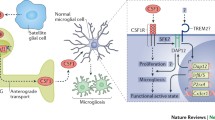
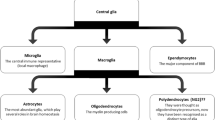
Abstract
Microglia are important cells involved in the regulation of neuropathic pain (NPP) and morphine tolerance. Information on their plasticity and polarity has been elucidated after determining their physiological structure, but there is still much to learn about the role of this type of cell in NPP and morphine tolerance. Microglia mediate multiple functions in health and disease by controlling damage in the central nervous system (CNS) and endogenous immune responses to disease. Microglial activation can result in altered opioid system activity, and NPP is characterized by resistance to morphine. Here we investigate the regulatory mechanisms of microglia and review the potential of microglial inhibitors for modulating NPP and morphine tolerance. Targeted inhibition of glial activation is a clinically promising approach to the treatment of NPP and the prevention of morphine tolerance. Finally, we suggest directions for future research on microglial inhibitors.
摘要
概要
小胶质细胞是参与调节神经性疼痛(NPP)和吗 啡耐受性的重要细胞.在确定它们的生理结构 后,已经阐明了有关其可塑性和极性的信息,但 关于这种类型的细胞在NPP 和吗啡耐受性中的 作用,仍有许多知识要学习.小胶质细胞通过控 制中枢神经系统的损伤和对疾病的内源性免疫 反应,介导健康和疾病的多种功能.小胶质细胞 活化可导致阿片样物质系统活性改变,而NPP 的 特征在于对吗啡的抗性.在这里,我们研究小胶 质细胞的调节机制,并综述了小胶质细胞抑制剂 抑制NPP 和吗啡耐受性的潜力.靶向的神经胶质 活化是治疗NPP 和预防吗啡耐受的临床有前途 的方法.最后,我们为小胶质细胞抑制剂的未来 研究提出了建议.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceves M, Terminel MN, Okoreeh A, et al., 2019. Morphine increases macrophages at the lesion site following spinal cord injury: protective effects of minocycline. Brain Behav Immun, 79:125–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.01.023
Aggarwal BB, Sung B, 2009. Pharmacological basis for the role of curcumin in chronic diseases: an age-old spice with modern targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 30(2):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2008.11.002
Benoit-Vical F, Saléry M, Soh PN, et al., 2008. Girolline: a potential lead structure for antiplasmodial drug research. Planta Med, 74(4):438–444. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1034348
Berger SB, Harris P, Nagilla R, et al., 2015. Characterization of GSK’963: a structurally distinct, potent and selective inhibitor of RIP1 kinase. Cell Death Discov, 1:15009. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.9
Berta T, Liu YC, Xu ZZ, et al., 2013. Tissue plasminogen activator contributes to morphine tolerance and induces mechanical allodynia via astrocytic IL-1β and ERK signaling in the spinal cord of mice. Neuroscience, 247:376385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.018
Bisht K, Sharma K, Tremblay ME, 2018. Chronic stress as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: roles of microglia-mediated synaptic remodeling, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Neurobiol Stress, 9:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ynstr.2018.05.003
Block ML, Li G, Qin L, et al., 2006. Potent regulation of microglia-derived oxidative stress and dopaminergic neuron survival: substance P vs. dynorphin. FASEB J, 20(2):251–258. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.05-4553com
Blommaart EFC, Krause U, Schellens JPM, et al., 1997. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors wortmannin and LY294002 inhibit autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem, 243(1–2):240–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.0240a.x
Bobermin LD, Souza DO, Goncalves CA, et al., 2018. Resveratrol prevents ammonia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular redox imbalance in C6 astroglial cells. Nutr Neurosci, 21(4):276–285. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415x.2017.1284375
Bolós M, Perea JR, Terreros-Roncal J, et al., 2018. Absence of microglial CX3CR1 impairs the synaptic integration of adult-born hippocampal granule neurons. Brain Behav Immun, 68:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.10.002
Bulduk EB, Kurt G, Barun S, et al., 2019. The effects of minocycline on the hippocampus in lithium-pilocarpine induced status epilepticus in rat: relations with microglial/ astrocytic activation and serum S100B level. Turk Neurosurg, 29(1):95–105. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.Jtn.22744-18.1
Cai Y, Kong H, Pan YB, et al., 2016. Procyanidins alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. J Neuroinflammation, 13(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0520-z
