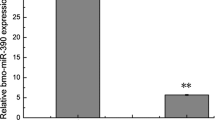
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small endogenous RNAs molecules, approximately 21–23 nucleotides in length, which regulate gene expression by base-pairing with 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of target mRNAs. However, the functions of only a few miRNAs in organisms are known. Recently, the expression vector of artificial miRNA has become a promising tool for gene function studies. Here, a method for easy and rapid construction of eukaryotic miRNA expression vector was described. The cytoplasmic actin 3 (A3) promoter and flanked sequences of miRNA-9a (miR-9a) precursor were amplified from genomic DNA of the silkworm (Bombyx mori) and was inserted into pCDNA3.0 vector to construct a recombinant plasmid. The enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene was used as reporter gene. The Bombyx mori N (BmN) cells were transfected with recombinant miR-9a expression plasmid and were harvested 48 h post transfection. Total RNAs of BmN cells transfected with recombinant vectors were extracted and the expression of miR-9a was evaluated by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Northern blot. Tests showed that the recombinant miR-9a vector was successfully constructed and the expression of miR-9a with EGFP was detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros, V., 2003. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell, 113(6): 673–676. [doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00428-8]
Bartel, D.P., 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell, 116(2):281–297. [doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5]
Bartel, D.P., 2009. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell, 136(2):215–233. [doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002]
Bejarano, F., Smibert, P., Lai, E.C., 2009. miR-9a prevents apoptosis during wing development by repressing Drosophila LIM-only. Dev. Biol., 338(1):63–73. [doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.11.025]
Biryukova, I., Asmar, J., Abdesselem, H., Heitzler, P., 2009. Drosophila mir-9a regulates wing development via fine-tuning expression of the LIM only factor, dLMO. Dev. Biol., 327(2):487–496. [doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.12.036]
Bushati, N., Cohen, S.M., 2007. microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 23(1):175–205. [doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123406]
Cai, X., Hagedorn, C.H., Cullen, B.R., 2004. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA, 10(12): 1957–1966. [doi:10.1261/rna.7135204]
Cai, Y., Yu, X., Zhou, Q., Yu, C., Hu, H., Liu, J., Lin, H., Yang, J., Zhang, B., Cui, P., et al., 2010. Novel microRNAs in silkworm (Bombyx mori). Funct. Integr. Genomics, 10(3):405–415. [doi:10.1007/s10142-010-0162-7]
Cao, J., Tong, C., Wu, X., Lv, J., Yang, Z., Jin, Y., 2008. Identification of conserved microRNAs in Bombyx mori (silkworm) and regulation of fibroin L chain production by microRNAs in heterologous system. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 38(12):1066–1071. [doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.09.008]
Chang, K., Elledge, S.J., Hannon, G.J., 2006. Lessons from Nature: microRNA-based shRNA libraries. Nat. Methods, 3(9):707–714. [doi:10.1038/nmeth923]
Chen, C., Ridzon, D.A., Broomer, A.J., Zhou, Z., Lee, D.H., Nguyen, J.T., Barbisin, M., Xu, N.L., Mahuvakar, V.R., Andersen, M.R., et al., 2005. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic. Acids Res., 33(20):e179. [doi:10.1093/nar/gni178]
Chen, C.Z., Li, L., Lodish, H.F., Bartel, D.P., 2004. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science, 303(5654):83–86. [doi:10.1126/science.1091903]
