Abstract
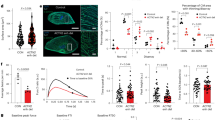
Viral myocarditis (VMC) is one of the most common acquired heart diseases in children and teenagers. However, its pathogenesis is still unclear, and effective treatments are lacking. This study aimed to investigate the regulatory pathway by which exosomes alleviate ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes (CMCs) induced by coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3). CVB3 was utilized for inducing the VMC mouse model and cellular model. Cardiac echocardiography, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and left ventricular fractional shortening (LVFS) were implemented to assess the cardiac function. In CVB3-induced VMC mice, cardiac insufficiency was observed, as well as the altered levels of ferroptosis-related indicators (glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), glutathione (GSH), and malondialdehyde (MDA)). However, exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSCs-exo) could restore the changes caused by CVB3 stimulation. Let-7a-5p was enriched in hucMSCs-exo, and the inhibitory effect of hucMSCs-exolet-7a-5p mimic on CVB3-induced ferroptosis was higher than that of hucMSCs-exomimic NC (NC: negative control). Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 (SMAD2) increased in the VMC group’ while the expression of zinc-finger protein 36 (ZFP36) decreased. Let-7a-5p was confirmed to interact with SMAD2 messenger RNA (mRNA), and the SMAD2 protein interacted directly with the ZFP36 protein. Silencing SMAD2 and overexpressing ZFP36 inhibited the expression of ferroptosis-related indicators. Meanwhile, the levels of GPX4, solute carrier family 7, member 11 (SLC7A11), and GSH were lower in the SMAD2 overexpression plasmid (oe-SMAD2)+let-7a-5p mimic group than in the oe-NC+let-7a-5p mimic group, while those of MDA, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and Fe2+ increased. In conclusion, these data showed that ferroptosis could be regulated by mediating SMAD2 expression. Exo-let-7a-5p derived from hucMSCs could mediate SMAD2 to promote the expression of ZFP36, which further inhibited the ferroptosis of CMCs to alleviate CVB3-induced VMC.
摘要
病毒性心肌炎(VMC)是儿童和青少年最常见的获得性心脏病之一。其发病机制尚不明确, 且缺乏有效的治疗方法。本研究旨在探讨外泌体减轻柯萨奇病毒B3(CVB3)诱导的心肌细胞(CMCs)铁死亡的调控通路。我们用CVB3诱导小鼠VMC模型和细胞模型, 使用心脏超声心动图、左室射血分数(LVEF)和左室短轴缩短率(LVFS)评价心功能。在CVB3诱导的VMC小鼠中, 我们观察到小鼠心功能不全和铁死亡相关指标(谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4(GPX4)、谷胱甘肽(GSH)和丙二醛(MDA))的表达失调。然而, 人脐带间充质干细胞来源的外泌体(hucMSCs-exo)可以恢复CVB3引起的改变。Let-7a-5p富集于hucMSCs-exo中, 且hucMSCs-exolet-7a-5p mimic对CVB3诱导的铁死亡的抑制作用高于hucMSCs-exomimic NC。在VMC组中, SMAD2表达升高, 而ZFP36表达降低。Let-7a-5p靶向SMAD2信使RNA(mRNA), 且SMAD2蛋白与ZFP36蛋白直接相互作用。沉默SMAD2和过表达ZFP36均可抑制铁死亡相关指标的表达。同时, 与oe-NC+let-7a-5p mimic组比较, oe-SMAD2+let-7a-5p mimic组中的GPX4、溶质载体家族7成员11(SLC7A11)和GSH水平降低, 而MDA、活性氧(ROS)和Fe2+水平升高。综上所述, 这些数据表明铁死亡可以通过介导SMAD2的表达来调节。HucMSCs来源的exo-let-7a-5p可以通过介导SMAD2促进ZFP36的表达, 进一步抑制CMCs的铁死亡, 从而缓解CVB3诱导的VMC。
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The dataset used or analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bao MH, Feng X, Zhang YW, et al., 2013. Let-7 in cardiovascular diseases, heart development and cardiovascular differentiation from stem cells. Int J Mol Sci, 14(11):23086–23102. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141123086
Camaschella C, Nai A, Silvestri L, 2020. Iron metabolism and iron disorders revisited in the hepcidin era. Haematologica, 105(2):260–272. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.232124
Chen B, Sang YT, Song XJ, et al., 2021. Exosomal miR-500a-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through targeting USP28. Theranostics, 11(8):3932–3947. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.53412
Chen CY, Choong OK, Liu LW, et al., 2019. MicroRNA let-7-TGFBR3 signalling regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis after infarction. EBioMedicine, 46:236–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.001
Chen P, Xie YQ, Shen E, et al., 2011. Astragaloside IV attenuates myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1 signaling in coxsackievirus B3-induced cardiomyopathy. Eur J Pharmacol, 658(2–3):168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.02.040
Chen X, Comish PB, Tang DL, et al., 2021. Characteristics and biomarkers of ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol, 9:637162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.637162
Dong LY, Wang Y, Zheng TT, et al., 2021. Hypoxic hUCMSC-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate allergic airway inflammation and airway remodeling in chronic asthma mice. Stem Cell Res Ther, 12:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-02072-0
el Andaloussi S, Mäger I, Breakefield XO, et al., 2013. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 12(5):347–357. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3978
