Abstract
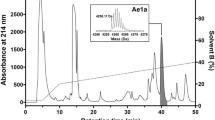
Selenocosmia huwena and Selenocosmia hainana are two tarantula species found in southern China. Their venoms contain abundant peptide toxins. Two new neurotoxic peptides, huwentoxin-III (HWTX-III) and hainantoxin-VI (HNTX-VI), were obtained from the venom using ion-exchange chromatography and reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). The mechanism of action of HWTX-III and HNTX-VI on insect neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) was studied via whole-cell patch clamp techniques. In a fashion similar to δ-atracotoxins, HNTX-VI can induce a slowdown of current inactivation of the VGSC and reduction in the peak of Na+ current in cockroach dorsal unpaired median (DUM) neurons. Meanwhile, 10 μmol/L HNTX-IV caused a positive shift of steady-state inactivation of sodium channel. HWTX-III inhibited VGSCs on DUM neurons (concentration of toxin at half-maximal inhibition (IC50)≈1.106 μmol/L) in a way much similar to tetrodotoxin (TTX). HWTX-III had no effect on the kinetics of activation and inactivation. The shift in the steady-state inactivation curve was distinct from other depressant spider toxins. The diverse effect and the mechanism of action of the two insect toxins illustrate the diverse biological activities of spider toxins and provide a fresh theoretical foundation to design and develop novel insecticides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alami, M., Vacher, H., Bosmans, F., Devaux, C., Rosso, J.P., Bougis, P.E., Tytgatt, J., Darbon, H., Martin-Eauclaire, M.F., 2003. Characterization of Amm VIII from Androctonus mauretanicus mauretanicus: a new scorpion toxin that discriminates between neuronal and skeletal sodium channels. Biochemical Journal, 375(3):551–560. [doi:10.1042/BJ20030688]
Catterall, W.A., 2000. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron, 26(1):13–25. [doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81133-2]
de Lima, M.E., Stankiewicz, M., Hamon, A., Figueiredo, S.G., Cordeiro, M.N., Diniz, C.R., Martin-Eauclaire, M.F., Pelhate, M., 2002. The toxin Tx4 (6-1) from the spider Phoneutria nigriventer slows down Na+ current inactivation in insect CNS via binding to receptor site 3. Journal of Insect Physiology, 48(1):53–61. [doi:10.1016/S0022-1910(01)00143-3]
Goldin, A.L., Barchi, R.L., Caldwell, J.H., Hofmann, F., Howe, J.R., Hunter, J.C., Kallen, R.G., Mandel, G., Meisler, M.H., Netter, Y.B., et al., 2000. Nomenclature of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron, 28(2):365–368. [doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00116-1]
Grolleau, F., Stankiewicz, M., Birinyi-Strachan, L.C., Wang, X.H., Nicholson, G.M., Pelhate, M., Lapied, B., 2001. Electrophysiological analysis of the neurotoxic action of a funnel-web spider toxin, δ-atracotoxin-HV1a on insect voltage-gated Na+ channels. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 204(4):711–721.
Haigeny, M.C., Lakatta, E.G., Stern, M.D., Silverman, H.S., 1994. Sodium channel blockade reduces hypoxic sodium loading and sodium-dependent calcium loading. Circulation, 90(1):391–399.
Huang, R.H., Liu, Z.H., Liang, S.P., 2003. Purification and characterization of a neurotoxic peptide huwentoxin-III and a natural inactive mutant from the venom of the spider Selenocosmia huwena Wang (Ornithoctonus huwena Wang). Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, 35(11): 976–980.
Li, D., Xiao, Y., Hu, W., Xie, J., Bosmans, F., Tytgat, J., Liang, S., 2003. Function and solution structure of hainantoxin-I, a novel insect sodium channel inhibitor from the Chinese bird spider Selenocosmia hainana. FEBS Letters, 555(3): 616–622. [doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01303-6]
Li, D.L., Xiao, Y.C., Xu, X., Xiong, X., Lu, S.Y., Liu, Z.H., Zhu, Q., Wang, M.C., Gu, X.C., Liang, S.P., 2004. Structure-activity relationships of hainantoxin-IV and structure determination of active and inactive sodium channel blockers. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(36): 37734–37740. [doi:10.1074/jbc.M405765200]
Meng, Z.Q., Nie, A.F., 2005. Enhancement of sodium metabisulfite on sodium currents in acutely isolated rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 20(1):35–41. [doi:10.1016/j.etap.2004.10.003]
Nicholson, G.M., 2007. Insect-selective spider toxins targeting voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxicon, 49(4):490–512. [doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.11.027]
Nicholson, G.M., Walsh, R., Little, M.J., Tyler, M.I., 1998. Characterisation of the effects of robustoxin, the lethal neurotoxin from the Sydney funnel-web spider Atrax robustus, on sodium channel activation and inactivation. Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology, 436(1): 117–126. [doi:10.1007/s004240050612]
Pan, J.Y., Hu, W.J., Liang, S.P., 2002. Purification, sequencing and characterization of hainantoxin-VI, a neurotoxin from the Chinese bird spider Selenocosmia hainana. Zoological Research, 23(4):280–283 (in Chinese).
