Abstract
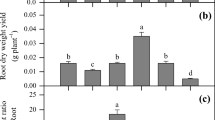
The elucidation of a natural strategy for metal hyperaccumulation enables the rational design of technologies for the clean-up of metal-contaminated soils. Organic acid has been suggested to be involved in toxic metallic element tolerance, translocation, and accumulation in plants. The impact of exogenous organic acids on cadmium (Cd) uptake and translocation in the zinc (Zn)/Cd co-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii was investigated in the present study. By the addition of organic acids, short-term (2 h) root uptake of 109Cd increased significantly, and higher 109Cd contents in roots and shoots were noted 24 h after uptake, when compared to controls. About 85% of the 109Cd taken up was distributed to the shoots in plants with citric acid (CA) treatments, as compared with 75% within controls. No such effect was observed for tartaric acid (TA). Reduced growth under Cd stress was significantly alleviated by low CA. Long-term application of the two organic acids both resulted in elevated Cd in plants, but the effects varied with exposure time and levels. The results imply that CA may be involved in the processes of Cd uptake, translocation and tolerance in S. alfredii, whereas the impact of TA is mainly on the root uptake of Cd.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao, T., Sun, L.N., Sun, T.H., 2011. The effects of Fe deficiency on low molecular weight organic acid exudation and cadmium uptake by Solanum nigrum L. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci., 61(4):305–312. [doi:10.1080/09064710.2010.493529]
Boominathan, R., Doran, P.M., 2003. Organic acid complexation, heavy metal distribution and the effect of ATPase inhibition in hairy roots of hyperaccumulator plant species. J. Biotechnol., 101(2):131–146. [doi:10. 1016/S0168-1656(02)00320-6]
Chaney, R.L., Angle, J.S., Mclntosh, M.S., Reeves, R.D., Li, Y.M., Brewer, E.P., Chen, K.Y., Roseberg, R.J., Perner, H., Synkowski, E.C., et al., 2005. Using hyperaccumulator plants to phytoextract soil Ni and Cd. Z. Naturforsch. C, 60(3–4):190–198.
Chen, Y.X., Lin, Q., Luo, Y.M., He, Y.F., Zhen, S.J., Yu, Y.L., Tian, G.M., Wong, M.H., 2003. The role of citric acid on the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 50(6):807–811. [doi:10.1016/S0045-6535 (02)00223-0]
Cui, S., Zhou, Q.X., Wei, S.H., Zhang, W., Cao, L., Ren, L.P., 2007. Effects of exogenous chelators on phytoavailability and toxicity of Pb in Zinnia elegans Jacq. J. Hazard. Mater., 146(1–2):341–346. [doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006. 12.028]
Dakora, F.D., Phillips, D.A., 2002. Root exudates as mediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant Soil, 245(1):35–47. [doi:10.1023/A:102080940 0075]
do Nascimento, C.W.A., Amarasiriwardena, D., Xing, B.S., 2006. Comparison of natural organic acids and synthetic chelates at enhancing phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut., 140(1): 114–123. [doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.06.017]
Duarte, B., Delgado, M., Cacador, I., 2007. The role of citric acid in cadmium and nickel uptake and translocation, in Halimione portulacoides. Chemosphere, 69(5):836–840. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.05.007]
Durrett, T.P., Gassmann, W., Rogers, E.E., 2007. The FRD3-mediated efflux of citrate into the root vasculature is necessary for efficient iron translocation. Plant Physiol., 144(1):197–205. [doi:10.1104/pp.107.097162]
Ebbs, S.D., Lasat, M.M., Brady, D.J., Cornish, J., Gordon, R., Kochian, L.V., 1997. Phytoextraction of cadmium and zinc from a contaminated soil. J. Environ. Qual., 26(5):1424–1430. [doi:10.2134/jeq1997.00472425002600050032x]
Han, F., Shan, X.Q., Zhang, S.Z., Wen, B., Owens, G., 2006. Enhanced cadmium accumulation in maize roots-the impact of organic acids. Plant Soil, 289(1-2):355–368. [doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9145-9]
