Abstract
Marsdeniae tenacissimae extract (MTE) has been used as an adjuvant medicine for cancer therapy for a long time. Although massive studies demonstrated its considerable anti-cancer effect, there is no research on its influence on erythrocytes, which are firstly interacted with MTE in the circulation. To investigate the influence of MTE on erythrocytes, we used a flow cytometer to detect the MTE-treated alternations of morphology, calcium concentration, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in erythrocytes. We used hemolysis under different osmotic solutions to evaluate the fragility of erythrocytes. Data showed that MTE treatment dose-dependently increased the ratio of erythrocyte fragmentation (P<0.001) and shrinking, and elevated the forward scatter (FSC) value (P<0.001) and calcium accumulation (P<0.001). MTE induced ROS production of erythrocytes under the high glucose condition (P<0.01) and consequently caused a rise in fragility (P<0.05). These results suggest that MTE induces cytotoxicity and aging in erythrocytes in a dose-dependent manner, and presents the possibility of impairment on cancer patients’ circulating erythrocytes when MTE is used as an anti-cancer adjuvant medicine.
中文概要
题目
乌骨藤提取物对人红细胞的毒性研究
目的
评估乌骨藤提取物对红细胞形态及生理功能的影响,并初步探讨其作用机制。
创新点
首次检测乌骨藤提取物对红细胞的毒性作用,并 且初步探索此毒性作用与乌骨藤导致的红细胞 内活性氧(ROS)和钙离子水平的相关性。
方法
不同浓度乌骨藤提取物(0、64、128 和256 μg/ml) 处理红细胞24 h,通过流式细胞术检测前向角散 射(FSC)和侧向角散射(SSC),计算红细胞破 碎率和大小改变,通过显微镜观察形态学的变 化;装载2',7'-二氯荧光黄双乙酸盐(DCFH-DA) 和钙荧光探针Fluo-4 染料,通过流式细胞术分别 检测红细胞ROS 和钙离子荧光强度的变化;通过 观察一系列低渗生理盐水下红细胞的溶胀情况, 评估乌骨藤提取物对红细胞脆性的改变。
结论
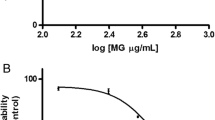
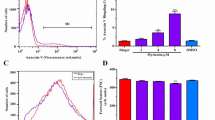
乌骨藤提取物剂量依赖性地增加红细胞的破碎率 (图1),导致FSC 增加(图2),同时高浓度乌 骨藤提取物(256 μg/ml)导致红细胞圆盘状结构 消失(图3);128 和256 μg/ml 乌骨藤提取物处 理红细胞导致胞内钙离子显著增加(图4);乌骨 藤提取物在高糖环境中诱导红细胞ROS 累计,并 最终导致红细胞脆性增加(图5)。上述结果显示, 乌骨藤提取物对红细胞有毒性作用,并有可能在 临床抗癌治疗中破坏红细胞引起潜在的毒副作 用(图6)。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed, M., Artunc, F., Alzoubi, K., et al., 2014. Suicidal erythrocyte death in end-stage renal disease. J. Mol. Med., 92(8): 871–879. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1151-4
Bogdanova, A., Makhro, A., Wang, J., et al., 2013. Calcium in red blood cells—a perilous balance. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 14(5): 9848–9872. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059848
Bouguerra, G., Aljanadi, O., Bissinger, R., et al., 2015. Embelin-induced phosphatidylserine translocation in the erythrocyte cell membrane. Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 37(4): 1629–1640. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000438529
Chen, B.Y., Chen, D., Lyu, J.X., et al., 2016. Marsdeniae tenacissimae extract (MTE) suppresses cell proliferation by attenuating VEGF/VEGFR2 interactions and promotes apoptosis through regulating PKC pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Chin. J. Nat. Med., 14(12): 922–930. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5364(17)30017-1
Ellsworth, M.L., Ellis, C.G., Goldman, D., et al., 2009. Erythrocytes: oxygen sensors and modulators of vascular tone. Physiology, 24(2): 107–116. http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00038.2008
Fan, W., Sun, L., Zhou, J.Q., et al., 2015. Marsdenia tenacissima extract induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in human esophageal carcinoma cells by inhibiting mitogenactivated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med., 13(6): 428–437. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5364(15)30036-4
Han, S.Y., Zhao, M.B., Zhuang, G.B., et al., 2012. Marsdenia tenacissima extract restored gefitinib sensitivity in resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer, 75(1): 30–37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.06.001
Han, S.Y., Ding, H.R., Zhao, W., et al., 2014. Enhancement of gefitinib-induced growth inhibition by Marsdenia tenacissima extract in non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing wild or mutant EGFR. BMC Complement. Altern. Med., 14:165. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-165
Huang, Z., Wang, Y., Chen, J., et al., 2013a. Effect of Xiaoaiping injection on advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in patients. J. Tradit. Chin. Med., 33(1): 34–38. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0254-6272(13)60097-7
Huang, Z., Lin, H., Wang, Y., et al., 2013b. Studies on the anti-angiogenic effect of Marsdenia tenacissima extract in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Lett., 5(3): 917–922. http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/ol.2013.1105
Lang, F., Abed, M., Lang, E., et al., 2014. Oxidative stress and suicidal erythrocyte death. Antioxid. Redox Signal., 21(1): 138–153. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5747
Li, D., Li, C., Song, Y., et al., 2015. Marsdenia tenacssima extract and its functional components inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human Burkitt leukemia/ lymphoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Leuk. Lymphoma, 57(2): 419–428. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2015.1043546