Garbo S, Maione R, Tripodi M, et al., 2022. Next RNA therapeutics: the mine of non-coding. Int J Mol Sci, 23(13):7471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137471
Gu XH, Li YC, Chen KX, et al., 2020. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate viral myocarditis through activating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy flux pathway. J Cell Mol Med, 24(13):7515–7530. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15378
Hu Y, Zhang Y, Ni CY, et al., 2020. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells-derived extracellular vesicles exert potent bone protective effects by CLEC11A-mediated regulation of bone metabolism. Theranostics, 10(5):2293–2308. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.39238
Huber SA, 2016. Viral myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy: etiology and pathogenesis. Curr Pharm Des, 22(4):408–426. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666151222160500
Inamdar AA, Inamdar AC, 2016. Heart failure: diagnosis, management and utilization. J Clin Med, 5(7):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5070062
Jiang XJ, Stockwell BR, Conrad M, 2021. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 22(4):266–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, et al., 2005. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature, 438(7068):685–689. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04303
Li DP, Wang Y, Jin XR, et al., 2020. NK cell-derived exosomes carry miR-207 and alleviate depression-like symptoms in mice. J Neuroinflammation, 17:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01787-4
Li J, Xie YW, Li LW, et al., 2021. MicroRNA-30a modulates type I interferon responses to facilitate coxsackievirus B3 replication via targeting tripartite motif protein 25. Front Immunol, 11:603437. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.603437
Li JH, Tu JH, Gao H, et al., 2021. MicroRNA-425-3p inhibits myocardial inflammation and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in mice with viral myocarditis through targeting TGF-β1. Immun Inflamm Dis, 9(1):288–298. https://doi.org/10.1002/iid3.392
Li KL, Yan GH, Huang HJ, et al., 2022. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of the extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on osteoarthritis via M2 macrophages. J Nanobiotechnol, 20:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-01236-1
Li MY, Li Y, Li SQ, et al., 2022. The nano delivery systems and applications of mRNA. Eur J Med Chem, 227:113910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113910
Li XX, Xiong L, Wen Y, et al., 2021. Comprehensive analysis of the tumor microenvironment and ferroptosis-related genes predict prognosis with ovarian cancer. Front Genet, 12:774400. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.774400
Liu C, Yan XJ, Zhang YJ, et al., 2022. Oral administration of turmeric-derived exosome-like nanovesicles with anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving bioactions for murine colitis therapy. J Nanobiotechnol, 20:206. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01421-w
Liu G, Ma JY, Hu G, et al., 2021. Identification and validation of a novel ferroptosis-related gene model for predicting the prognosis of gastric cancer patients. PLoS ONE, 16(7):e0254368. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0254368
Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhou SR, et al., 2022. Circular RNA: an emerging frontier in RNA therapeutic targets, RNA therapeutics, and mRNA vaccines. J Control Release, 348:84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.043
Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G, et al., 2019. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol, 21(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0250-9
Murphy DE, de Jong OG, Brouwer M, et al., 2019. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med, 51(3):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-019-0223-5
Qiao C, Xu W, Zhu W, et al., 2008. Human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the umbilical cord. Cell Biol Int. 32(1):8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellbi.2007.08.002
Rodríguez-Graciani KM, Chapa-Dubocq XR, Ayala-Arroyo EJ, et al., 2022. Effects of ferroptosis on the metabolome in cardiac cells: the role of glutaminolysis. Antioxidants (Basel), 11(2):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020278
Shao MY, Xu Q, Wu ZR, et al., 2020. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate IL-6-induced acute liver injury through miR-455-3p. Stem Cell Res Ther, 11:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-1550-0
Silva AKA, Morille M, Piffoux M, et al., 2021. Development of extracellular vesicle-based medicinal products: a position paper of the group “Extracellular Vesicle translation to clinicaL perspectiVEs–EVOLVE France”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 179:114001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.114001
