Abstract
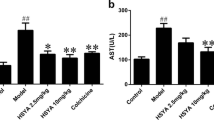
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is the most frequent liver disease worldwide, resulting in severe harm to personal health and posing a serious burden to public health. Based on the reported antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities of scutellarin (SCU), this study investigated its protective role in male BALB/c mice with acute alcoholic liver injury after oral administration (10, 25, and 50 mg/kg). The results indicated that SCU could lessen serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels and improve the histopathological changes in acute alcoholic liver; it reduced alcohol-induced malondialdehyde (MDA) content and increased glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), catalase (CAT), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Furthermore, SCU decreased tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL-Iβ messenger RNA (mRNA) expression levels, weakened inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity, and inhibited nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation. Mechanistically, SCU suppressed cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily E member 1 (CYP2E1) upregulation triggered by alcohol, increased the expression of oxidative stress-related nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathways, and suppressed the inflammation-related degradation of inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-α (IκBα) as well as activation of NF-κB by mediating the protein kinase B (AKT) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. These findings demonstrate that SCU protects against acute alcoholic liver injury via inhibiting oxidative stress by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and suppressing inflammation by regulating the AKT, p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathways.
摘要
肝病(ALD)是世界上最常见的肝脏疾病, 严重危害个人健康, 对公共卫生造成严重负担. 基于灯盏花乙素(SCU)抗氧化和抗炎能力的报道, 本研究探究了SCU(10、 25和50 mg/kg, 口服给药)对急性酒精性肝损伤BALB/c小鼠的保护作用. 结果表明: SCU可降低血清谷丙转氨酶(ALT)和天冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)水平, 改善急性酒精性肝组织病理改变; 降低酒精诱导的丙二醛(MDA)含量, 提高谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)、 过氧化氢酶(CAT)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性. 此外, SCU会降低肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、 白细胞介素6(IL-6)和IL-1β的mRNA表达水平, 削弱诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)活性和抑制NOD样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)炎症小体激活. 从机制方面而言, SCU可抑制酒精诱导的CYP450代谢酶家族中的CYP2E1上调, 增加氧化应激相关的核因子E2相关因子2(Nrf2)和血红素加氧酶-1(HO-1)通路的表达, 通过介导蛋白激酶B(AKT)和p38 MAPK通路抑制炎症相关核因子-κB抑制蛋白α因子(IκBα)的降解以及核因子-κB因子(NF-κB)的激活. 这些结果表明, SCU通过调控Nrf2/HO-1通路抑制氧化应激, 通过调控AKT、p38 MAPK/NF-κB通路抑制炎症反应, 从而保护急性酒精性肝损伤.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An YN, Zhang HF, Wang C, et al., 2019. Activation of ROS/MAPKs/NF-κB/NLRP3 and inhibition of efferocytosis in osteoclast-mediated diabetic osteoporosis. FASEB J, 33(11): 12515–12527. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201802805RR
Bataille AM, Manautou JE, 2012. Nrf2: a potential target for new therapeutics in liver disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 92(3):340–348. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2012.110
Bian HT, Wang GH, Huang JJ, et al., 2020. Scutellarin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioral deficits by inhibiting neuroinflammation and microglia activation in rats. Int Immunopharmacol, 88:106943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106943
Ceni E, Mello T, Galli A, 2014. Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: role of oxidative metabolism. World J Gastroenterol, 20(47):17756–17772. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17756
Chen MF, Gong F, Zhang YY, et al., 2019. Preventive effect of YGDEY from tilapia fish skin gelatin hydrolysates against alcohol-induced damage in HepG2 cells through ROS-mediated signaling pathways. Nutrients, 11(2):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020392
Chen YR, Que RY, Lin LB, et al., 2020. Inhibition of oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome by Saikosaponin-d alleviates acute liver injury in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatitis in mice. Int J Immunopathol Pharmarol, 34: 2058738420950593. https://doi.org/10.1177/2058738420950593
Chen YY, Zhang CL, Zhao XL, et al., 2014. Inhibition of cytochrome P4502E1 by chlormethiazole attenuated acute ethanol-induced fatty liver. Chem Biol Interact, 222:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2014.08.009