Hanikenne, M., Talke, I.N., Haydon, M.J., Lanz, C., Nolte, A., Motte, P., Kroymann, J., Weigel, D., Kramer, U., 2008. Evolution of metal hyperaccumulation required cis-regulatory changes and triplication of HMA4. Nature, 453(7193):391–395. [doi:10.1038/nature06877]
Huang, H.G., Li, T.X., Tian, S.K., Gupta, D.K., Zhang, X.Z., Yang, X.E., 2008. Role of EDTA in alleviating lead toxicity in accumulator species of Sedum alfredii H. Biores. Technol., 99(14):6088–6096. [doi:10.1016/j. biortech.2007.12.056]
Jean, L., Bordas, F., Gautier-Moussard, C., Vernay, P., Hitmi, A., Bollinger, J.C., 2008. Effect of citric acid and EDTA on chromium and nickel uptake and translocation by Datura innoxia. Environ. Pollut., 153(3): 555–563. [doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.09.013]
Jones, D.L., Edwards, A.C., Donachie, K., Darrah, P.R., 1994. Role of Proteinaceous Amino-Acids Released in Root Exudates in Nutrient Acquisition from the Rhizosphere. Plant Soil, 158(2):183–192. [doi:10.1007/BF00009493]
Kramer, U., Pickering, I.J., Prince, R.C., Raskin, I., Salt, D.E., 2000. Subcellular localization and speciation of nickel in hyperaccumulator and non-accumulator Thlaspi species. Plant Physiol., 122(4):1343–1354. [doi:10.1104/pp.122. 4.1343]
Kupper, H., Mijovilovich, A., Meyer-Klaucke, W., Kroneck, P.M.H., 2004. Tissue- and age-dependent differences in the complexation of cadmium and zinc in the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges ecotype) revealed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Plant Physiol., 134(2):748–757. [doi:10. 1104/pp.103.032953]
Li, W.C., Ye, Z.H., Wong, M.H., 2007. Effects of bacteria an enhanced metal uptake of the Cd/Zn-hyperaccumulating plant, Sedum alfredii. J. Exp. Bot., 58(15–16):4173–4182. [doi:10.1093/jxb/erm274]
Lopez-Bucio, J., Nieto-Jacobo, M.F., Ramirez-Rodriguez, V., Herrera-Estrella, L., 2000. Organic acid metabolism in plants: from adaptive physiology to transgenic varieties for cultivation in extreme soils. Plant Sci., 160(1):1–13. [doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00347-2]
Lu, L.L., Tian, S.K., Yang, X.E., Wang, X.C., Brown, P., Li, T.Q., He, Z.L., 2008. Enhanced root-to-shoot translocation of cadmium in the hyperaccumulating ecotype of Sedum alfredii. J. Exp. Bot., 59(11): 3203–3213. [doi:10.1093/jxb/ern174]
Lu, L.L., Tian, S.K., Yang, X.E., Li, T.Q., He, Z.L., 2009. Cadmium uptake and xylem loading are active processes in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J. Plant Physiol., 166(6):579–587. [doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2008.09.001]
Ma, J.F., Hiradate, S., 2000. Form of aluminium for uptake and translocation in buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). Planta, 211(3):355–360. [doi:10.1007/s004 250000292]
Ma, J.F., Ryan, P.R., Delhaize, E., 2001. Aluminium tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids. Trends Plant Sci., 6(6):273–278. [doi:10.1016/S1360-1385 (01)01961-6]
Nigam, R., Srivastava, S., Prakash, S., Srivastava, M.M., 2000. Effect of organic acids on the availability of cadmium in wheat. Chem. Spec. Bioavailab., 12(4):125–132. [doi:10. 3184/095422900782775481]
Pence, N.S., Larsen, P.B., Ebbs, S.D., Letham, D.L.D., Lasat, M.M., Garvin, D.F., Eide, D., Kochian, L.V., 2000. The molecular physiology of heavy metal transport in the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. PNAS, 97(9):4956–4960. [doi:10.1073/pnas.97.9.4956]
Quartacci, M.F., Baker, A.J.M., Navari-Izzo, F., 2005. Nitrilotriacetate- and citric acid-assisted phytoextraction of cadmium by Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czernj, Brassicaceae). Chemosphere, 59(9):1249–1255. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.053]
Romkens, P., Bouwman, L., Japenga, J., Draaisma, C., 2002. Potentials and drawbacks of chelate-enhanced phytoremediation of soils. Environ. Pollut., 116(1): 109–121. [doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00150-6]
