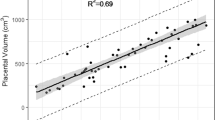
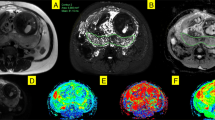
Abstract
Objective: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common endocrine-metabolic dysfunction in reproductiveaged women, may be involved in compromised pregnancy and offspring outcomes. This study aimed to investigate whether maternal PCOS affects fetal growth, fetal development, and placental features. Methods: This retrospective case-control study included 60 pregnant women with PCOS (PCOS group) and 120 healthy pregnant women without PCOS (control group). Fetal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed followed by an ultrasound examination and indications for imaging, including known or suspected fetal pathology, history of fetal abnormality in previous pregnancy or in a family member, and concern for placenta accreta. Fetal MRI images were analyzed for head circumference (HC), abdomen circumference (AC), lung-to-liver signal intensity ratio (LLSIR, a prenatal marker of fetal lung maturity), lengths of liver and kidney diameters in fetuses, and placental relative signal intensity on T2-weighted single-shot fast spin echo (SSFSE) imaging (rSISSFSE), and placental relative apparent diffusion coefficient value (rADC). Data on height and weight of offspring were collected through telephone follow-up. Results: Compared to the control group, the PCOS group showed the following characteristics: (1) smaller biparietal diameter and femur length in fetuses (P=0.026 and P=0.005, respectively), (2) smaller HC in fetuses (evident after 32 weeks; P=0.044), (3) lower LLSIR and smaller dorsoventral length of liver in fetuses (evident before 32 weeks; P=0.005 and P=0.019, respectively), and (4) smaller placental thickness (evident before 32 weeks; P=0.017). No significant differences in placental rSISSFSE or rADC were observed between the groups (all P>0.05). No significant differences in height and weight of offspring during childhood existed between the groups (all P>0.05). Conclusions: There exist alterations of fetal growth, fetal development, and placental features from women with PCOS.
概要
目的
探讨母亲多囊卵巢综合征(PCOS)对子代胎儿 期生长发育和胎盘特征的影响。
创新点
首次关注到PCOS 女性孕期的胎儿和胎盘磁共振 成像(MRI)特征,通过影像学和临床疾病的结 合,对胎儿和胎盘MRI 图像进行全面分析和测 量,评估胎儿生长发育和胎盘特征,并追踪产科 和子代随访结局,以期为PCOS 对子代的潜在影 响提供科学依据。
方法
本研究对浙江大学医学院附属妇产科医院2013~ 2018 年行胎儿MRI 检查的妊娠女性病例行回顾 性分析,根据鹿特丹诊断标准纳入PCOS 妊娠女 性60 例,随机选取与其胎儿MRI 检查孕周相匹 配的非PCOS 妊娠女性120 例作为对照,收集胎 儿和胎盘MRI 图像信息,统计学分析比较PCOS 妊娠女性与非PCOS 妊娠女性影像学测量指标, 包括胎儿的双顶径、头围、腹围、肝脏和肾脏各 径线,胎儿肺和肝的信号强度,胎盘异常情况、 胎盘厚度、胎盘信号强度和表观扩散系数值 (ADC),并比较分析人口学数据、产科和新生 儿结局,随访子代儿童期的生长情况。
结论
母亲PCOS 会造成子代胎儿期生长发育和胎盘特 征的改变。因本研究为回顾性研究、样本量偏小 及一些潜在的偏差,结论有待进一步证实。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlsson FSE, Diderholm B, Ewald U, et al., 2007. Lipolysis and insulin sensitivity at birth in infants who are large for gestational age. Pediatrics, 120(5):958–965. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2007-0165
Bonel HM, Stolz B, Diedrichsen L, et al., 2010. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the placenta in fetuses with placental insufficiency. Radiology, 257(3):810–819. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10092283
Bozdag G, Mumusoglu S, Zengin D, et al., 2016. The prevalence and phenotypic features of polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod, 31(12):2841–2855. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dew218
Cannie M, Neirynck V, de Keyzer F, et al., 2007. Prenatal magnetic resonance imaging demonstrates linear growth of the human fetal kidneys during gestation. J Urol, 178(4S):1570–1574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.178
Cesta CE, Öberg AS, Ibrahimson A, et al., 2020. Maternal polycystic ovary syndrome and risk of neuropsychiatric disorders in offspring: prenatal androgen exposure or genetic confounding? Psychol Med, 50(4):616–624. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291719000424
Committee on Obstetric Practice, 2012. Committee opinion No. 529: placenta accreta. Obstet Gynecol, 120(1):207–211. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e318262e340
Daan NMP, Koster MPH, Steegers-Theunissen RP, et al., 2017. Endocrine and cardiometabolic cord blood characteristics of offspring born to mothers with and without polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril, 107(1):261–268.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.042
Doherty DA, Newnham JP, Bower C, et al., 2015. Implications of polycystic ovary syndrome for pregnancy and for the health of offspring. Obstet Gynecol, 125(6):1397–1406. https://doi.org/10.1097/aog.0000000000000852