Sun LF, Zhu M, Feng W, et al., 2019. Exosomal miRNA let-7 from menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells alleviates pulmonary fibrosis through regulating mitochon-drial DNA damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019:4506303. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4506303
Sun YT, Chen P, Zhai BT, et al., 2020. The emerging role of ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother, 127:110108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110108
Thakur D, Taliaferro O, Atkinson M, et al., 2022. Inhibition of nuclear factor κB in the lungs protect bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Mol Biol Rep, 49(5):3481–3490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07185-8
Ueta M, Nishigaki H, Komai S, et al., 2023. Positive regulation of innate immune response by miRNA-let-7a-5p. Front Genet, 13:1025539. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.1025539
Velot É, Madry H, Venkatesan JK, et al., 2021. Is extracellular vesicle-based therapy the next answer for cartilage regeneration? Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 9:645039. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.645039
Wang GY, Yuan JT, Cai X, et al., 2020. HucMSC-exosomes carrying miR-326 inhibit neddylation to relieve inflammatory bowel disease in mice. Clin Transl Med, 10(2):e113. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.113
Wu TT, Liu Y, Cao Y, et al., 2022. Engineering macrophage exosome disguised biodegradable nanoplatform for enhanced sonodynamic therapy of glioblastoma. Adv Mater, 34(15):2110364. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202110364
Xia YZ, Shan GF, Yang H, et al., 2021. Cisatracurium regulates the CXCR4/let-7a-5p axis to inhibit colorectal cancer progression by suppressing TGF-β/7SMAD2/3 signalling. Chem Biol Interact, 339:109424. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBI.2021.109424
Yan C, Zhou QY, Wu J, et al., 2021. Csi-let-7a-5p delivered by extracellular vesicles from a liver fluke activates M1-like macrophages and exacerbates biliary injuries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 118(46):e2102206118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2102206118
Yuan XQ, Li TF, Shi L, et al., 2021. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-26a-5p via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis through METTL14/NLRP3. Mol Med, 27:91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00355-7
Zhu DS, Liu S, Huang K, et al., 2022. Intrapericardial exo-some therapy dampens cardiac injury via activating Foxo3. Circ Res, 131(10):e135–e150. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.122.321384
Zhu JM, Liu B, Wang ZY, et al., 2019. Exosomes from nicotine-stimulated macrophages accelerate atherosclerosis through miR-21-3p/PTEN-mediated VSMC migration and proliferation. Theranostics, 9(23):6901–6919. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.37357
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2022M712252) and the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province, China (No. 2023NSFSC1634).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xin LI made significant contributions to conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, validation, and writing of the original draft. Yanan HU, Yueting WU, Zuocheng YANG, and Yang LIU contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, software, validation, and writing of the original draft. Hanmin LIU contributed significantly to conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, and review. All authors have read and approved the final version, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Xin LI, Yanan HU, Yueting WU, Zuocheng YANG, Yang LIU, and Hanmin LIU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
The entire operation and experiments related to animals were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China (No. 2022-137). All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Additional information
Supplementary information
Materials and methods; Figs. S1–S4
Supplementary information
11585_2024_77_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Exosomal let-7a-5p derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates coxsackievirus B3-induced cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via the SMAD2/ZFP36 signal axis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Hu, Y., Wu, Y. et al. Exosomal let-7a-5p derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates coxsackievirus B3-induced cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via the SMAD2/ZFP36 signal axis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 25, 422–437 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300077
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300077
Key words
- Exosome
- Let-7a-5p
- Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 (SMAD2)
- Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3)
- Ferroptosis