Abstract
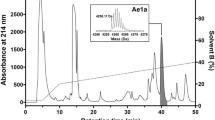
Spiders are the most successful insect predators given that they use their venom containing insecticidal peptides as biochemical weapons for preying. Due to the high specificity and potency of peptidic toxins, discoveries of insecticidal toxins from spider venom have provided an opportunity to obtain natural compounds for agricultural applications without affecting human health. In this study, a novel insecticidal toxin (μ-NPTX-Nc1a) was identified and characterized from the venom of Nephila clavata. Its primary sequence is GCNPDCTGIQCGWPRCPGGQNPVMDKCVSCCPFCPPKSAQG which was determined by automated Edman degradation, cDNA cloning, and MS/MS analysis. BLAST search indicated that Nc1a shows no similarity with known peptides or proteins, indicating that Nc1a belongs to a novel family of insecticidal peptide. Nc1a displayed inhibitory effects on NaV and KV channels in cockroach dorsal unpaired median neurons. The median lethal dose (LD50) of Nc1a on cockroach was 573 ng/g. Herein, a study that identifies a novel insecticidal toxin, which can be a potential candidate and/or template for the development of bioinsecticides, is presented.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barslund AF, Poulsen MH, Bach TB, Lucas S, Kristensen AS, Stromgaard K (2011) Solid-phase synthesis and biological evaluation of joro spider toxin-4 from Nephila clavata. J Nat Prod 74:483–486
Bass C, Field LM (2011) Gene amplification and insecticide resistance. Pest Manag Sci 67:886–890
Bende NS, Dziemborowicz S, Mobli M, Herzig V, Gilchrist J, Wagner J, Nicholson GM, King GF, Bosmans F (2014) A distinct sodium channel voltage-sensor locus determines insect selectivity of the spider toxin Dc1a. Nat Commun 11(5):4350
Bende NS, Dziemborowicz S, Herzig V, Ramanujam V, Brown GW, Bosmans F, Nicholson GM, King GF, Mobli M (2015) The insecticidal spider toxin sfi1 is a knottin peptide that blocks the pore of insect voltage-gated sodium channels via a large beta-hairpin loop. The FEBS J 282:904–920
Borges CR, Sherma ND (2014) Techniques for the analysis of cysteine sulfhydryls and oxidative protein folding. Antioxid Redox Signal 21(3):511–531
Clement H, Flores V, Diego-Garcia E, Corrales-Garcia L, Villegas E, Corzo GA (2015) Comparison between the recombinant expression and chemical synthesis of a short cysteine-rich insecticidal spider peptide. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis 21:19
Demkovich M, Siegel JP, Higbee BS, Berenbaum MR (2015) Mechanism of resistance acquisition and potential associated fitness costs in Amyelois transitella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) exposed to pyrethroid insecticides. Environ Entomol 44(3):855–863
Figueiredo SG, Garcia ME, Valentim AC, Cordeiro MN, Diniz CR, Richardson M (1995) Purification and amino acid sequence of the insecticidal neurotoxin Tx4(6–1) from the venom of the “armed” spider Phoneutria nigriventer (Keys). Toxicon 33:83–93
Gunning SJ, Maggio F, Windley MJ, Valenzuela SM, King GF, Nicholson GM (2008) The janus-faced atracotoxins are specific blockers of invertebrate k(ca) channels. FEBS J 275:4045–4059
Hakim MA, Jiang W, Luo L, Li B, Yang S, Song Y, Lai R (2015) Scorpion toxin, bmp01, induces pain by targeting trpv1 channel. Toxins 7:3671–3687
Herzig V, Ikonomopoulou M, Smith JJ, Dziemborowicz S, Gilchrist J, Kuhn-Nentwig L, Rezende FO, Moreira LA, Nicholson GM, Bosmans F, King GF (2016) Molecular basis of the remarkable species selectivity of an insecticidal sodium channel toxin from the African spider Augacephalus ezendami. Sci Rep 7(6):29538
Hisada M, Fujita T, Naoki H, Itagaki Y, Irie H, Miyashita M, Nakajima T (1998) Structures of spider toxins: hydroxyindole-3-acetylpolyamines and a new generalized structure of type-e compounds obtained from the venom of the joro spider, Nephila clavata. Toxicon 36:1115–1125
Højland DH, Nauen R, Foster SP, Williamson MS, Kristensen M (2015) Incidence, spread and mechanisms of pyrethroid resistance in european populations of the cabbage stem flea beetle, Psylliodes chrysocephala L. (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). PLoS One 10(12):e0146045
Jiang WB, Hakim M, Luo L, Li BW, Yang SL, Song YZ, Lai R, Lu QM (2015) Purification and characterization of cholecystokinin from the skin of salamander Tylototriton verrucosus. Dongwuxue Yanjiu 36:174–177
Jones CM, Haji KA, Khatib BO, Bagi J, Mcha J, Devine GJ, Daley M, Kabula B, Ali AS, Majambere S, Ranson H (2013) The dynamics of pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles arabiensis from Zanzibar and an assessment of the underlying genetic basis. Parasit Vectors 6(6):343
Joo HS, Park GC, Cho WR, Tak E, Paik SR, Chang CS (2002) Purification and characterization of a prothrombin-activating protease from Nephila clavata. Toxicon 40:289–296
King GF, Hardy MC (2013) Spider-venom peptides: structure, pharmacology, and potential for control of insect pests. Annu Rev Entomol 58:475–496
