoeven, J. G. M. Roelofs, and L. P. M. Lamers. 2008. Sediment Fe:PO4 ratio as a diagnostic and prognostic tool for the restoration of macrophyte biodiversity in fen waters. Freshwater Biology 53:2101–16.
Gunnars, A., S. Blomquist, P. Johansson, and C. Andersson. 2002. Formation of Fe(III) oxyhydroxide colloids in freshwater and brackish seawater, with incorporation of phosphate and calcium. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 66:745–58.
Heagle, D. J., M. Hayashi, and G. van der Kamp. 2007. Use of solute mass balance to quantify geochemical processes in a prairie recharge wetland. Wetlands 27:806–18.
Hines, M. E., S. L. Knollmeyer, and J. B. Tugel. 1989. Sulfate reduction and other sedimentary biogeochemistry in a northern New England salt marsh. Limnology and Oceanography 34:578–90.
Holmer, M. and P. Storkholm. 2001. Sulphate reduction and sulphur cycling in lake sediments: a review. Freshwater Biology 46:431–51.
Hupfer, H. and J. Lewandowski. 2008. Oxygen controls the phosphorus release from lake sediments — a long-lasting paradigm in limnology. International Review of Hydrobiology 93:415–32.
Ingvorsen, K. and B. B. Jorgensen. 1984. Kinetics of sulfate uptake by freshwater and marine species ofDesulfovibrio. Archives of Microbiology 139:61–66.
Jensen, H. S., P. Kristensen, E. Jeppesen, and A. Skytthe. 1992. Iron:phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 235/236:731–43.
Joosten, H. and D. Clarke. 2002. Wise use of mires and peatlands — background and principles including a framework for decision-making. International Mire Conservation Group. NHBS Ltd., Totnes, Finland,
Kleeberg, A. 2003. Re-assessment of Wundsch’s (1940) ‘H2S-Oscillatoria-Lake’ type using the eutrophic Lake Scharmutzel (Brandenburg, NE Germany) as an example. Hydrobiologia 501:1–5.
Lamers, L. P. M., S. J. Falla, E. M. Samborska, I. A. R. van Dulken, G. van Hengstum, and J. G. M. Roelofs. 2002. Factors controlling the extent of eutrophication and toxicity in sulfatepolluted freshwater wetlands. Limnology and Oceanography 47:585–93.
Lucassen, E. C. H. E. T., A. J. P. Smolders, J. van de Crommenacker, and J. G. M. Roelofs. 2004. Effects of stagnating sulphate-rich groundwater on the mobility of phosphate in freshwater wetlands: a field experiment. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 160:117–31.
Lovley, D. R. and M. J. Klug. 1982. Intermediary metabolism of organic matter in the sediments of a eutrophic lake. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 43:552–60.
Lovley, D. R. and E. J. P. Phillips. 1986. Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 51: 683–89.
Murphy, J. and J. P. Riley. 1962. A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27:31–36.
Neubauer, S. C., K. Gilver, S. K. Valentine, and J. P. Megonigal. 2005. Seasonal patterns and plant mediated controls of subsurface wetland biogeochemistry. Ecology 86:3334–44.
Ohle, W. 1938. Die Bedeutung der Austauschvorgänge zwischen Schlamm und Wasser fü r den Stoffwechsel der Gewässer. Vom Wasser 13:87–97.
Okruszko, H. 1995. Influence of hydrological differentiation of fens on their transformation after dehydration and on possibilities for restoration. p. 113–19.In B. D. Wheeler, S. C. Shaw, W. J. Fojt, and R. A. Robertson (eds.) Restoration of Temperate Wetlands. Wiley, Chichester, UK.
Parkhurst, D. L. and C. A. J. Appelo. 1999. User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2) — a computer program for speciation, batch reaction, one dimensional transport, and inverse agrochemicals calculations. Water-Resources Investigations Report 4259, US Department of the Interior, Denver, CO, USA.
Puustjärvi, V. 1970. Degree of humification. Peat Plant News 3:48–52.
Roden, E. E. and J. W. Edmonds. 1997. Phosphate mobilization in iron-rich anaerobic sediments: microbial Fe(III) oxide reduction versus iron-sulfide formation. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 139:347–78.
Roelofs, J. G. M. 1991. Inlet of alkaline river water into peaty lowlands: effect on water quality andStratiotes aloides L. stands. Aquatic Botany 46:267–93.
Scheffer, B. and J. Blankenburg. 1993. The determination of the bulk density of peat soils. Agribiological Research 46: 46–53.
Sinke, A. J. C., A. A. Cornlese, T. E. Cappenberg, and A. J. B. Zehnder. 1992. Seasonal variation in sulfate reduction and methanogenesis in peaty sediments of eutrophic Lake Loosdrecht, The Netherlands. Biogeochemistry 16:43–61.
Smolders, A. J. P., L. P. M. Lamers, M. Moonen, K. Zwaga, and J. G. M. Roelofs. 2001. Controlling phosphate release from phosphate-enriched sediments by adding various iron compounds. Biogeochemistry 54:219–28.
Smolders, A. and J. G. M. Roelofs. 1993. Sulphate-mediated iron limitation and eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Aquatic Botany 46:247–53.
Smolders, A. J. P., M. Moonen, K. Zwaga, E. C. H. E. T. Lucassen, L. P. M. Lamers, and J. G. M. Roelofs. 2006. Changes in pore water chemistry of desiccating freshwater sediments with different sulphur contents. Geoderma 132:372–83.
Stoddard, J. L., et al. (22 authors). 1999. Regional trends in aquatic recovery from acidification in North America and Europe. Nature 401:575–78.
Urban, N. R., P. L. Brezonik, L. A. Baker, and L. A. Sherman. 1994. Sulfate reduction and diffusion in sediments of Little Rock Lake, Wisconsin. Limnology and Oceanography 39:797–815.
Van der Welle, M. E. W., J. G. M. Roelofs, and L. P. M. Lamers. 2008. Multi-level effects of sulphur-iron interactions in freshwater wetlands in The Netherlands. Science of the Total Environment 406:426–29.
Wang, F. and P. M. Chapman. 1999. Biological implications of sulphide in sediment — a review focusing on sediment toxicity. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 18:2526–32.
Whitmire, S. L. and S. K. Hamilton. 2005. Rapid removal of nitrate and sulfate in freshwater wetland sediments. Journal of Environmental Quality 34:2062–71.
Zak, D. and J. Gelbrecht. 2007. The mobilization of phosphorus, organic carbon and ammonium in the initial stage of fen rewetting (a case study from NE Germany). Biogeochemistry 85:141–51.
Zak, D., J. Gelbrecht, and C. E. W. Steinberg. 2004. Phosphorus retention at the redox interface of peatlands adjacent to surface waters in northeast Germany. Biogeochemistry 70:357–68.
Zak, D., J. Gelbrecht, C. Wagner, and C. E. W. Steinberg. 2008. Evaluation of phosphorus mobilization potential in rewetted fens by an improved sequential chemical extraction procedure. European Journal of Soil Science 59:1191–201.
Zak, D., A. Kleeberg, and M. Hupfer. 2006. Sulphate-mediated phosphorus mobilization in riverine sediments at increasing sulphate concentration, River Spree, NE Germany. Biogeochemistry 80:109–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zak, D., Rossoll, T., Exner, HJ. et al. Mitigation of sulfate pollution by rewetting of fens — A conflict with restoring their phosphorus sink function?. Wetlands 29, 1093–1103 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1672/09-102D.1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1672/09-102D.1