Sarret, G., Balesdent, J., Bouziri, L., Garnier, J.M., Marcus, M.A., Geoffroy, N., Panfili, F., Manceau, A., 2004. Zn speciation in the organic horizon of a contaminated soil by micro-x-ray fluorescence, micro- and powder-EXAFS spectroscopy, and isotopic dilution. Environ. Sci. Technol., 38(10):2792–2801. [doi:10.1021/es035171t]
Senden, M.H.M.N., Vandermeer, A.J.G.M., Verburg, T.G., Wolterbeek, H.T., 1995. Citric-acid in tomato plant-roots and its effect on cadmium uptake and distribution. Plant Soil, 171(2):333–339. [doi:10.1007/BF00010289]
Sun, R.L., Zhou, Q.X., Jin, C.X., 2006. Cadmium accumulation in relation to organic acids in leaves of Solanum nigrum L. as a newly found cadmium hyperaccumulator. Plant Soil, 285(1–2):125–134. [doi:10.1007/s11104-006-0064-6]
Sun, Y.B., Zhou, Q.X., Diao, C.Y., 2008. Effects of cadmium and arsenic on growth and metal accumulation of Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Biores. Technol., 99(5):1103–1110. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007. 02.035]
Sun, Y.B., Zhou, Q.X., An, J., Liu, W.T., Liu, R., 2009. Chelator-enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil irrigated by industrial wastewater with the hyperaccumulator plant (Sedum alfredii Hance). Geoderma, 150(1–2):106–112. [doi:10.1016/j.geoderma. 2009.01.016]
Tian, S.K., Lu, L.L., Yang, X.E., Labavitch, J.M., Huang, Y.Y., Brown, P., 2009. Stem and leaf sequestration of zinc at the cellular level in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. New Phytol., 182(1):116–126. [doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137. 2008.02740.x]
Tian, S.K., Lu, L.L., Labavitch, J., Yang, X.E., He, Z.L., Hu, H.N., Sarangi, R., Newville, M., Commisso, J., Brown, P., 2011. Cellular sequestration of cadmium in the hyperaccumulator plant species Sedum alfredii. Plant Physiol., 157(4):1914–1925. [doi:10.1104/pp.111.183947]
Turgut, C., Pepe, M.K., Cutright, T.J., 2004. The effect of EDTA and citric acid on phytoremediation of Cd, Cr, and Ni from soil using Helianthus annuus. Environ. Pollut., 131(1):147–154. [doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.01.017]
Yang, X., Li, T.Q., Yang, J.C., He, Z.L., Lu, L.L., Meng, F.H., 2006. Zinc compartmentation in root, transport into xylem, and absorption into leaf cells in the hyperaccumulating species of Sedum alfredii Hance. Planta, 224(1):185–195. [doi:10.1007/s00425-005-0194-8]
Yang, X.E., Long, X.X., Ye, H.B., He, Z.L., Calvert, D.V., Stoffella, P.J., 2004. Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant Soil, 259(1–2):181–189. [doi:10.1023/B:PLSO.0000020956.24027.f2]
Ye, H.B., Yang, X.E., He, B., Long, X.X., Shi, W.Y., 2003. Growth response and metal accumulation of Sedum alfredii to Cd/Zn complex-polluted ion levels. Acta Bot. Sin., 45(9):1030–1036.
Zhao, F.J., Jiang, R.F., Dunham, S.J., McGrath, S.P., 2006. Cadmium uptake, translocation and tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. New Phytol., 172(4):646–654. [doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01867.x]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31000935), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2012FZA6008), and the Department of Science & Technology of Zhejiang Province (No. 2011C22077), China
Electronic supplementary materials: The online version of this article (doi:10.1631/jzus.B1200211) contains supplementary materials, which are available to authorized users
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Ll., Tian, Sk., Yang, Xe. et al. Improved cadmium uptake and accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii: the impact of citric acid and tartaric acid. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 14, 106–114 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200211
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200211