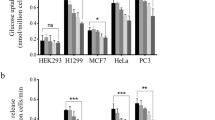
Abstract
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) controls cellular anabolism, and mTOR signaling is hyperactive in most cancer cells. As a result, inhibition of mTOR signaling benefits cancer patients. Rapamycin is a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug, a specific mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) inhibitor, for the treatment of several different types of cancer. However, rapamycin is reported to inhibit cancer growth rather than induce apoptosis. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHc) is the gatekeeper for mitochondrial pyruvate oxidation. PDHc inactivation has been observed in a number of cancer cells, and this alteration protects cancer cells from senescence and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) exhaustion. In this paper, we describe our finding that rapamycin treatment promotes pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit alpha 1 (PDHA1) phosphorylation and leads to PDHc inactivation dependent on mTOR signaling inhibition in cells. This inactivation reduces the sensitivity of cancer cells’ response to rapamycin. As a result, rebooting PDHc activity with dichloroacetic acid (DCA), a pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK) inhibitor, promotes cancer cells’ susceptibility to rapamycin treatment in vitro and in vivo.
摘要
哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白 (mTOR) 控制细胞的合成代谢, 并且在大多数的肿瘤细胞中 mTOR 信号通路高度活化, 因此抑制 mTOR 信号通路对癌症患者有益. 雷帕霉素是一种美国食品药品监督管理局 (FDA) 批准的临床一线药物, 是 mTORC1 的特异性抑制剂, 用于治疗多种不同类型的癌症. 然而, 研究发现雷帕霉素仅抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖并不引起细胞的凋亡. 丙酮酸脱氢酶复合体 (PDHc) 在线粒体丙酮酸氧化过程起着决定作用. 许多肿瘤细胞中的 PDHc 处于失活状态, 这一变化可以使肿瘤细胞免于衰老和 NAD+耗竭. 本研究中, 雷帕霉素处理细胞导致依赖 mTOR 信号通路抑制的丙酸脱氢酶 α1 (PDHA1) 磷酸化水平升高, 并导致 PDHc 酶活降低. PDHc 失活直接引起肿瘤细胞对雷帕霉素敏感度下降. 因此, 在体内和体外的实验中通过使用丙酮酸脱氢酶激酶 (PDK) 的抑制剂二氯乙酸 (DCA) 可以重新激活 PDHc 的活力, 进而增加肿瘤细胞对雷帕霉素的敏感性.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo NC, Sampaio Goncalves de Lucena SB, da Silveira Rioja S, 2014. Effect of rapamycin on spleen size in longstanding renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc, 46(5):1319–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2014.03.011
Bai ZS, Peng YL, Ye XY, et al., 2022. Autophagy and cancer treatment: four functional forms of autophagy and their therapeutic applications. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 23(2):89–101. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100804
Benjamin D, Colombi M, Moroni C, et al., 2011. Rapamycin passes the torch: a new generation of mTOR inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 10(11):868–880. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3531
Beretta L, Gingras AC, Svitkin YV, et al., 1996. Rapamycin blocks the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and inhibits cap-dependent initiation of translation. EMBO J, 15(3):658–664.
Bernardi R, Guernah I, Jin D, et al., 2006. PML inhibits HIF-1α translation and neoangiogenesis through repression of mTOR. Nature, 442(7104):779–785. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05029
Cao WG, Yacoub S, Shiverick KT, et al., 2008. Dichloroacetate (DCA) sensitizes both wild-type and over expressing Bcl-2 prostate cancer cells in vitro to radiation. Prostate, 68(11):1223–1231. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20788
Fan QW, Aksoy O, Wong RA, et al., 2017. A kinase inhibitor targeted to mTORC1 drives regression in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell, 31(3):424–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.01.014
Ghobrial IM, Siegel DS, Vij R, et al., 2016. TAK-228 (formerly MLN0128), an investigational oral dual TORC1/2 inhibitor: a phase I dose escalation study in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, or Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Am J Hematol, 91(4):400–405. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24300
Guba M, von Breitenbuch P, Steinbauer M, et al., 2002. Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor growth by antiangiogenesis: involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor. Nat Med, 8(2):128–135. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0202-128
Holness MJ, Sugden MC, 2003. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity by reversible phosphorylation. Biochem Soc Trans, 31(6): 1143–1151. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0311143
Hsieh AC, Liu Y, Edlind MP, et al., 2012. The translational landscape of mTOR signalling steers cancer initiation and metastasis. Nature, 485(7396):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10912
Jacinto E, Loewith R, Schmidt A, et al., 2004. Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol, 6(11):1122–1128. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1183
Jacobs KE, Visser BC, Gayer G, 2012. Changes in spleen volume after resection of hepatic colorectal metastases. Clin Radiol, 67(10):982–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2012.03.013
Kaplon J, Zheng L, Meissl K, et al., 2013. A key role for mitochondrial gatekeeper pyruvate dehydrogenase in oncogene-induced senescence. Nature, 498(7452):109–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12154
Kim J, Guan KL, 2019. mTOR as a central hub of nutrient signalling and cell growth. Nat Cell Biol, 21(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0205-1
Lamming DW, Ye L, Katajisto P, et al., 2012. Rapamycin-induced insulin resistance is mediated by mTORC2 loss and uncoupled from longevity. Science, 335(6076):1638–1643. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1215135
Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A, 2017. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 17(9):528–542. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.53
Lorusso PM, 2016. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in solid tumors. J Clin Oncol, 34(31):3803–3815. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.59.0018
Lucido CT, Miskimins WK, Vermeer PD, 2018. Propranolol promotes glucose dependence and synergizes with dichloroacetate for anti-cancer activity in HNSCC. Cancers (Basel), 10(12):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10120476