Du, G., Yonekubo, J., Zeng, Y., Osisami, M., Frohman, M.A., 2006. Design of expression vectors for RNA interference based on miRNAs and RNA splicing. FEBS J., 273(23): 5421–5427. [doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05534.x]
Feng, J., Wang, K., Liu, X., Chen, S., Chen, J., 2009. The quantification of tomato microRNAs response to viral infection by stem-loop real-time RT-PCR. Gene, 437(1–2): 14–21. [doi:10.1016/j.gene.2009.01.017]
Filipowicz, W., Bhattacharyya, S.N., Sonenberg, N., 2008. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet., 9:102–114. [doi:10.1038/nrg2290]
Friedman, R.C., Farh, K.K., Burge, C.B., Bartel, D.P., 2009. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res., 19(1):92–105. [doi:10.1101/gr.082701.108]
Fukuda, Y., Kawasaki, H., Taira, K., 2006. Construction of microRNA-containing vectors for expression in mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol., 338:167–173. [doi:10.1385/1-59745-097-9:167]
Gou, D., Zhang, H., Baviskar, P.S., Liu, L., 2007. Primer extension-based method for the generation of a siRNA/miRNA expression vector. Physiol. Genomics, 31(3): 554–562. [doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00005.2007]
Han, J., Lee, Y., Yeom, K.H., Nam, J.W., Heo, I., Rhee, J.K., Sohn, S.Y., Cho, Y., Zhang, B.T., Kim, V.N., 2006. Molecular basis for the recognition of primary microRNAs by the Drosha-DGCR8 complex. Cell, 125(5):887–901. [doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.043]
He, P.A., Nie, Z., Chen, J., Lv, Z., Sheng, Q., Zhou, S., Gao, X., Kong, L., Wu, X., Jin, Y., et al., 2008. Identification and characteristics of microRNAs from Bombyx mori. BMC Genomics, 9(1):248. [doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-248]
Hong, X., Hammell, M., Ambros, V., Cohen, S.M., 2009. Immunopurification of Ago1 miRNPs selects for a distinct class of microRNA targets. PNAS, 106(35):15085–15090. [doi:10.1073/pnas.0908149106]
Hu, T., Fu, Q., Chen, P., Ma, L., Sin, O., Guo, D., 2009. Construction of an artificial microRNA expression vector for simultaneous inhibition of multiple genes in mammalian cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 10(5):2158–2168. [doi:10.3390/ijms10052158]
Hu, T., Chen, P., Fu, Q., Liu, Y., Ishaq, M., Li, J., Ma, L., Guo, D., 2010. Comparative studies of various artificial microRNA expression vectors for RNAi in mammalian cells. Mol. Biotechnol., 46(1):34–40. [doi:10.1007/s12033-010-9264-7]
Huang, Y., Zou, Q., Tang, S.M., Wang, L.G., Shen, X.J., 2009. Computational identification and characteristics of novel microRNAs from the silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Mol. Biol. Rep., 37(7):3171–3176. [doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9897-4]
Jagadeeswaran, G., Zheng, Y., Sumathipala, N., Jiang, H., Arrese, E.L., Soulages, J.L., Zhang, W., Sunkar, R., 2010. Deep sequencing of small RNA libraries reveals dynamic regulation of conserved and novel microRNAs and microRNA-stars during silkworm development. BMC Genomics, 11(1):52. [doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-52]
Li, Y., Wang, F., Lee, J.A., Gao, F.B., 2006. MicroRNA-9a ensures the precise specification of sensory organ precursors in Drosophila. Genes. Dev., 20(20):2793–2805. [doi:10.1101/gad.1466306]
Liu, J., 2008. Control of protein synthesis and mRNA degradation by microRNAs. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 20(2): 214–221. [doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2008.01.006]