Chen C, Liu JM, Luo YP, 2020. MicroRNAs in tumor immunity: functional regulation in tumor-associated macrophages. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(1):12–28. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900452
Chen YJ, Huo YH, Hong YG, 2017. Effects of intrathecal administration of AM22-52 on mechanical allodynia and CCL2 expression in DRG in bone cancer rats. Acta Phys Sin, 69(1):70–76 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13294/j.aps.2016.0086
Ciddi V, Dodda D, 2014. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol in diabetic complications: in vitro and in vivo studies. Pharmacol Rep, 66(5):799–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.04.006
Cogut V, Bruintjes JJ, Eggen BJL, et al., 2018. Brain inflammatory cytokines and microglia morphology changes throughout hibernation phases in Syrian hamster. Brain Behav Immun, 68:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.10.009
Colburn RW, Rickman AJ, DeLeo JA, 1999. The effect of site and type of nerve injury on spinal glial activation and neuropathic pain behavior. Exp Neurol, 157(2):289–304. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1999.7065
Crowley BM, Stump CA, Nguyen DN, et al., 2015. Novel oxazolidinone calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonists for the acute treatment of migraine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 25(21):4777–4781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.021
Cui Y, Liao XX, Liu W, et al., 2008. A novel role of minocycline: attenuating morphine antinociceptive tolerance by inhibition of p38 MAPK in the activated spinal microglia. Brain Behav Immun, 22(1):114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2007.07.014
Dai Z, Chu HC, Ma JH, et al., 2018. The regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of microRNAs: from chronic pain to morphine tolerance. Front Mol Neurosci, 11:80. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00080
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, et al., 2000. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J, 351(1):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1042/0264-6021:3510095
Deane R, Singh I, Sagare AP, et al., 2012. A multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest, 122(4):1377–1392. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci58642
di Pierro F, Settembre R, 2013. Safety and efficacy of an add-on therapy with curcumin phytosome and piperine and/or lipoic acid in subjects with a diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy treated with dexibuprofen. J Pain Res, 6:497–503. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.S48432
Edwards RR, Dworkin RH, Turk DC, et al., 2016. Patient phenotyping in clinical trials of chronic pain treatments: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain, 157(9):1851–1871. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000602
Esmaeili-Mahani S, Ebrahimi B, Abbasnejad M, et al., 2015. Satureja khuzestanica prevents the development of morphine analgesic tolerance through suppression of spinal glial cell activation in rats. J Nat Med, 69(2):165–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-013-0796-6
Fan Y, Chen ZL, Pathak JL, et al., 2018. Differential regulation of adhesion and phagocytosis of resting and activated microglia by dopamine. Front Cell Neurosci, 12:309. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00309
Feng QX, Feng F, Feng XY, et al., 2012. Resolvin D1 reverses chronic pancreatitis-induced mechanical allodynia, phosphorylation of NMDA receptors, and cytokines expression in the thoracic spinal dorsal horn. BMC Gastroenterol, 12:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230x-12-148
Ghavimi H, Hassanzadeh K, Maleki-Dizaji N, et al., 2014. Pioglitazone prevents morphine antinociception tolerance and withdrawal symptoms in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 387(9):811–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-0996-y
Ghavimi H, Charkhpour M, Ghasemi S, et al., 2015. Pioglitazone prevents morphine antinociceptive tolerance via ameliorating neuroinflammation in rat cerebral cortex. Pharmacol Rep, 67(1):78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.08.003
Ghorab MM, El-Gazzar MG, Alsaid MS, 2014. Design and synthesis of novel thiophenes bearing biologically active aniline, aminopyridine, benzylamine, nicotinamide, pyrimidine and triazolopyrimidine moieties searching for cytotoxic agents. Acta Pol Pharm, 71(3):401–407.
