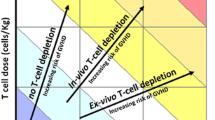
Abstract
Tumor recurrence is one of the major life-threatening complications after liver transplantation for liver cancer. In addition to the common mechanisms underlying tumor recurrence, another unavoidable problem is that the immunosuppressive therapeutic regimen after transplantation could promote tumor recurrence and metastasis. Transplant oncology is an emerging field that addresses oncological challenges in transplantation. In this context, a comprehensive therapeutic management approach is required to balance the anti-tumor treatment and immunosuppressive status of recipients. Double-negative T cells (DNTs) are a cluster of heterogeneous cells mainly consisting of two subsets stratified by T cell receptor (TCR) type. Among them, TCRαβ+ DNTs are considered to induce immune suppression in immune-mediated diseases, while TCRγδ+ DNTs are widely recognized as tumor killers. As a composite cell therapy, healthy donor-derived DNTs can be propagated to therapeutic numbers in vitro and applied for the treatment of several malignancies without impairing normal tissues or being rejected by the host. In this work, we summarized the biological characteristics and functions of DNTs in oncology, immunology, and transplantation. Based on the multiple roles of DNTs, we propose that a new balance could be achieved in liver transplant oncology using them as an off-the-shelf adoptive cell therapy (ACT).
摘要
肿瘤复发是肝癌肝移植术后危及生命的主要并发症之一. 除了常见的肿瘤复发机制外, 另一个不可避免的问题是移植后的免疫抑制治疗方案可能促进肿瘤复发和转移. 移植肿瘤学是一个新兴领域以解决肝移植相关的肿瘤学问题. 在此背景下, 需要综合治疗管理方法来平衡受者的抗肿瘤治疗和免疫抑制状态. 双阴性T细胞 (DNTs) 是一群异质性细胞, 主要由T细胞受体 (TCR) 不同类型的两个亚群组成. 其中, TCRαβ+ DNTs 被认为在免疫性疾病中诱导免疫抑制, 而 TCRγδ+ DNTs 被广泛认为是肿瘤杀伤细胞. 作为一种复合细胞疗法, 健康供体来源的 DNTs 可在体外增殖至治疗量级, 并应用于多种恶性肿瘤的治疗, 同时既不损伤正常组织, 也不被宿主排斥. 本文就 DNTs 的生物学特性及其在肿瘤学、 免疫学和移植领域等方面的研究进展进行综述. 基于 DNTs 的多重作用, 我们建议将其作为一种现成的过继性细胞治疗 (ACT), 从而为移植肿瘤学提供一种新的平衡.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achita P, Dervovic D, Ly D, et al., 2018. Infusion of ex-vivo expanded human TCR-αβ+ double-negative regulatory T cells delays onset of xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Exp Immunol, 193(3):386–399. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.13145
Almeida CF, Smith DGM, Cheng TY, et al., 2021. Benzofuran sulfonates and small self-lipid antigens activate type II NKT cells via CD1d. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 118(34): e2104420118. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.2104420118
Bafor EE, Valencia JC, Young HA, 2022. Double negative T regulatory cells: an emerging paradigm shift in reproductive immune tolerance? Front Immunol, 13:886645. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.886645
Broutier L, Mastrogiovanni G, Verstegen MMA, et al., 2017. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat Med, 23(12): 1424–1435. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4438
Capsomidis A, Benthall G, van Acker HH, et al., 2018. Chimeric antigen receptor-engineered human gamma delta T cells: enhanced cytotoxicity with retention of cross presentation. Mol Ther, 26(2):354–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.12.001
Chakraverty R, Teshima T, 2021. Graft-versus-host disease: a disorder of tissue regeneration and repair. Blood, 138(18): 1657–1665. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2021011867
Chen B, Lee JB, Kang H, et al., 2018. Targeting chemotherapy-resistant leukemia by combining DNT cellular therapy with conventional chemotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 37:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0756-9
Chen J, Hu PB, Wu GH, et al., 2019. Antipancreatic cancer effect of DNT cells and the underlying mechanism. Pancreatology, 19(1):105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2018.12.006
Chen WH, Zhou DJ, Torrealba JR, et al., 2005. Donor lymphocyte infusion induces long-term donor-specific cardiac xenograft survival through activation of recipient doublenegative regulatory T cells. J Immunol, 175(5):3409–3416. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.175.53409
Chowdhary VR, Krogman A, Tilahun AY, et al., 2017. Concomitant disruption of CD4 and CD8 genes facilitates the development of double negative αβTCR+ peripheral T cells that respond robustly to staphylococcal superantigen. J Immunol, 198(1):4413–4424. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1601991
