Abstract
Objective
To provide comprehensive data to understand mechanisms of vascular endothelial cell (VEC) response to hypoxia/re-oxygenation.
Methods
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were employed to construct hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced VEC transcriptome profiling. Cells incubated under 5% O2, 5% CO2, and 90% N2 for 3 h followed by 95% air and 5% CO2 for 1 h were used in the hypoxia/re-oxygenation group. Those incubated only under 95% air and 5% CO2 were used in the normoxia control group.
Results
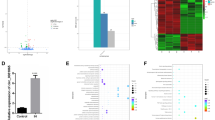
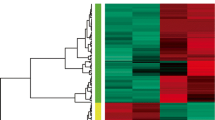
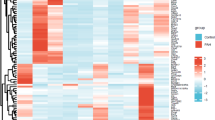
By using a well-established microarray chip consisting of 58 339 probes, the study identified 372 differentially expressed genes. While part of the genes are known to be VEC hypoxia/re-oxygenation-related, serving as a good control, a large number of genes related to VEC hypoxia/re-oxygenation were identified for the first time. Through bioinformatic analysis of these genes, we identified that multiple pathways were involved in the reaction. Subsequently, we applied real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and western blot techniques to validate the microarray data. It was found that the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, like pleckstrin homology-like domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1), was also consistently up-regulated in the hypoxia/re-oxygenation group. STRING analysis found that significantly differentially expressed genes SLC38A3, SLC5A5, Lnc-SLC36A4-1, and Lnc-PLEKHJ1-1 may have physical or/and functional protein-protein interactions with PHLDA1.
Conclusions
The data from this study have built a foundation to develop many hypotheses to further explore the hypoxia/re-oxygenation mechanisms, an area with great clinical significance for multiple diseases.
概要
目 的
应用全转录组芯片研究缺氧/复氧诱导下人脐静脉内皮细胞 (HUVEC) 的转录组轮廓.
创新点
血管内皮细胞 (VEC) 缺氧/复氧损伤被视定为许多生理和病理过程中导致器官功能障碍的重要驱动因素. 然而, 其详细病理生理机制和基因表达谱信息尚未阐明. 本研究首次应用全转录组芯片技术研究 VEC 缺氧/复氧诱导下的转录组轮廓.
方 法
用缺氧孵育 3 h 后复氧 1 h 的 HUVEC 为缺氧/复氧组, 同时常氧孵育的 HUVEC 为常氧对照组. 应用含 58 339 条探针的全转录组芯片检测每组三个样本. 对差异表达基因进行生信分析和功能验证.
结 论
本研究发现 372 个有意义的差异表达基因探针. 相关基因涵盖多种途径和功能, 例如氧自由基的产生、 钙超载、 炎症、 糖脂代谢、 内皮细胞增殖、 分化、 细胞骨架及通透性调节、 细胞裂解、 凋亡和血管生成. 另外, 实验进一步表明, 差异表达基因 pleckstrin 同源样域家族A成员 1(PHLDA1) 的 mRNA 和蛋白质表达结果与微阵列结果一致. STRING 分析发现, PHLDA1 可能与差异表达基因 SLC38A3、 SLC5A5、 Lnc-SLC36A4-1 和 Lnc-PLEKHJ1-1 具有物理性和/或功能性相互作用, 这有望揭示 VEC 在缺氧/复氧环境下长链非编码RNA (lncRNA) 的相关机制.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkeson A, Yeh SY, Malhotra A, et al., 2009. Endothelial function in obstructive sleep apnea. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 51(5):351–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.08.002
Bader AM, Klose K, Bieback K, et al., 2015. Hypoxic preconditioning increases survival and pro-angiogenic capacity of human cord blood mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. PLoS ONE, 10(9):e0138477. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138477
Baldea I, Teacoe I, Olteanu DE, et al., 2018. Effects of different hypoxia degrees on endothelial cell cultures—time course study. Mech Ageing Dev, 172:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2017.11.003
Basile DP, Friedrich JL, Spahic J, et al., 2011. Impaired endothelial proliferation and mesenchymal transition contribute to vascular rarefaction following acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 300(3):F721–F733. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00546.2010
Carden DL, Granger DN, 2000. Pathophysiology of ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Pathol, 190(3):255–266. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(200002)190:3<255::AID-PATH526>3.0.CO;2-6
E S, Costa MC, Kurc S, et al., 2018. The circulating non-coding RNA landscape for biomarker research: lessons and prospects from cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 39(7):1085–1099. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2018.35
Eltzschig HK, Collard CD, 2004. Vascular ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Br Med Bull, 70(1):71–86. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldh025
Fearon AE, Carter EP, Clayton NS, et al., 2018. PHLDA1 mediates drug resistance in receptor tyrosine kinase-driven cancer. Cell Rep, 22(9):2469–2481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.028
Ferrucci M, Biagioni F, Ryskalin L, et al., 2018. Ambiguous effects of autophagy activation following hypoperfusion/ischemia. Int J Mol Sci, 19(9):2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092756
Filippi I, Saltarella I, Aldinucci C, et al., 2018. Different adaptive responses to hypoxia in normal and multiple myeloma endothelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem, 46(1):203–212. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488423