Liu J, Jiang J, Wu Z, Xie F (2012) Antimicrobial peptides from the skin of the Asian frog, Odorrana jingdongensis: de novo sequencing and analysis of tandem mass spectrometry data. J Proteom 75(18):5807–5821
Liu Z, Deng M, Xiang J, Ma H, Hu W, Zhao Y, Li DW, Liang S (2012b) A novel spider peptide toxin suppresses tumor growth through dual signaling pathways. Curr Mol Med 12:1350–1360
Liu WH, Chen Y, Bai XW, Yao HM, Zhang XG, Yan XW, Lai R (2016) Identification and characterization of a novel neuropeptide (neuropeptide Y-HS) from leech salivary gland of Haemadipsa sylvestris. Chin J Nat Med 14:677–682
Mourao CB, Heghinian MD, Barbosa EA, Mari F, Bloch CJ, Restano-Cassulini R, Possani LD, Schwartz EF (2013) Characterization of a novel peptide toxin from Acanthoscurria paulensis spider venom: a distinct cysteine assignment to the HWTX-II family. Biochemistry 52:2440–2452
Nicholson GM (2007a) Fighting the global pest problem: preface to the special toxicon issue on insecticidal toxins and their potential for insect pest control. Toxicon 49:413–422
Nicholson GM (2007b) Insect-selective spider toxins targeting voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxicon 49:490–512
Oliveira LC, Campos FV, Figueiredo SG, Cordeiro MN, Adaime BR, Richardson M, Pimenta AM, Martin-Eauclaire MF, Beirao PS, De Lima ME (2015) Beta/delta-prit1, a highly insecticidal toxin from the venom of the brazilian spider Phoneutria reidyi (f.O. Pickard-cambridge, 1897). Toxicon 104:73–82. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.07.010
Paiva AL, Matavel A, Peigneur S, Cordeiro MN, Tytgat J, Diniz MR, de Lima ME (2016) Differential effects of the recombinant toxin pntx4(5–5) from the spider Phoneutria nigriventer on mammalian and insect sodium channels. Biochimie 121:326–335
Schuhmacher LN, Srivats S, Smith ES (2015) Structural domains underlying the activation of acid-sensing ion channel 2a. Mol Pharmacol 87:561–571
Smith JJ, Herzig V, King GF, Alewood PF (2013) The insecticidal potential of venom peptides. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 70:3665–3693
Tedford HW, Fletcher JI, King GF (2001) Functional significance of the beta hairpin in the insecticidal neurotoxin omega-atracotoxin-Hv1a. J Biol Chem 276:26568–26576
Vassilevski AA, Sachkova MY, Ignatova AA, Kozlov SA, Feofanov AV, Grishin EV (2013) Spider toxins comprising disulfide-rich and linear amphipathic domains: a new class of molecules identified in the lynx spider Oxyopes takobius. FEBS J 280:6247–6261
Windley MJ, Herzig V, Dziemborowicz SA, Hardy MC, King GF, Nicholson GM (2012) Spider-venom peptides as bioinsecticides. Toxins 4:191–227
Yang S, Liu Z, Xiao Y, Li Y, Rong M, Liang S, Zhang Z, Yu H, King GF, Lai R (2012) Chemical punch packed in venoms makes centipedes excellent predators. Mol Cell Proteom MCP 11:640–650
Yang S, Xiao Y, Kang D, Liu J, Li Y, Undheim EA, Klint JK, Rong M, Lai R, King GF (2013) Discovery of a selective nav1.7 inhibitor from centipede venom with analgesic efficacy exceeding morphine in rodent pain models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:17534–17539
Zambrowicz A, Pokora M, Setner B, Dąbrowska A, Szołtysik M, Babij K, Szewczuk Z, Trziszka T, Lubec G, Chrzanowska J (2015) Multifunctional peptides derived from an egg yolk protein hydrolysate: isolation and characterization. Amino Acids 47:369–380
Zhang PF, Chen P, Hu WJ, Liang SP (2003) Huwentoxin-V, a novel insecticidal peptide toxin from the spider Selenocosmia huwena, and a natural mutant of the toxin: indicates the key amino acid residues related to the biological activity. Toxicon 42:15–20
Zhong Y, Song B, Mo G, Yuan M, Li H, Wang P, Yuan M, Lu Q (2014) A novel neurotoxin from venom of the spider, Brachypelma albopilosum. PloS One 9:e110221
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Zeng Lin for technical advice and assistance on MS/MS spectra analysis. This work was supported by funding from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2013CB911304), National Science Foundation of China (331372208 and U1302221), Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA12040209, QYZDJ-SSW-SMC012), Science and technology office of Jiangsu Province (BE2016742) and Yunnan Province (2015HA023) to R.L., National Science Foundation of China (31640071) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA12020334 and Youth Innovation Promotion Association) to S.Y., and National Science Foundation of China (31201717), Jiangsu Province (Q0201600440) to X.W.Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Handling Editor: J. S. Metcalf.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, L., Fang, M., Chen, M. et al. An insecticidal toxin from Nephila clavata spider venom. Amino Acids 49, 1237–1245 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2425-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2425-2