Ginhoux F, Lim S, Hoeffel G, et al., 2013. Origin and differentiation of microglia. Front Cell Neurosci, 7:45. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00045
Guo GW, Bhat NR, 2006. Hypoxia/reoxygenation differentially modulates NF-κB activation and iNOS expression in astrocytes and microglia. Antioxid Redox Signal, 8(5–6):911–918. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2006.8.911
Guo YW, Hong WM, Wang XM, et al., 2019. MicroRNAs in microglia: how do microRNAs affect activation, inflammation, polarization of microglia and mediate the interaction between microglia and glioma? Front Mol Neurosci, 12:125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2019.00125
Hannam JA, Borrat X, Trocóniz IF, et al., 2016. Modeling respiratory depression induced by remifentanil and propofol during sedation and analgesia using a continuous noninvasive measurement of pCO2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 356(3):563–573. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.115.226977
Harris PA, King BW, Bandyopadhyay D, et al., 2016. DNA-encoded library screening identifies benzo[b][1,4] oxazepin-4-ones as highly potent and monoselective receptor interacting protein 1 kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem, 59(5):2163–2178. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01898
Hay DL, Conner AC, Howitt SG, et al., 2004. The pharmacology of adrenomedullin receptors and their relationship to CGRP receptors. J Mol Neurosci, 22(1–2):105–113. https://doi.org/10.1385/jmn:22:1-2:105
He XF, Wei JJ, Shou SY, et al., 2017. Effects of electroacu-puncture at 2 and 100 Hz on rat type 2 diabetic neuropathic pain and hyperalgesia-related protein expression in the dorsal root ganglion. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(3):239–248. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600247
Hickman SE, Allison EK, el Khoury J, 2008. Microglial dysfunction and defective β-amyloid clearance pathways in aging Alzheimer’s disease mice. J Neurosci, 28(33):8354–8360. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0616-08.2008
Hu XY, Huang F, Szymusiak M, et al., 2015. Curcumin attenuates opioid tolerance and dependence by inhibiting Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II α activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 352(3):420–428. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.114.219303
Huang BQ, Hong YG, 2015. Involvement of adrenomedullin in the pathogenesis of inflammatory pain and morphine tolerance. Acta Phys Sin, 67(4):431–436 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13294/j.aps.2015.0053
Inoue K, 2017. Purinergic signaling in microglia in the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, 93(4):174–182. https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.93.011
Ji RR, Berta T, Nedergaard M, 2013. Glia and pain: is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain, 154(S1):S10–S28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.022
Jiang C, Xu L, Chen L, et al., 2015. Selective suppression of microglial activation by paeoniflorin attenuates morphine tolerance. Eur J Pain, 19(7):908–919. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.617
Jokinen V, Sidorova Y, Viisanen H, et al., 2018. Differential spinal and supraspinal activation of glia in a rat model of morphine tolerance. Neuroscience, 375:10–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.01.048
Koh YQ, Mitchell MD, Almughlliq FB, et al., 2018. Regulation of inflammatory mediator expression in bovine endometrial cells: effects of lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Physiol Rep, 6(9):e13676. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13676
Kuhn SA, van Landeghem FKH, Zacharias R, et al., 2004. Microglia express GABAB receptors to modulate interleukin release. Mol Cell Neurosci, 25(2):312–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2003.10.023
Kwiatkowski K, Popiolek-Barczyk K, Piotrowska A, et al., 2019. Chemokines CCL2 and CCL7, but not CCL12, play a significant role in the development of pain-related behavior and opioid-induced analgesia. Cytokine, 119:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2019.03.007