Richard Benzinger, G., Tonkovich, G.S., Hanck, D.A., 1999. Augmentation of recovery from inactivation by site-3 Na channel toxins. A single-channel and whole-cell study of sustained currents. The Journal of General Physiology, 113(2):333–346. [doi:10.1085/jgp.113.2.333]
Rogers, J.C., Qu, Y., Tanada, T.N., Scheuer, T., Catterall, W.A., 1996. Molecular determinants of high affinity binding of alpha-scorpion toxin and sea anemone toxin in the S3–S4 extracellular loop in domain IV of the Na+ channel alpha subunit. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(27):15950–15962. [doi:10.1074/jbc.271.27.15950]
Shon, K.J., Olivera, B.M., Watkins, M., Jacobsen, R.B., Gray, W.R., Floresca, C.Z., Cruz, L.J., Hillyard, D.R., Brink, A., Terlau, H., et al., 1998. μ-Conotoxin PIIIA, a new peptide for discriminating among tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na channel subtypes. The Journal of Neuroscience, 18(12): 4473–4481.
Shu, Q., Liang, S.P., 1999. Purification and characterization of huwentoxin-II, a neurotoxic peptide from the venom of the Chinese bird spider Selenocosmia huwena. Journal of Peptide Research, 53(5):486–491. [doi:10.1034/j.1399-3011.1999.00039.x]
Szeto, T.H., Birinyi-Strachan, L.C., Smith, R.W., Connor, M., Christie, M.J., King, G., Nicholson, G.M., 2000. Isolation and pharmacological characterisation of δ-atracotoxin-Hv1b, a vertebrate-selective sodium channel toxin. FEBS Letters, 470(3):293–299. [doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01339-9]
Taylor, C.P., Meldrum, B., 1995. Na+ channels as targets for neuroprotective drugs. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 16(9):309–316. [doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)89060-4]
Wang, M.C., Guan, X., Liang, S.P., 2007. The cross channel activities of spider neurotoxin huwentoxin-I on rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 357(3):579–583. [doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.168]
Warmke, J.W., Reenan, R.A., Wang, P., Qian, S., Arena, J.P., Wang, J., Wunderler, D., Liu, K., Kaczorowski, G.J., van der Ploeg, L.H., et al., 1997. Functional expression of Drosophila para sodium channels. Modulation by the membrane protein TipE and toxin pharmacology. The Journal of General Physiology, 110(2):119–133. [doi:10.1085/jgp.110.2.119]
Xiao, Y.C., Liang, S.P., 2003a. Purification and characterization of hainantoxin-V, a tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channel inhibitor from the venom of the spider Selenocosmia hainana. Toxicon, 41(6):643–650. [doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(02)00280-5]
Xiao, Y.C., Liang, S.P., 2003b. Inhibition of neuronal tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na+ channels by two spider toxins: hainantoxin-III and hainantoxin-IV. European Journal of Pharmacology, 477(1):1–7. [doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(03)02190-3]
Yu, F.H., Westenbroek, R.E., Silos-Santiago, I., McCormick, K.A., Lawson, D., Ge, P., Ferriera, H., Lilly, J., DiStefano, P.S., Catterall, W.A., et al., 2003. Sodium channel β4, a new disulfide-linked auxiliary subunit with similarity to β2. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23(20):7577–7585.
Zlotkin, E., 1999. The insect voltage-gated sodium channel as target of insecticides. Annual Review of Entomology, 44(1):429–455. [doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.44.1.429]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30500146) and the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. 2006CB708508)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Rl., Yi, S. & Liang, Sp. Mechanism of action of two insect toxins huwentoxin-III and hainantoxin-VI on voltage-gated sodium channels. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 11, 451–457 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0900393
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0900393