Luengo A, Li ZQ, Gui DY, et al., 2021. Increased demand for NAD+ relative to ATP drives aerobic glycolysis. Mol Cell, 81(4):691–707.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.12.012
Menon S, Manning BD, 2008. Common corruption of the mTOR signaling network in human tumors. Oncogene, 27:S43–S51. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.352
Patel MS, Nemeria NS, Furey W, et al., 2014. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes: structure-based function and regulation. J Biol Chem, 289(24): 16615–16623. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R114.563148
Phung TL, Ziv K, Dabydeen D, et al., 2006. Pathological angiogenesis is induced by sustained Akt signaling and inhibited by rapamycin. Cancer Cell, 10(2):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.07.003
Robitaille AM, Christen S, Shimobayashi M, et al., 2013. Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveal mTORC1 activates de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Science, 339(6125): 1320–1323. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1228771
Rodrik-Outmezguine VS, Chandarlapaty S, Pagano NC, et al., 2011. mTOR kinase inhibition causes feedback-dependent biphasic regulation of AKT signaling. Cancer Discov, 1(3):248–259. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0085
Rodrik-Outmezguine VS, Okaniwa M, Yao Z, et al., 2016. Overcoming mTOR resistance mutations with a new-generation mTOR inhibitor. Nature, 534(7606):272–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17963
Sabatini DM, Erdjument-Bromage H, Lui M, et al., 1994. RAFT1: a mammalian protein that binds to FKBP12 in a rapamycin-dependent fashion and is homologous to yeast TORs. Cell, 78(1):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(94)90570-3
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, et al., 2006. Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell, 22(2):159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.029
Škorja Milić N, Dolinar K, Miš K, et al., 2021. Suppression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase by dichloroacetate in cancer and skeletal muscle cells is isoform specific and partially independent of HIF-1α. Int J Mol Sci, 22(16):8610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168610
Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Kinnaird A, et al., 2013. Mitochondrial activation by inhibition of PDKII suppresses HIF1α signaling and angiogenesis in cancer. Oncogene, 32(13): 1638–1650. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.198
Tataranni T, Piccoli C, 2019. Dichloroacetate (DCA) and cancer: an overview towards clinical applications. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019:8201079. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8201079
Tso SC, Qi XB, Gui WJ, et al., 2014. Structure-guided development of specific pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase inhibitors targeting the ATP-binding pocket. J Biol Chem, 289(7):4432–4443. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.533885
Valvezan AJ, Turner M, Belaid A, et al., 2017. mTORC1 couples nucleotide synthesis to nucleotide demand resulting in a targetable metabolic vulnerability. Cancer Cell, 32(5): 624–638.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.09.013
Verma A, Lam YM, Leung YC, et al., 2019. Combined use of arginase and dichloroacetate exhibits anti-proliferative effects in triple negative breast cancer cells. J Pharm Pharmacol, 71(3):306–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.13033
Wu JG, Zhao YL, Park YK, et al., 2018. Loss of PDK4 switches the hepatic NF-κB/TNF pathway from pro-survival to pro-apoptosis. Hepatology, 68(3): 1111–1124. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29902
Yang HJ, Jiang XL, Li BR, et al., 2017. Mechanisms of mTORC1 activation by RHEB and inhibition by PRAS40. Nature, 552(7685):368–373. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25023
Yang WC, Pang DJ, Chen MN, et al., 2021. Rheb mediates neuronal-activity-induced mitochondrial energetics through mTORC1-independent PDH activation. Dev Cell, 56(6): 811–825.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2021.02.022
Zhang S, Qian GQ, Zhang QQ, et al., 2019. mTORC2 suppresses GSK3-dependent snail degradation to positively regulate cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res, 79(14):3725–3736. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0180
Zhuang HQ, Bai J, Chang JY, et al., 2016. MTOR inhibition reversed drug resistance after combination radiation with erlotinib in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget, 7(51):84688–84694. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12423
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFA0806503), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81972625), the Dalian Science and Technology Innovation Funding (No. 2019J12SN52), and the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC2002035), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huan CHEN and Hai-long PIAO conceived the project, designed and performed most of the experiments and the data analysis, and wrote the manuscript with input from all other authors. Hai-long PIAO supervised the project. Kunimg LIANG performed the most of experiments. Huan CHEN, Kunimg LIANG, and Cong HOU provided significant intellectual input. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Huan CHEN, Kunming LIANG, Cong HOU, and Hailong PIAO declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All work performed with animals was approved by the Medical Animal Care and Use Committee of China Medical University, Shenyang, China (No. KT2020061).
Additional information
Materials and methods
Detailed methods are provided in the electronic supplementary materials of this paper.
Supplementary information
Materials and methods
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Liang, K., Hou, C. et al. Dichloroacetic acid and rapamycin synergistically inhibit tumor progression. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 24, 397–405 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200356
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200356
Key words
- Dichloroacetic acid (DCA)
- Rapamycin
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit alpha 1 (PDHA1)
- Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)