Labuzek K, Liber S, Marcol W, et al., 2012. Controlling newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus with metformin managed pain symptoms in a patient affected with Dercum’s disease. Pain Med, 13(11):1526–1527. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2012.01487.x
Lee JW, Nam H, Kim LE, et al., 2019. TLR4 (Toll-like receptor 4) activation suppresses autophagy through inhibition of FOXO3 and impairs phagocytic capacity of microglia. Autophagy, 15(5):753–770. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1556946
Li H, Jiao YB, Xie MJ, 2017. Paeoniflorin ameliorates atherosclerosis by suppressing TLR4-mediated NF-κB activation. Inflammation, 40(6):2042–2051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0644-z
Li J, Deng GY, Wang HW, et al., 2017. Interleukin-1β pre-treated bone marrow stromal cells alleviate neuropathic pain through CCL7-mediated inhibition of microglial activation in the spinal cord. Sci Rep, 7(1):42260. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42260
Lin XF, Chen WM, Qiu ZX, et al., 2015. Design and synthesis of orally bioavailable aminopyrrolidinone histone deacetylase 6 inhibitors. J Med Chem, 58(6):2809–2820. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm502011f
Liu Q, Zhang YL, Liu S, et al., 2019. Cathepsin C promotes microglia M1 polarization and aggravates neuroinflammation via activation of Ca2+-dependent PKC/p38MAPK/ NF-κB pathway. J Neuroinflammation, 16(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1398-3
Merighi S, Gessi S, Varani K, et al., 2013. Morphine mediates a proinflammatory phenotype via μ-opioid receptor-PKCe-Akt-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in activated microglial cells. Biochem Pharmacol, 86(4):487–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.05.027
Mika J, 2008. Modulation of microglia can attenuate neuropathic pain symptoms and enhance morphine effectiveness. Pharmacol Rep, 60(3):297–307.
Mika J, Osikowicz M, Makuch W, et al., 2007. Minocycline and pentoxifylline attenuate allodynia and hyperalgesia and potentiate the effects of morphine in rat and mouse models of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol, 560(2–3):142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.013
Mitsikostas DD, Reuter U, 2017. Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies for migraine prevention: comparisons across randomized controlled studies. Curr Opin Neurol, 30(3):272–280. https://doi.org/10.1097/wco.0000000000000438
Moini-Zanjani T, Ostad SN, Labibi F, et al., 2016. Minocycline effects on IL-6 concentration in macrophage and microglial cells in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Iran Biomed J, 20(5):273–279. https://doi.org/10.22045/ibj.2016.04
Morgenweck J, Griggs RB, Donahue RR, et al., 2013. PPARy activation blocks development and reduces established neuropathic pain in rats. Neuropharmacology, 70:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.01.020
Ochiai W, Kaneta M, Nagae M, et al., 2016. Mice with neuropathic pain exhibit morphine tolerance due to a decrease in the morphine concentration in the brain. Eur J Pharm Sci, 92:298–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2016.03.019
Ossipov MH, Lai J, Vanderah TW, et al., 2003. Induction of pain facilitation by sustained opioid exposure: relationship to opioid antinociceptive tolerance. Life Sci, 73(6):783–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00410-7
Otto KJ, Wyse BD, Cabot PJ, et al., 2011. Insulin implants prevent the temporal development of mechanical allodynia and opioid hyposensitivity for 24-wks in streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic Wistar rats. Pain Med, 12(5):782–793. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2011.01102.x
Pan YB, Sun XD, Jiang L, et al., 2016. Metformin reduces morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation, 13(1):294. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0754-9