Fu PF, Zheng X, Fan X, et al., 2019. Role of cytoplasmic lncRNAs in regulating cancer signaling pathways. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 20(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800254
Gudenas BL, Wang J, Kuang SZ, et al., 2019. Genomic data mining for functional annotation of human long noncoding RNAs. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 20(6):476–487. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900162
Guo YX, Jia PY, Chen YQ, et al., 2020. PHLDA1 is a new therapeutic target of oxidative stress and ischemia reperfusion-induced myocardial injury. Life Sci, 245:117347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117347
Haybar H, Shokuhian M, Bagheri M, et al., 2019. Involvement of circulating inflammatory factors in prognosis and risk of cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 132:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.05.010
Jiang JK, Fang W, Hong LJ, et al., 2017. Distribution and differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells after fluid resuscitation in mice with hemorrhagic shock. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(1):48–58. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600510
Johnson EO, Chang KH, de Pablo Y, et al., 2011. PHLDA1 is a crucial negative regulator and effector of Aurora A kinase in breast cancer. J Cell Sci, 124(16):2711–2722. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.084970
Li F, Lee KE, Simon MC, 2018. Detection of hypoxia and HIF in paraffin-embedded tumor tissues. In: Huang LE (Ed.), Hypoxia: Methods and Protocols. Humana Press, New York, p.277–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7665-2_24
Li WY, Zhao YL, Fu P, 2018. Hypoxia induced factor in chronic kidney disease: friend or foe? Front Med (Lausanne), 4:259. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2017.00259
Liao JK, Zulueta JJ, Yu FS, et al., 1995. Regulation of bovine endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase by oxygen. J Clin Invest, 96(6):2661–2666. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI118332
Lim To WK, Kumar P, Marshall JM, 2015. Hypoxia is an effective stimulus for vesicular release of ATP from human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Placenta, 36(7): 759–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2015.04.005
Mansoori Z, Ghaedi H, Sadatamini M, et al., 2018. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNAs LINC00523 and LINC00994 in type 2 diabetes in an Iranian cohort. Mol Biol Rep, 45(5):1227–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4276-7
McQuillan LP, Leung GK, Marsden PA, et al., 1994. Hypoxia inhibits expression of eNOS via transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. Am J Physiol, 267(5):H1921–H1927. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1994.267.5.H1921
Mineo M, Ricklefs F, Rooj AK, et al., 2016. The long non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS2 facilitates the maintenance of mesenchymal glioblastoma stem-like cells in hypoxic niches. Cell Rep, 15(11):2500–2509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.018
Moad AIH, Muhammad TST, Oon CE, et al., 2013. Rapamycin induces apoptosis when autophagy is inhibited in T-47D mammary cells and both processes are regulated by Phlda1. Cell Biochem Biophys, 66(3):567–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9504-5
Nagai MA, 2016. Pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1 (PHLDA1) and cancer (Review). Biomed Rep, 4(3):275–281. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2016.580
Nallamshetty S, Chan SY, Loscalzo J, 2013. Hypoxia: a master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity. Free Radic Biol Med, 64:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.022
Niu QF, Li DL, Yang Y, et al., 2019. Establishment of human vascular endothelial hypoxia/reoxygeneration injury cell model. China J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 17(4):295–299 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.19438/j.cjoms.2019.04.002
Pan H, Wang BH, Li ZB, et al., 2019. Mitochondrial super-oxide anions induced by exogenous oxidative stress determine tumor cell fate: an individual cell-based study. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 20(4):310–321. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800319
Pan J, Zhu JY, Kee HS, et al., 2015. A review of compression, ventilation, defibrillation, drug treatment, and targeted temperature management in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Chin Med J (Engl), 128(4):550–554. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.151115