Ding RB, Tian K, Cao YW, et al., 2015. Protective effect of Panax notoginseng saponins on acute ethanol-induced liver injury is associated with ameliorating hepatic lipid accumulation and reducing ethanol-mediated oxidative stress. J Agric Food Chem, 63(9):2413–2422. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf502990n
Fan H, Ma XD, Lin P, et al., 2017. Scutellarin prevents nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and hyperlipidemia via PI3K/AKT-dependent activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) in rats. Med Sci Monit, 23:5599–5612. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.907530
Fan H, Tu TT, Zhang X, et al., 2022. Sinomenine attenuates alcohol-induced acute liver injury via inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Food Chem Toxicol, 159:112759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112759
Galicia-Moreno M, Lucano-Landeros S, Monroy-Ramirez HC, et al., 2020. Roles of Nrf2 in liver diseases: molecular, pharmacological, and epigenetic aspects. Antioxidants, 9(10):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100980
Gouillon ZQ, Lucas D, Li J, et al., 2000. Inhibition of ethanol-induced liver disease in the intragastric feeding rat model by chlormethiazole. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med, 224(4):302–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1373.2000.22435.x
Guo FF, Xiao M, Wang SY, et al., 2020. Downregulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in chronic ethanol-induced fatty liver. Toxicol Mech Methods, 30(6): 407–416. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2020.1747126
Guo XL, Cui RB, Zhao JJ, et al., 2016. Corosolic acid protects hepatocytes against ethanol-induced damage by modulating mitogen-activated protein kinases and activating autophagy. Eur J Pharmacol, 791:578–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.09.031
Hayes JD, Dinkova-Kostova AT, 2014. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci, 39(4):199–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.002
He Y, Hara H, Núñez G, 2016. Mechanism and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem Sci, 41(12):1012–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.002
Hoek JB, Pastorino JG, 2004. Cellular signaling mechanisms in alcohol-induced liver damage. Semin Liver Dis, 24(3): 257–272. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-832939
Hu X, Wu XF, Zhao B, et al., 2019. Scutellarin protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced oxidative damage. Cell Biosci, 9:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-019-0276-0
Iranshahy M, Iranshahi M, Abtahi SR, et al., 2018. The role of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in hepatoprotective activity of natural products: a review. Food Chem Toxicol, 120:261–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.07.024
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, et al., 1997. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 236(2):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1997.6943
Ji WL, Liang K, An R, et al., 2019. Baicalin protects against ethanol-induced chronic gastritis in rats by inhibiting Akt/NF-κB pathway. Life Sci, 239:117064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117064
Kim MS, Ong M, Qu XQ, 2016. Optimal management for alcoholic liver disease: conventional medications, natural therapy or combination? World J Gastroenterol, 22(1):8–23. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.8
Kirpich IA, Miller ME, Cave MC, et al., 2016. Alcoholic liver disease: update on the role of dietary fat. Biomolecules, 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6010001
Kong LZ, Chandimali N, Han YH, et al., 2019. Pathogenesis, early diagnosis, and therapeutic management of alcoholic liver disease. Int J Mol Sci, 20(11):2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112712
Kubes P, Mehal WZ, 2012. Sterile inflammation in the liver. Gastroenterology, 143(5):1158–1172. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.008
Leung TM, Nieto N, 2013. CYP2E1 and oxidant stress in alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol, 58(2):395–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.08.018
Li B, Nasser MI, Masood M, et al., 2020. Efficiency of traditional Chinese medicine targeting the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother, 126:110074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110074
Li XJ, Mu YM, Li TT, et al., 2015. Gynura procumbens reverses acute and chronic ethanol-induced liver steatosis through MAPK/SREBP-1c-dependent and -independent pathways. J Agric Food Chem, 63(38):8460–8471. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03504