Crosby CM, Kronenberg M, 2018. Tissue-specific functions of invariant natural killer T cells. Nat Rev Immunol, 18(9): 559–574. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-018-0034-2
de Gassart A, Le KS, Brune P, et al., 2021. Development of ICT01, a first-in-class, anti-BTN3A antibody for activating Vγ9Vδ2 T cell-mediated antitumor immune response. Sci Transl Med, 13(616):eabj0835. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj0835
Depil S, Duchateau P, Grupp SA, et al., 2020. ‘Off-the-shelf allogeneic CAR T cells: development and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 19(3):185–199. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0051-2
Fang LN, Ly D, Wang SS, et al., 2019. Targeting late-stage non-small cell lung cancer with a combination of DNT cellular therapy and PD-1 checkpoint blockade. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 38:123. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1126-y
Fischer K, Voelkl S, Heymann J, et al., 2005. Isolation and characterization of human antigen-specific TCRαβ+ CD4−CD8− double-negative regulatory T cells. Blood, 105(7): 2828–2835. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-07-2583
Ford MS, Young KJ, Zhang ZX, et al., 2002. The immune regulatory function of lymphoproliferative double negative T cells in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med, 196(2):261–267. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20020029
Galluzzi L, Chan TA, Kroemer G, et al., 2018. The hallmarks of successful anticancer immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med, 10(459):eaat7807. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aat7807
Gálvez NMS, Bohmwald K, Pacheco GA, et al., 2021. Type I natural killer T cells as key regulators of the immune response to infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev, 34(2): e00232–20. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00232-20
Hibi T, Sapisochin G, 2019. What is transplant oncology? Surgery, 165(2):281–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2018.10.024
Hibi T, Itano O, Shinoda M, et al., 2017. Liver transplantation for hepatobiliary malignancies: a new era of “Transplant Oncology” has begun. Surg Today, 47(4):403–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-016-1337-1
Hoeres T, Smetak M, Pretscher D, et al., 2018. Improving the efficiency of Vγ9Vδ2 T-Cell immunotherapy in cancer. Front Immunol, 9:800. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00800
Hsu J, Krishnan A, Lee SA, et al., 2021. CD3+CD4−CD8− double-negative αβ T cells attenuate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 161(1): E81–E90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2019.09.188
Hu SH, Zhang LH, Gao J, et al., 2021. NKG2D enhances double-negative T cell regulation of B cells. Front Immunol, 12:650788. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.650788
Juvet SC, Zhang L, 2012. Double negative regulatory T cells in transplantation and autoimmunity: recent progress and future directions. J Mol Cell Biol, 4(1):48–58. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjr043
Kabelitz D, Serrano R, Kouakanou L, et al., 2020. Cancer immunotherapy with γδ T cells: many paths ahead of us. Cell Mol Immunol, 17(9):925–939. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0504-x
Khan AA, Liu ZK, Xu X, 2021. Recent advances in immuno-therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 20(6):511–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbpd.2021.06.010
Kjer-Nielsen L, Corbett AJ, Chen ZJ, et al., 2018. An overview on the identification of MAIT cell antigens. Immunol Cell Biol, 96(6):573–587. https://doi.org/10.1111/imcb.12057
Lee JB, Minden MD, Chen WC, et al., 2018. Allogeneic human double negative T cells as a novel immunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia and its underlying mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res, 24(2):370–382. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2228
Lee JB, Kang H, Fang LN, et al., 2019. Developing allogeneic double-negative T cells as a novel off-the-shelf adoptive cellular therapy for cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 25(7):2241–2253. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2291
Legoux F, Salou M, Lantz O, 2017. Unconventional or preset αβ T cells: evolutionarily conserved tissue-resident T cells recognizing nonpeptidic ligands. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 33:511–535. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100616-060725