Dumesic DA, Goodarzi MO, Chazenbalk GD, et al., 2014. Intrauterine environment and polycystic ovary syndrome. Semin Reprod Med, 32(3):159–165. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1371087
Hales CN, Barker DJ, 2001. The thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Br Med Bull, 60:5–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/60.1.5
Hamabe Y, Hirose A, Yamada S, et al., 2013. Morphology and morphometry of fetal liver at 16–26 weeks of gestation by magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with embryonic liver at Carnegie stage 23. Hepatol Res, 43(6):639–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12000
Han AR, Kim HO, Cha SW, et al., 2011. Adverse pregnancy outcomes with assisted reproductive technology in nonobese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a casecontrol study. Clinical Exp Reprod Med, 38(2):103–108. https://doi.org/10.5653/cerm.2011.38.2.103
Himoto Y, Kido A, Mogami H, et al., 2016. Placental function assessed visually using half-Fourier acquisition singleshot turbo spin-echo (HASTE) magnetic resonance imaging. Placenta, 39:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2016.01.007
Hjorth-Hansen A, Salvesen Ø, Hanem LGE, et al., 2018. Fetal growth and birth anthropometrics in metformin-exposed offspring born to mothers with PCOS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 103(2):740–747. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-01191
Kelley AS, Smith YR, Padmanabhan V, 2019. A narrative review of placental contribution to adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 104(11):5299–5315. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2019-00383
Kim MA, Han GH, Kim YH, 2019. Prediction of small-forgestational age by fetal growth rate according to gestational age. PLoS ONE, 14(4):e0215737. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0215737
Kiserud T, Piaggio G, Carroli G, et al., 2017. The World Health Organization fetal growth charts: a multinational longitudinal study of ultrasound biometric measurements and estimated fetal weight. PLoS Med, 14(1):e1002220. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002220
Kjerulff LE, Sanchez-Ramos L, Duffy D, 2011. Pregnancy outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a metaanalysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 204(6):558.e1–558.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2011.03.021
Kosova G, Urbanek M, 2013. Genetics of the polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 373(1–2):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2012.10.009
Koster MPH, de Wilde MA, Veltman-Verhulst SM, et al., 2015. Placental characteristics in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod, 30(12):2829–2837. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dev265
Li R, Zhang QF, Yang DZ, et al., 2013. Prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome in women in China: a large community-based study. Hum Reprod, 28(9):2562–2569. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/det262
Longtine MS, Nelson DM, 2011. Placental dysfunction and fetal programming: the importance of placental size, shape, histopathology, and molecular composition. Semin Reprod Med, 29(3):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1275515
Mailath-Pokorny M, Polterauer S, Worda K, et al., 2015. Isolated short fetal femur length in the second trimester and the association with adverse perinatal outcome: experiences from a tertiary referral center. PLoS ONE, 10(6): e0128820. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128820
Maliqueo M, Lara HE, Sanchez F, et al., 2013. Placental steroidogenesis in pregnant women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 166(2): 151–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.10.015
Maliqueo M, Poromaa IS, Vanky E, et al., 2015. Placental STAT3 signaling is activated in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod, 30(3):692–700. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deu351
McDonnell R, Hart RJ, 2017. Pregnancy-related outcomes for women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Womens Health (Lond), 13(3):89–97. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745505717731971
Mehrabian F, Kelishadi R, 2012. Comparison of the metabolic parameters and androgen level of umbilical cord blood in newborns of mothers with polycystic ovary syndrome and controls. J Res Med Sci, 17(3):207–211.