Parkinson FE, Paterson ARP, Young JD, et al., 1993. Inhibitory effects of propentofylline on [3H]adenosine influx: a study of three nucleoside transport systems. Biochem Pharmacol, 46(5):891–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(93)90499-m
Pérez-Severiano F, Bermúdez-Ocaña DY, López-Sánchez P, et al., 2008. Spinal nerve ligation reduces nitric oxide synthase activity and expression: effect of resveratrol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 90(4):742–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.05.024
Piotrowska A, Popiolek-Barczyk K, Pavone F, et al., 2017. Comparison of the expression changes after botulinum toxin type A and minocycline administration in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat microglial and astroglial cultures. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 7:141. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00141
Popiolek-Barczyk K, Mika J, 2016. Targeting the microglial signaling pathways: new insights in the modulation of neuropathic pain. Curr Med Chem, 23(26):2908–2928. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666160607120124
Popiolek-Barczyk K, Piotrowska A, Makuch W, et al., 2017. Biphalin, a dimeric enkephalin, alleviates LPS-induced activation in rat primary microglial cultures in opioid receptor-dependent and receptor-independent manners. Neural Plast, 2017:3829472. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3829472
Qiu SW, Feng YM, LeSage G, et al., 2015. Chronic morphine-induced microRNA-124 promotes microglial immuno-suppression by modulating P65 and TRAF6. J Immunol, 194(3):1021–1030. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1400106
Qu J, Tao XY, Teng P, et al., 2017. Blocking ATP-sensitive potassium channel alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting HSP70-TLR4-NLRP3-mediated neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation, 14(1):228. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0997-0
Ransohoff RM, el Khoury J, 2015. Microglia in health and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 8(1):a020560. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a020560
Redivo DDB, Jesus CHA, Sotomaior BB, et al., 2019. Acute antinociceptive effect of fish oil or its major compounds, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on diabetic neuropathic pain depends on opioid system activation. Behav Brain Res, 372:111992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111992
Ruan JP, Chen L, Ma ZL, 2019. Activation of spinal extacellular signal-regulated kinases and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways contributes to morphine-induced acute and chronic hyperalgesia in mice. J Cell Biochem, 120(9):15045–15056. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28766
Sakai A, Suzuki H, 2013. Nerve injury-induced upregulation of miR-21 in the primary sensory neurons contributes to neuropathic pain in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 435(2):176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.04.089
Salter MW, Beggs S, 2014. Sublime microglia: expanding roles for the guardians of the CNS. Cell, 158(1):15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.008
Scandroglio F, Tórtora V, Radi R, et al., 2014. Metabolic control analysis of mitochondrial aconitase: influence over respiration and mitochondrial superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production. Free Radic Res, 48(6):684–693. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2014.900175
Stoetzer C, Reuter S, Doll T, et al., 2016. Inhibition of the cardiac Na+ channel α-subunit Nav1.5 by propofol and dexmedetomidine. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol, 389(3):315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1195-1
Stokes L, Layhadi JA, Bibic L, et al., 2017. P2X4 receptor function in the nervous system and current breakthroughs in pharmacology. Front Pharmacol, 8:291. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00291
Su XM, 2008. α-Synuclein and Microglial Activation in Parkinson’s Disease. PhD Dissemination, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA.