Liu, S., Zhang, L., Li, Q., Zhao, P., Duan, J., Cheng, D., Xiang, Z., Xia, Q., 2009. MicroRNA expression profiling during the life cycle of the silkworm (Bombyx mori). BMC Genomics, 10(1):455. [doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-455]
Liu, S., Li, D., Li, Q., Zhao, P., Xiang, Z., Xia, Q., 2010. MicroRNAs of Bombyx mori identified by Solexa sequencing. BMC Genomics, 11(1):148. [doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-148]
Molnar, A., Bassett, A., Thuenemann, E., Schwach, F., Karkare, S., Ossowski, S., Weigel, D., Baulcombe, D., 2009. Highly specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J., 58(1):165–174. [doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03767.x]
Niu, Q.W., Lin, S.S., Reyes, J.L., Chen, K.C., Wu, H.W., Yeh, S.D., Chua, N.H., 2006. Expression of artificial microRNAs in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana confers virus resistance. Nat. Biotechnol., 24(11):1420–1428. [doi:10.1038/nbt1255]
Parizotto, E.A., Dunoyer, P., Rahm, N., Himber, C., Voinnet, O., 2004. In vivo investigation of the transcription, processing, endonucleolytic activity, and functional relevance of the spatial distribution of a plant miRNA. Genes Dev., 18(18):2237–2242. [doi:10.1101/gad.307804]
Park, W., Zhai, J., Lee, J.Y., 2009. Highly efficient gene silencing using perfect complementary artificial miRNA targeting AP1 or heteromeric artificial miRNA targeting AP1 and CAL genes. Plant Cell Rep., 28(3):469–480. [doi:10.1007/s00299-008-0651-5]
Pillai, R.S., Bhattacharyya, S.N., Filipowicz, W., 2007. Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol., 17(3):118–126. [doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2006.12.007]
Qiu, L., Wang, H., Xia, X., Zhou, H., Xu, Z., 2008. A construct with fluorescent indicators for conditional expression of miRNA. BMC Biotechnol., 8(1):77. [doi:10.1186/1472-6750-8-77]
Ritchie, W., Legendre, M., Gautheret, D., 2007. RNA stemloops: to be or not to be cleaved by RNAse III. RNA, 13(4):457–462. [doi:10.1261/rna.366507]
Rumi, M., Ishihara, S., Aziz, M., Kazumori, H., Ishimura, N., Yuki, T., Kadota, C., Kadowaki, Y., Kinoshita, Y., 2006. RNA polymerase II mediated transcription from the polymerase III promoters in short hairpin RNA expression vector. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 339(2): 540–547. [doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.037]
Sakurai, H., Izumi, S., Tomino, S., 1990. In vitro transcription of the plasma protein genes of Bombyx mori. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1087(1):18–24. [doi:10.1016/0167-4781(90)90115-I]
Scherr, M., Eder, M., 2007. Gene silencing by small regulatory RNAs in mammalian cells. Cell Cycle, 6(4):444–449. [doi:10.4161/cc.6.4.3807]
Schmollinger, S., Strenkert, D., Schroda, M., 2010. An inducible artificial microRNA system for Chlamydomonas reinhardtii confirms a key role for heat shock factor 1 in regulating thermotolerance. Curr. Genet., 56(4): 383–389. [doi:10.1007/s00294-010-0304-4]
Shan, Z., Lin, Q., Deng, C., Li, X., Huang, W., Tan, H., Fu, Y., Yang, M., Yu, X., 2009. An efficient method to enhance gene silencing by using precursor microRNA designed small hairpin RNAs. Mol. Biol. Rep., 36(6):1483–1489. [doi:10.1007/s11033-008-9339-8]
Shan, Z., Lin, Q., Deng, C., Zhou, Z., Tan, H., Fu, Y., Li, X., Zhu, J., Mai, L., Kuang, S., et al., 2010. Comparison of approaches for efficient gene silencing induced by microRNA-based short hairpin RNA and indicator gene expression. Mol. Biol. Rep., 37(4):1831–1839. [doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9618-z]
Shibata, A., Iwaki, A., Fukumaki, Y., 2007. A novel expression system for artificial miRNAs containing no endogenous miRNA precursor sequences. J. RNAi Gene Silencing, 3(1):237–247.