Liu JY, 2014. Ethanol and liver: recent insights into the mechanisms of ethanol-induced fatty liver. World J Gastroenterol, 20(40):14672–14685. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14672
Liu SY, Tsai IT, Hsu YC, 2021. Alcohol-related liver disease: basic mechanisms and clinical perspectives. Int J Mol Sci, 22(10):5170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105170
Liu X, Wang YN, Wu D, et al., 2019a. Magnolol prevents acute alcoholic liver damage by activating PI3K/Nrf2/PPARγ and inhibiting NLRP3 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol, 10:1459. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01459
Liu X, Hou RL, Yan JJ, et al., 2019b. Purification and characterization of Inonotus hispidus exopolysaccharide and its protective effect on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice. Int J Biol Macromol, 129:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.011
Liu YG, Wang J, Zhang XR, et al., 2019. Scutellarin exerts hypoglycemic and renal protective effects in db/db mice via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019:1354345. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1354345
Lu YB, Wahl LM, 2005. Production of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by activated human monocytes involves a phosphatidylino-sitol-3 kinase/Akt/IKKα/NF-κB pathway. J Leukoc Biol, 78(1):259–265. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0904498
Morgan K, French SW, Morgan TR, 2002. Production of a cytochrome P450 2E1 transgenic mouse and initial evaluation of alcoholic liver damage. Hepatology, 36(1):122–134. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2002.33720
Niu CW, Sheng YC, Yang R, et al., 2015. Scutellarin protects against the liver injury induced by diosbulbin B in mice and its mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol, 164:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.031
Nowak AJ, Relja B, 2020. The impact of acute or chronic alcohol intake on the NF-κB signaling pathway in alcohol-related liver disease. Int J Mol Sci, 21(24):9407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249407
Orman ES, Odena G, Bataller R, 2013. Alcoholic liver disease: pathogenesis, management, and novel targets for therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 28(S1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12030
Otterbein LE, Soares MP, Yamashita K, et al., 2003. Heme oxygenase-1: unleashing the protective properties of heme. Trends Immunol, 24(8):449–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1471-4906(03)00181-9
Qian LH, Li NG, Tang YP, et al., 2011. Synthesis and bio-activity evaluation of scutellarein as a potent agent for the therapy of ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci, 12(11):8208–8216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12118208
Shim YR, Jeong WI, 2020. Recent advances of sterile inflammation and inter-organ cross-talk in alcoholic liver disease. Exp Mol Med, 52(5):772–780. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0438-5
Song XL, Liu ZH, Zhang JJ, et al., 2018. Anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects of exopolysaccharides isolated from Pleurotus geesteranus on alcohol-induced liver injury. Sci Rep, 8:10493. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28785-0
Sporn MB, Liby KT, 2012. NRF2 and cancer: the good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat Rev Cancer, 12(8): 564–571. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3278
Sun J, Fu JQ, Li L, et al., 2018. Nrf2 in alcoholic liver disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 357:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.08.019
Szabo G, Kamath PS, Shah VH, et al., 2019. Alcohol-related liver disease: areas of consensus, unmet needs and opportunities for further study. Hepatology, 69(5):2271–2283. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30369
Torres S, Segalés P, García-Ruiz C, et al., 2022. Mitochondria and the NLRP3 inflammasome in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cells, 11(9):1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091475
Wang J, Cui L, Feng L, et al., 2016. Isoalantolactone inhibits the migration and invasion of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells via suppression of the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncol Rep, 36(3):1269–1276. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.4954
Wang JM, Zhang YY, Zhang YS, et al., 2012. Protective effect of lysimachia christinae against acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Biosci Trends, 6(2):89–97.