Palomba S, Russo T, Falbo A, et al., 2013. Macroscopic and microscopic findings of the placenta in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod, 28(10):2838–2847. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/det250
Palomba S, Falbo A, Chiossi G, et al., 2014a. Early trophoblast invasion and placentation in women with different PCOS phenotypes. Reprod Biomed Online, 29(3):370–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.04.010
Palomba S, Falbo A, Chiossi G, et al., 2014b. Low-grade chronic inflammation in pregnant women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a prospective controlled clinical study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 99(8):2942–2951. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-1214
Palomba S, de Wilde MA, Falbo A, et al., 2015. Pregnancy complications in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod Update, 21(5):575–592. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmv029
Paltiel O, Tikellis G, Linet M, et al., 2015. Birthweight and childhood cancer: preliminary findings from the International Childhood Cancer Cohort Consortium (I4C). Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol, 29(4):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppe.12193
Pan XF, Tang L, Lee AH, et al., 2019. Association between fetal macrosomia and risk of obesity in children under 3 years in Western China: a cohort study. World J Pediatr, 15(2):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-018-0218-7
Pan XM, Lin Z, Li N, et al., 2018. Effects of body mass index on the outcomes of in vitro fertilization in Chinese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: a retrospective cohort study. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 19(6):490–496. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800113
Prayer D, Malinger G, Brugger PC, et al., 2017. ISUOG Practice Guidelines: performance of fetal magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 49(5):671–680. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.17412
Pugash D, Brugger PC, Bettelheim D, et al., 2008. Prenatal ultrasound and fetal MRI: the comparative value of each modality in prenatal diagnosis. Eur J Radiol, 68(2):214–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.06.031
Risnes KR, Vatten LJ, Baker JL, et al., 2011. Birthweight and mortality in adulthood: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Epidemiol, 40(3):647–661. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyq267
Roberts AB, Mitchell J, Murphy C, et al., 1994. Fetal liver length in diabetic pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 170(5):1308–1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(94)70147-4
Sir-Petermann T, Hitchsfeld C, Maliqueo M, et al., 2005. Birth weight in offspring of mothers with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Hum Reprod, 20(8):2122–2126. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dei009
Skiba MA, Islam RM, Bell RJ, et al., 2018. Understanding variation in prevalence estimates of polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update, 24(6):694–709. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmy022
The Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Consensus Workshop Group, 2004. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome. FertilSteril, 81(1):19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.10.004
Thornburg KL, Kolahi K, Pierce M, et al., 2016. Biological features of placental programming. Placenta, 48(S1):S47–S53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2016.10.012
Whitehouse AJ, Maybery MT, Hart R, et al., 2010. Free testosterone levels in umbilical-cord blood predict infant head circumference in females. Dev Med Child Neurol, 52(3):e73–e77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03546.x
Wissing ML, Bjerge MR, Olesen AIG, et al., 2014. Impact of PCOS on early embryo cleavage kinetics. Reprod Biomed Online, 28(4):508–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.11.017
Yamoto M, Iwazaki T, Takeuchi K, et al., 2018. The fetal lung-to-liver signal intensity ratio on magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of outcomes from isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Surg Int, 34(2):161–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-017-4184-2
Yu HF, Chen HS, Rao DP, et al., 2016. Association between polycystic ovary syndrome and the risk of pregnancy complications: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 95(51):e4863. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000004863
Zhu YH, Qu F, 2018. Towards a multidimensional scientific approach to improve clinical practices for infertility treatment. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 19(11):815–817. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1801014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fan QU designed the research, reviewed and edited the manuscript. Qing ZHANG and Zhong-kun BAO wrote the manuscript and performed data analysis. Mei-xiang DENG, Qiong XU, Dan-dan DING, Man-man PAN, and Xi XI collected the data. Fang-fang WANG and Yu ZOU explained the data. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Qing ZHANG, Zhong-kun BAO, Mei-xiang DENG, Qiong XU, Dan-dan DING, Man-man PAN, Xi XI, Fang-fang WANG, Yu ZOU, and Fan QU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study before all fetal magnetic resonance imaging procedures.
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81874480 and 81873837) and the Zhejiang Province Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. LR16H040001), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Bao, Zk., Deng, Mx. et al. Fetal growth, fetal development, and placental features in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: analysis based on fetal and placental magnetic resonance imaging. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 21, 977–989 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000350
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000350