Ling SB, Zhan QF, Jiang GJ, et al., 2022. E2F7 promotes mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Am J Transplant, 22(10):2323–2336. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.17124
Liu YX, Zhang C, 2020. The role of human γδ T cells in antitumor immunity and their potential for cancer immunotherapy. Cells, 9(5):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051206
Lu JQ, Liu JY, Li A, 2022. Roles of neutrophil reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in organ function impairment in sepsis. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 23(6):437–450. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2101075
Lu Y, Hu PB, Zhou HB, et al., 2019. Double-negative T cells inhibit proliferation and invasion of human pancreatic cancer cells in co-culture. Anticancer Res, 39(11):5911–5918. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.13795
Marabelle A, Tselikas L, de Baere T, et al., 2017. Intratumoral immunotherapy: using the tumor as the remedy. Ann Oncol, 28:xii33–xii43. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx683
Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R, et al., 1996. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med, 334(11): 693–700. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199603143341104
Merims S, Li X, Joe B, et al., 2011. Anti-leukemia effect of ex vivo expanded DNT cells from AML patients: a potential novel autologous T-cell adoptive immunotherapy. Leukemia, 25(9):1415–1422. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.99
Mizukoshi E, Kaneko S, 2019. Immune cell therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol, 12:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0742-5
Newman-Rivera AM, Kurzhagen JT, Rabb H, 2022. TCRαβ+ CD4−/CD8− “double negative” T cells in health and disease-implications for the kidney. Kidney Int, 102(1):25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.02.035
Nordness MF, Hamel S, Godfrey CM, et al., 2020. Fatal hepatic necrosis after nivolumab as a bridge to liver transplant for HCC: are checkpoint inhibitors safe for the pre-transplant patient? Am J Transplant, 20(3):879–883. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15617
Pauza CD, Liou ML, Lahusen T, et al., 2018. Gamma delta T cell therapy for cancer: it is good to be local. Front Immunol, 9:1305. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01305
Pellicci DG, Uldrich AP, 2018. Unappreciated diversity within the pool of CD1d-restricted T cells. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 84:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.031
Ponzetta A, Carriero R, Carnevale S, et al., 2019. Neutrophils driving unconventional T cells mediate resistance against murine sarcomas and selected human tumors. Cell, 178(2): 346–360.e24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.04
Raoul JL, Forner A, Bolondi L, et al., 2019. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: how and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat Rev, 72:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.11.002
Ronca V, Wootton G, Milani C, et al., 2020. The immunological basis of liver allograft rejection. Front Immunol, 11: 2155. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.02155
Soares F, Chen B, Lee JB, et al., 2021. CRISPR screen identifies genes that sensitize AML cells to double-negative T-cell therapy. Blood, 137(16):2171–2181. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019004108
Strippoli S, Fanizzi A, Negri A, et al., 2021. Examining the relationship between circulating CD4−CD8− double-negative T cells and outcomes of immuno-checkpoint inhibitor therapy—looking for biomarkers and therapeutic targets in metastatic melanoma. Cells, 10(2):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020406
Sun H, Cao S, Mashl RJ, et al., 2021. Comprehensive characterization of 536 patient-derived xenograft models prioritizes candidatesfor targeted treatment. Nat Commun, 12: 5086. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25177-3
Takada Y, Ito T, Ueda M, et al., 2007. Living donor liver transplantation for patients with HCC exceeding the Milan criteria: a proposal of expanded criteria. Dig Dis, 25(4): 299–302. https://doi.org/10.1159/000106908