Wang LP, Ma Q, 2018. Clinical benefits and pharmacology of scutellarin: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther, 190: 105–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.05.006
Wang P, Gao C, Guo N, et al., 2018. 2’-O-Galloylhyperin isolated from Pyrola incarnata Fisch. attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory response by activation of SIRT1/Nrf2 and inhibition of the NF-κB pathways in vitro and vivo. Front Pharmacol, 9:679. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00679
Wang YY, Fan XM, Fan B, et al., 2020. Scutellarin reduce the homocysteine level and alleviate liver injury in type 2 diabetes model. Front Pharmacol, 11:538407. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.538407
Wang ZG, Yao T, Song ZY, 2010. Involvement and mechanism of DGAT2 upregulation in the pathogenesis of alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Lipid Res, 51(11):3158–3165. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M007948
Wu DF, Wang XD, Zhou R, et al., 2012. Alcohol steatosis and cytotoxicity: the role of cytochrome P4502E1 and autophagy. Free Radic Biol Med, 53(6): 1346–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.005
Xiao T, Cui YL, Ji HY, et al., 2021. Baicalein attenuates acute liver injury by blocking NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 534:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.109
Xu L, Yu YF, Sang R, et al., 2018. Protective effects of tarax-asterol against ethanol-induced liver injury by regulating CYP2E1/Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018:8284107. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8284107
Xu LJ, Chen RC, Zhang X, et al., 2021. Scutellarin protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory response in mice. Ann Palliat Med, 10(3):2481–2493. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-19-516
Yu GL, Wang JX, Zhang W, et al., 2021. NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway involves in Vibrio harveyi-induced inflammatory response in murine peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 53(12):1590–1601. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmab137
Yu WZ, Tao MR, Zhao YL, et al., 2018. 4’-Methoxyresveratrol alleviated AGE-induced inflammation via RAGE-mediated NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Molecules, 23(6):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061447
Zeng J, Cai SN, 2017. Breviscapine suppresses the growth of non-small cell lung cancer by enhancing microRNA-7 expression. J Biosci, 42(1): 121–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-017-9670-0
Zeng T, Zhang CL, Zhao N, et al., 2018. Impairment of Akt activity by CYP2E1 mediated oxidative stress is involved in chronic ethanol-induced fatty liver. Redox Biol, 14: 295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.018
Zhang TM, Wang K, Fan H, et al., 2022. Ameliorative effect of scutellarin on acute alcohol brain injury in mice. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 23(3):258–264. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100763
Zhang XX, Ji RP, Sun HJ, et al., 2018. Scutellarin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through the PPARγ/PGC-1α-Nrf2 pathway. Free Radic Res, 52(2):198–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2017.1422602
Zhang ZH, Ren Z, Chen S, et al., 2018. ROS generation and JNK activation contribute to 4-methoxy-TEMPO-induced cytotoxicity, autophagy, and DNA damage in HepG2 cells. Arch Toxicol, 92(2):717–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-2084-9
Zhao L, Mehmood A, Yuan DD, et al., 2021. Protective mechanism of edible food plants against alcoholic liver disease with special mention to polyphenolic compounds. Nutrients, 13(5):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051612
Zhao N, Guo FF, Xie KQ, et al., 2018. Targeting Nrf-2 is a promising intervention approach for the prevention of ethanol-induced liver disease. Cell Mol Life Sci, 75(17): 3143–3157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2852-6
Zhao YL, Ma X, Wang JB, et al., 2016. A system review of anti-fibrogenesis effects of compounds derived from Chinese herbal medicine. Mini-Rev Med Chem, 16(2):163–175. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557515666150709121908
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science (Natural Science) Research Project of Higher Education of Jiangsu Province (Nos. 21KJB230001 and 21KJB350019), the Open Foundation of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Marine Pharmaceutical Compound Screening (No. HY202101), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Lianyungang (No. LYG20220013), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiao ZHANG, Zhicheng DONG, Hui FAN, and Guili YU performed the experimental research and data analysis. Xiao ZHANG, Nana HE, and Xueqing LI wrote and edited the manuscript. Qiankun YANG and Enzhuang PAN performed the establishment of animal models. Panpan ZHAO, Mian FU, and Jingquan DONG contributed to the study design, data analysis, writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Xiao ZHANG, Zhicheng DONG, Hui FAN, Qiankun YANG, Guili YU, Enzhuang PAN, Nana HE, Xueqing LI, Panpan ZHAO, Mian FU, and Jingquan DONG declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. The study was approved by the Jiangsu Ocean University Animal Ethics Committee (No. 2020220671), China.
Additional information
Supplementary information
Tables S1 and S2; Figs. S1 and S2
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Dong, Z., Fan, H. et al. Scutellarin prevents acute alcohol-induced liver injury via inhibiting oxidative stress by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting inflammation by regulating the AKT, p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathways. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 24, 617–631 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200612
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200612