Sumitani M, Ueda H, Hozumi J, et al., 2016. Minocycline does not decrease intensity of neuropathic pain intensity, but does improve its affective dimension. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother, 30(1):31–35. https://doi.org/10.3109/15360288.2014.1003674
Sun YE, Peng LY, Sun XF, et al., 2012. Intrathecal injection of spironolactone attenuates radicular pain by inhibition of spinal microglia activation in a rat model. PLoS ONE, 7(6):e39897. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039897
Takemoto M, Sunagawa M, Okada M, et al., 2016. Yokukansan, a Kampo medicine, prevents the development of morphine tolerance through the inhibition of spinal glial cell activation in rats. Integr Med Res, 5(1):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imr.2015.12.003
Tang Y, Le WD, 2016. Differential roles of M1 and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol, 53(2):1181–1194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9070-5
Tapocik JD, Ceniccola K, Mayo CL, et al., 2016. MicroRNAs are involved in the development of morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and regulate functionally relevant changes in Serpini1. Front Mol Neurosci, 9:20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2016.00020
Taylor A, Westveld AH, Szkudlinska M, et al., 2013. The use of metformin is associated with decreased lumbar radiculopathy pain. J Pain Res, 6:755–763. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.S52205
Tozaki-Saitoh H, Masuda J, Kawada R, et al., 2019. Transcription factor MafB contributes to the activation of spinal microglia underlying neuropathic pain development. Glia, 67(4):729–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23570
Tsai RY, Wang JC, Chou KY, et al., 2016. Resveratrol reverses morphine-induced neuroinflammation in morphine-tolerant rats by reversal HDAC1 expression. J Formos Med Assoc, 115(6):445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2015.05.010
Tsuda M, 2017. P2 receptors, microglial cytokines and chemokines, and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci Res, 95(6):1319–1329. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23816
Tsuda M, Koga K, Chen T, et al., 2017. Neuronal and micro-glial mechanisms for neuropathic pain in the spinal dorsal horn and anterior cingulate cortex. J Neurochem, 141(4):486–498. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14001
Vanelderen P, van Zundert J, Kozicz T, et al., 2015. Effect of minocycline on lumbar radicular neuropathic pain: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial with amitriptyline as a comparator. Anesthesiology, 122(2):399–406. https://doi.org/10.1097/aln.0000000000000508
Wang D, Li J, Chen P, et al., 2014. Upregulation of pronociceptive mediators and downregulation of opioid peptide by adrenomedullin following chronic exposure to morphine in rats. Neuroscience, 280:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.08.048
Wang J, Xu W, Zhong T, et al., 2016. miR-365 targets β-arrestin 2 to reverse morphine tolerance in rats. Sci Rep, 6(1):38285. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38285
Wang J, Xu W, Shao JL, et al., 2017. miR-219-5p targets CaMKIIγ to attenuate morphine tolerance in rats. Onco-target, 8(17):28203–28214. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15997
Wang ZY, Ma WY, Chabot JG, et al., 2009. Cell-type specific activation of p38 and ERK mediates calcitonin gene-related peptide involvement in tolerance to morphine-induced analgesia. FASEB J, 23(8):2576–2586. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.08-128348
Wang ZY, Ma WY, Chabot JG, et al., 2010a. Calcitonin gene-related peptide as a regulator of neuronal CaMKII-CREB, microglial p38-NFκB and astroglial ERK-Stat1/3 cascades mediating the development of tolerance to morphine-induced analgesia. Pain, 151(1):194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2010.07.006
Wang ZY, Ma WY, Chabot JG, et al., 2010b. Morphological evidence for the involvement of microglial p38 activation in CGRP-associated development of morphine antinociceptive tolerance. Peptides, 31(12):2179–2184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.08.020
Wen YR, Tan PH, Cheng JK, et al., 2011. Microglia: a promising target for treating neuropathic and postoperative pain, and morphine tolerance. J Formos Med Assoc, 110(8):487–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0929-6646(11)60074-0
Weng YQ, Wu J, Li L, et al., 2019. Circular RNA expression profile in the spinal cord of morphine tolerated rats and screen of putative key circRNAs. Mol Brain, 12(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-019-0498-4
Widerström-Noga E, 2017. Neuropathic pain and spinal cord injury: phenotypes and pharmacological management. Drugs, 77(9):967–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0747-8
Wu QF, Hwang CK, Zheng H, et al., 2013. MicroRNA 339 down-regulates μ-opioid receptor at the post-transcriptional level in response to opioid treatment. FASEB J, 27(2):522–535. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-213439