Thommen DS, Schumacher TN, 2018. T cell dysfunction in cancer. Cancer Cell, 33(4):547–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.03.012
Tuveson D, Clevers H, 2019. Cancer modeling meets human organoid technology. Science, 364(6444):952–955. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw6985
Vasic D, Lee JB, Leung Y, et al., 2022. Allogeneic doublenegative CAR-T cells inhibit tumor growth without offtumor toxicities. Sci Immunol, 7(70):eabl3642. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abl3642
Velikkakam T, Gollob KJ, Dutra WO, 2022. Double-negative T cells: setting the stage for disease control or progression. Immunology, 165(4):371–385. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13441
Verna EC, Patel YA, Aggarwal A, et al., 2020. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: management after the transplant. Am J Transplant, 20(2):333–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15697
Voelkl S, Moore TV, Rehli M, et al., 2009. Characterization of MHC class-I restricted TCRαβ+ CD4− CD8− double negative T cells recognizing the gp100 antigen from a melanoma patient after gp100 vaccination. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 58(5):709–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0593-3
Xu H, Zhu XX, Chen J, 2016. DNT cell inhibits the growth of pancreatic carcinoma via abnormal expressions of NKG2D and MICA in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 469(2):145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.11.085
Xu X, Lu D, Ling Q, et al., 2016. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria. Gut, 65(6):1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308513
Yang XY, Lu D, Wang R, et al., 2021. Single-cell profiling reveals distinct immune phenotypes that contribute to ischaemia-reperfusion injury after steatotic liver transplantation. Cell Prolif, 54(10):e13116. https://doi.org/10.1111/CPR.13116
Yao FY, Ferrell L, Bass NM, et al., 2001. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: expansion of the tumor size limits does not adversely impact survival. Hepatology, 33(6):1394–1403. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2001.24563
Yao JL, Ly D, Dervovic D, et al., 2019. Human double negative T cells target lung cancer via ligand-dependent mechanisms that can be enhanced by IL-15. J Immunother Cancer, 7(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0507-2
Ye QW, Ling SB, Zheng SS, et al., 2019. Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Mol Cancer, 18:114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1043-x
Young KJ, Yang LM, Phillips MJ, et al., 2002. Donor-lymphocyte infusion induces transplantation tolerance by activating systemic and graft-infiltrating double-negative regulatory T cells. Blood, 100(9):3408–3414. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-01-0235
Young KJ, Kay LS, Phillips MJ, et al., 2003. Antitumor activity mediated by double-negative T cells. Cancer Res, 63(22): 8014–8021.
Zhang YJ, Kong DR, Wang H, 2020. Mucosal-associated invariant T cell in liver diseases. Int J Biol Sci, 16(3): 460–470. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.39016
Zhuo JY, Su RY, Tan WY, et al., 2020. The ongoing trends of patient-derived xenograft models in oncology. Cancer Commun (Lond), 40(11):559–563. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12096
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Research & Development Plan of Zhejiang Province (Nos. 2019C03050 and 2021C03118), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFA1100500), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 92159202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhihang HU: writing–original draft. Modan YANG: data curation and visualization. Xiao XU and Di LU: conceptualization and writing–review & editing. Hao CHEN, Chiyu HE, Zuyuan LIN, Xinyu YANG, Huigang LI, and Wei SHEN: supervision and writing - review & editing. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Zhihang HU, Modan YANG, Hao CHEN, Chiyu HE, Zuyuan LIN, Xinyu YANG, Huigang LI, Wei SHEN, Di LU, and Xiao XU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Z., Yang, M., Chen, H. et al. Double-negative T cells: a promising avenue of adoptive cell therapy in transplant oncology. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 24, 387–396 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200528
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200528