Salvadori M, Rosso G, Bertoni E, 2015. Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: pathogenesis and treatment. World J Transplant, 5(2):52–67. https://doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v5.i2.52
Sellheyer K, Nelson P, 2011. Follicular stem cell marker PHLDA1 (TDAG51) is superior to cytokeratin-20 in differentiating between trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma in small biopsy specimens. J Cutan Pathol, 38(7):542–550. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0560.2011.01693.x
Shay JES, Celeste Simon M, 2012. Hypoxia-inducible factors: crosstalk between inflammation and metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 23(4):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.04.004
Sun Y, George J, Rocha S, 2015. Dose-dependent effects of allopurinol on human foreskin fibroblast cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells under hypoxia. PLoS ONE, 10(4):e0123649. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123649
Tang X, Lin CP, Guo DQ, et al., 2016. CLOCK promotes endothelial damage by inducing autophagy through reactive oxygen species. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016:9591482. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9591482
Taylor MA, Das BC, Ray SK, 2018. Targeting autophagy for combating chemoresistance and radioresistance in glioblastoma. Apoptosis, 23(11–12):563–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-018-1480-9
Urbanek T, Kuczmik W, Basta-Kaim A, et al., 2014. Rapamycin induces of protective autophagy in vascular endothelial cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation. Brain Res, 1553:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.01.017
Wang JC, Li XX, Sun X, et al., 2018. Activation of AMPK by simvastatin inhibited breast tumor angiogenesis via impeding HIF-1α-induced pro-angiogenic factor. Cancer Sci, 109(5):1627–1637. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13570
Wu JB, Lei Z, Yu JG, 2015. Hypoxia induces autophagy in human vascular endothelial cells in a hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent manner. Mol Med Rep, 11(4):2677–2682. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.3093
Xie XJ, Yang YM, Jiang JK, et al., 2017. Association between the vascular endothelial growth factor single nucleotide polymorphisms and diabetic retinopathy risk: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes, 9(8):738–753. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12480
Zampetaki A, Albrecht A, Steinhofel K, 2018. Long non-coding RNA structure and function: is there a link? Front Physiol, 9:1201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01201
Zhang Q, Fang W, Ma L, et al., 2018. VEGF levels in plasma in relation to metabolic control, inflammation, and microvascular complications in type-2 diabetes: a cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore), 97(14):e0415. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000010415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jia XU performed the experimental research and data analysis, wrote and edited the manuscript. Jiu-kun JIANG performed the establishment of models. Xiao-lin LI, Xiao-peng YU, and Ying-ge XU conducted molecular biology experiments. Yuan-qiang LU performed the study design, data analysis, writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Jia XU, Jiu-kun JIANG, Xiao-lin LI, Xiao-peng YU, Ying-ge XU, and Yuan-qiang LU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81801572 and 81272075), the Foundation of Key Discipline Construction of Zhejiang Province for Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2017-XKA36), the Foundation of Key Research Project of Zhejiang Province for Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2019ZZ014), the Medical and Health Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. 2019327552), the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2019C03076), the General Research Program of Zhejiang Provincial Department of Medical and Health (No. 2013KYA066), the Opening Foundation of State Key Laboratory for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases (Nos. 2018KF02 and 2019KF06), and the Program of Education Department of Zhejiang Province (No. Y201738150), China
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Jiang, Jk., Li, Xl. et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of vascular endothelial cells after hypoxia/re-oxygenation induction based on microarray technology. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 21, 291–304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000043
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000043
Key words
- Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs)
- Hypoxia
- Re-oxygenation
- Microarray
- Pleckstrin homology-like domain family A member 1 (PHLDA1)
- Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)