Wu XP, She RX, Yang YP, et al., 2018. MicroRNA-365 alleviates morphine analgesic tolerance via the inactivation of the ERK/CREB signaling pathway by negatively targeting β-arrestin2. J Biomed Sci, 25(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-018-0405-9
Xie RG, Gao YJ, Park CK, et al., 2018. Spinal CCL2 promotes central sensitization, long-term potentiation, and inflammatory pain via CCR2: further insights into molecular, synaptic, and cellular mechanisms. Neurosci Bull, 34(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-017-0106-5
Xie XJ, Ma LG, Xi K, et al., 2017. Effects of microRNA-223 on morphine analgesic tolerance by targeting NLRP3 in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain, 13:1744806917706582. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806917706582
Xu J, Chai H, Ehinger K, et al., 2014. Imaging P2X4 receptor subcellular distribution, trafficking, and regulation using P2X4-phluorin. J Gen Physiol, 144(1):81–104. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201411169
Xu L, He D, Bai Y, 2016. Microglia-mediated inflammation and neurodegenerative disease. Mol Neurobiol, 53(10):6709–6715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9593-4
Xu Z, Wang BR, Wang X, et al., 2006. ERK1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediate iNOS-induced spinal neuron degeneration after acute traumatic spinal cord injury. Life Sci, 79(20):1895–1905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2006.06.023
Yahyavi-Firouz-Abadi N, Tahsili-Fahadan P, Ostad SN, 2007. Effect of μ and κ opioids on injury-induced microglial accumulation in leech CNS: involvement of the nitric oxide pathway. Neuroscience, 144(3):1075–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.036
Youssef M, Ibrahim A, Akashi K, et al., 2019. PUFA-plasmalogens attenuate the LPS-induced nitric oxide production by inhibiting the NF-κB, p38 MAPK and JNK pathways in microglial cells. Neuroscience, 397:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.11.030
Yu LN, Sun LH, Wang M, et al., 2016. Research progress of the role and mechanism of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 5 (ERK5) pathway in pathological pain. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 17(10):733–741. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600188
Zeng X, Lin MY, Wang D, et al., 2014. Involvement of adrenomedullin in spinal glial activation following chronic administration of morphine in rats. Eur J Pain, 18(9):1323–1332. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2014.493.x
Zhang C, Zhang YP, Li YY, et al., 2019. Minocycline ameliorates depressive behaviors and neuro-immune dysfunction induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in the rat. Behav Brain Res, 356:348–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.07.001
Zhang L, Wang YJ, Li DX, et al., 2016. The absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of procyanidins. Food Funct, 7(3):1273–1281. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5fo01244a
Zhang X, Wang J, Yu TT, et al., 2015. Minocycline can delay the development of morphine tolerance, but cannot reverse existing tolerance in the maintenance period of neuropathic pain in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 42(1):94–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12316
Zhang Y, Tao GJ, Hu L, et al., 2017. Lidocaine alleviates morphine tolerance via AMPK-SOCS3-dependent neuroinflammation suppression in the spinal cord. J Neuroinflammation, 14(1):211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0983-6
Zhao H, Alam A, Chen Q, et al., 2017. The role of microglia in the pathobiology of neuropathic pain development: what do we know? Br J Anaesth, 118(4):504–516. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aex006
Zheng H, Zeng Y, Zhang XX, et al., 2010. μ -Opioid receptor agonists differentially regulate the expression of miR-190 and NeuroD. Mol Pharmacol, 77(1):102–109. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.109.060848
Zhou DL, Zhang SQ, Hu L, et al., 2019. Inhibition of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase by paeoniflorin attenuates neuroinflammation and ameliorates neuropathic pain. J Neuroinflammation, 16(1):83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1476-6
Zilliox LA, 2017. Neuropathic pain. CONTINUUM: Lifelong Learn Neurol, 23(2):512–532. https://doi.org/10.1212/con.0000000000000462
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Er-rong DU, Rong-ping FAN, Li-lou RONG, and Zhen XIE wrote and edited the manuscript. Chang-shui XU contributed the study design of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Er-rong DU, Rong-ping FAN, Li-lou RONG, Zhen XIE and Chang-shui XU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81660199)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Er., Fan, Rp., Rong, Ll. et al. Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of microglial inhibitors in neuropathic pain and morphine tolerance. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 21, 204–217 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900425
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900425