Li, J.L., Gao, Z.B., Zhao, W.M., 2016. Identification and evaluation of antiepileptic activity of C21 steroidal glycosides from the roots of Cynanchum wilfordii. J. Nat. Prod., 79(1): 89–97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00766
Lupescu, A., Jilani, K., Zelenak, C., et al., 2012. Induction of programmed erythrocyte death by gambogic acid. Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 30(2): 428–438. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000339036
Maher, A.D., Kuchel, P.W., 2003. The Gárdos channel: a review of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel in human erythrocytes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 35(8): 1182–1197. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(02)00310-2
Pretorius, E., Olumuyiwa-Akeredolu, O.O., Mbotwe, S., et al., 2016. Erythrocytes and their role as health indicator: using structure in a patient-orientated precision medicine approach. Blood Rev., 30(4): 263–274. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2016.01.001
Qian, E.W., Ge, D.T., Kong, S.K., 2011. Salidroside promotes erythropoiesis and protects erythroblasts against oxidative stress by up-regulating glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin. J. Ethnopharmacol., 133(2): 308–314. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.09.025
Qian, E.W., Ge, D.T., Kong, S.K., 2012. Salidroside protects human erythrocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. J. Nat. Prod., 75(4): 531–537. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np200555s
Shaik, N., Zbidah, M., Lang, F., 2012. Inhibition of Ca2+ entry and suicidal erythrocyte death by naringin. Cell Physiol. Biochem., 30(3): 678–686. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000341448
Tziakas, D., Chalikias, G., Grapsa, A., et al., 2012. Red blood cell distribution width—a strong prognostic marker in cardiovascular disease—is associated with cholesterol content of erythrocyte membrane. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc., 51(4): 243–254. http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/CH-2012-1530
Wang, Q., Cao, J., Wang, P., et al., 2015. Antitumor effect of C21 steroidal glycosides on adenoid cystic carcinoma cell line SACC83. Clin. Lab., 61(10): 1553–1560.
Yang, J.T., Tang, L.H., Liu, Y.Q., et al., 2015. Cisplatin combined with hyperthermia kills HepG2 cells in intraoperative blood salvage but preserves the function of erythrocytes. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B (Biomed. & Biotechnol.), 16(5): 395–403. http://dx.doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1400224
Ye, B., Li, J., Li, Z., et al., 2014a. Anti-tumor activity and relative mechanism of ethanolic extract of Marsdenia tenacissima (Asclepiadaceae) against human hematologic neoplasm in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol., 153(1): 258–267. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.035
Ye, B., Yang, J., Li, J., et al., 2014b. In vitro and in vivo antitumor activities of tenacissoside C from Marsdenia tenacissima. Planta Med., 80(1): 29–38. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1360128
Yin, Z.Q., Yu, S.L., Wei, Y.J., et al., 2016. C21 steroidal glycosides from Cynanchum stauntonii induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Steroids, 106:55–61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2015.12.008
Zelenak, C., Pasham, V., Jilani, K., et al., 2012. Tanshinone IIA stimulates erythrocyte phosphatidylserine exposure. Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 30(1): 282–294. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000339064
Zhang, H., Tan, A.M., Zhang, A.Y., et al., 2010. Five new C21 steroidal glycosides from the stems of Marsdenia tenacissima. Steroids, 75(2): 176–183. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2009.11.003
Zhu, R.J., Shen, X.L., Dai, L.L., et al., 2014. Total aglycones from Marsdenia tenacissima increases antitumor efficacy of paclitaxel in nude mice. Molecules, 9(9): 13965–13975. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules190913965
Ziobro, A., Duchnowicz, P., Mulik, A., et al., 2013. Oxidative damages in erythrocytes of patients with metabolic syndrome. Mol. Cell. Biochem., 378(1-2): 267–273. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1617-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Project supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. LQ16H070003, LY15H280010, and LY15C090004), the Key Project of Chinese Medicine in Zhejiang Province (No. 2015ZZ001), the Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. 2014ZB007), the Traditional Chinese Medicine Outstanding Young Talent Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. 2014ZQ005), and the Medicine and Health Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. 2015ZDA002), China
ORCID: Ke HAO, http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8013-9277
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, K., Chen, By., Li, Kq. et al. Cytotoxicity of anti-tumor herbal Marsdeniae tenacissimae extract on erythrocytes. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 18, 597–604 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600228
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600228