Silva, J.M., Li, M.Z., Chang, K., Ge, W., Golding, M.C., Rickles, R.J., Siolas, D., Hu, G., Paddison, P.J., Schlabach, M.R., et al., 2005. Second-generation shRNA libraries covering the mouse and human genomes. Nat. Genet., 37:1281–1288. [doi:10.1038/ng1650]
Stefani, G., Slack, F.J., 2008. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 9(3): 219–230. [doi:10.1038/nrm2347]
Sun, D., Melegari, M., Sridhar, S., Rogler, C.E., Zhu, L., 2006. Multi-miRNA hairpin method that improves gene knockdown efficiency and provides linked multi-gene knockdown. Biotechniques, 41(1):59–63. [doi:10.2144/000112203]
Sun, H., Li, Q.W., Lv, X.Y., Ai, J.Z., Yang, Q.T., Duan, J.J., Bian, G.H., Xiao, Y., Wang, Y.D., Zhang, Z., et al., 2010. MicroRNA-17 post-transcriptionally regulates polycystic kidney disease-2 gene and promotes cell proliferation. Mol. Biol. Rep., 37(6):2951–2958. [doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9861-3]
Tang, G., Tang, X., Mendu, V., Jia, X., Chen, Q.J., He, L., 2008. The art of microRNA: various strategies leading to gene silencing via an ancient pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1779(11):655–662. [doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.06.006]
Tong, C.Z., Jin, Y.F., Zhang, Y.Z., 2006. Computational prediction of microRNA genes in silkworm genome. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B, 7(10):806–816. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2006.B0806]
Trujillo, R.D., Yue, S.B., Tang, Y., O’Gorman, W.E., Chen, C.Z., 2010. The potential functions of primary microRNAs in target recognition and repression. EMBO J., 29(19):3272–3285. [doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.208]
Vaucheret, H., Vazquez, F., Crete, P., Bartel, D.P., 2004. The action of ARGONAUTE1 in the miRNA pathway and its regulation by the miRNA pathway are crucial for plant development. Genes Dev., 18(10):1187–1197. [doi:10.1101/gad.1201404]
Xu, J., Zeng, J.Q., Wan, G., Hu, G.B., Yan, H., Ma, L.X., 2009. Construction of siRNA/miRNA expression vectors based on a one-step PCR process. BMC Biotechnol., 9(1):53. [doi:10.1186/1472-6750-9-53]
Yu, X., Zhou, Q., Li, S.C., Luo, Q., Cai, Y., Lin, W.C., Chen, H., Yang, Y., Hu, S., Yu, J., 2008. The silkworm (Bombyx mori) microRNAs and their expressions in multiple developmental stages. PLoS One, 3(8):e2997. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002997]
Yu, X., Zhou, Q., Cai, Y., Luo, Q., Lin, H., Hu, S., Yu, J., 2009. A discovery of novel microRNAs in the silkworm (Bombyx mori) genome. Genomics, 94(6):438–444. [doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2009.08.007]
Zeng, Y., Cullen, B.R., 2005. Efficient processing of primary microRNA hairpins by Drosha requires flanking nonstructured RNA sequences. J. Biol. Chem., 280(30): 27595–27603. [doi:10.1074/jbc.M504714200]
Zeng, Y., Wagner, E.J., Cullen, B.R., 2002. Both natural and designed microRNAs can inhibit the expression of cognate mRNAs when expressed in human cells. Mol. Cell, 9(6):1327–1333. [doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00541-5]
Zhang, Y., Zhou, X., Ge, X., Jiang, J., Li, M., Jia, S., Yang, X., Kan, Y., Miao, X., Zhao, G., et al., 2009. Insect-specific microRNA involved in the development of the silkworm Bombyx mori. PLoS One, 4(3):e4677. [doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004677]
Zhou, H., Xia, X.G., Xu, Z., 2005. An RNA polymerase II construct synthesizes short-hairpin RNA with a quantitative indicator and mediates highly efficient RNAi. Nucleic Acids Res., 33(6):e62. [doi:10.1093/nar/gni061]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. 2005CB121004), the National High-Tech R & D Program (863) of China (No. 2006AA10A119), the Innovation Foundation for Graduate Students of Jiangsu Province, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61001013)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Zou, Q., Wang, Sp. et al. Construction and detection of expression vectors of microRNA-9a in BmN cells. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 527–533 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000296
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000296