Abstract
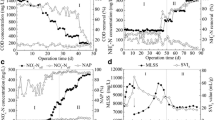
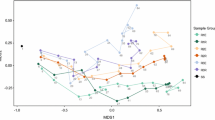
A sequencing batch reactor (SBR) seeded with activated sludge was established for landfill leachate treatment. Small bio-aggregates began to appear after 40-d operation, and gradually changed to mature aerobic granules, with a mean size of 0.36–0.60 mm. Their sludge volume index at 5 min (SVI5 min), mixed liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS), and wet density were around 35 ml/g, 3.4 g/L, and 1.062 g/cm3, respectively. The settling velocities of the granules in distilled water ranged from 0.3 to 1.3 cm/s, which were faster than those in landfill leachate with a salt content of 1.4% (w/v), and also slightly faster than those predicted by Stokes’ law for porous but impermeable particles. Microbial community evolution during the granulation process and stages under different nitrogen loading rates (NLRs) were monitored and analyzed by polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE), cloning, and sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) fragments. Results revealed that some primary and dominant communities in inoculating activated sludge died out gradually; while a few common bacteria, inhabiting soils, municipal wastewater, or activated sludge systems, dominated in the SBR system throughout. In addition, some other dominant species, associated with the aerobic granulation process, were thought to play a significant role in the formation and growth of aerobic granular sludge. During the stable operation time under low NLR, a few species were present in abundance, and may have been responsible for the high organic removal efficiency at this time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav, S.S., Chen, M.Y., Lee, D.J, Ren, N.Q., 2007. Degradation of phenol by Acinetobacter strain isolated from aerobic granules. Chemosphere, 67(8):1566–1572. [doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.11.067]
APHA, 1998. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th Edition. American Public Health Association, Washington DC, USA.
Bao, R.L., Yu, S.L., Zuo, X.T., Wang, J., 2009. Shut-cut nitrification characteristics of aerobic granule in a sequencing batch airlift reactor at low temperature. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 16(4):570–575.
Di Iaconi, C., Ramadori, R., Lopez, A., 2006. Combined biological and chemical degradation for treating a mature municipal landfill leachate. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 31(1):118–124. [doi:10.1016/j.bej.2006.06.002]
Ford, D.L., Churchwell, R.L., Kachtick, J.W., 1980. Comprehensive analysis of nitrification of chemical processing wastewaters. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 52(11):2726–2746.
Hirooka, K., Asano, R., Nakai, Y., 2009. Change in the community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge during selective incubation for MPN determination. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 36(5):679–685. [doi:10.1007/s10295-009-0537-8]
LaPara, T.M., Nakatsu, C.H., Pantea, L.M., Alleman, J.E., 2002. Stability of the bacterial communities supported by a severn-stage biological process treating pharmaceutical wastewater as revealed by PCR-DGGE. Water Research, 36(3):638–646. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00277-9]
Li, A.J., Yang, S.F., Li, X.Y., Gu, J.D., 2008. Microbial population dynamics during aerobic sludge granulation at different organic loading rates. Water Research, 42(13): 3552–3560. [doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.05.005]
Li, D.H., Ganczarczyk, J., 1989. Fractal geometry of particle aggregates generated in water and wastewater treatment processes. Environmental Science and Technology, 23(11):1385–1389. [doi:10.1021/es00069a009]
Li, J.T., Ji, S.L., Liu, Z.P., Qin, Z.P., Liu, Y., Yang, Y.Y., 2009. Bacteria composition of aerobic granular sludge analyzed with 16S rDNA clone library. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(10):1218–1223 (in Chinese).
Li, P., Wang, Y.X., Wang, Y.H., Liu, K., Tong, L., 2010. Bacterial community structure and diversity during establishment of an anaerobic bioreactor to treat swine wastewater. Water Science and Technology, 61(1):243–252. [doi:10.2166/wst.2010.807]
Li, X.Y., Yuan, Y., 2002. Settling velocities and permeabilities of microbial aggregates. Water Research, 36(12):3110–3120. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00541-3]
Li, X.Z., Zhao, Q.L., 1999. Inhibition of microbial activity of activated sludge by ammonia in leachate. Environment International, 25(8):961–968. [doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(99)00068-9]
Liu, X.C., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., Wang, Z.Y., Lv, W.Z., 2007. Analysis of bacterial community structures in two sewage treatment plants with different sludge properties and treatment performance by nested PCR-DGGE method. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(1):60–66. [doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60010-2]
Moreno, Y., Botella, S., Alonso, J.L., Ferrus, M.A., Hernandez, M., Hernandez, J., 2003. Specific detection of Arcobacter and Campylobacter strains in water and sewage by PCR and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(2):1181–1186. [doi:10.1128/AEM.69.2.1181-1186.2003]
Muyzer, G., Waal, E.C., Uitterlinden, A.G., 1993. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction amplified genes encoding for 16S rRNA. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59(3):695–700.
Ni, B.J., Yu, H.Q., 2010. Mathematical modeling of aerobic granular sludge: a review. Biotechnology Advance, 28(6): 895–909. [doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.08.004]
Osaka, T., Yoshie, S., Tsuneda, S., Hirata, A., Iwami, N., Inamori, Y., 2006. Identification of acetate- or methanol-assimilating bacteria under nitrate-reducing conditions by stable-isotope probing. Microbial Ecology, 52(8):253–266. [doi:10.1007/s00248-006-9071-7]
Parsley, L.C., Consuegra, E.J., Thomas, S.J., Bhavsar, J., Land, A.M., Bhuiyan, N.N., Mazher, M.A., Waters, R.J., Wommack, K.E., Harper, W.F.Jr., et al., 2010. Census of the viral metagenome within an activated sludge microbial assemblage. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(8):2673–2677. [doi:10.1128/AEM.02520-09]
Sanguinetti, C.J., Dias, N.E., Simpson, A.J., 1994. Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques, 17(5):914–921.
Su, K.Z., Yu, H.Q., 2005. Formation and characterization of aerobic granules in a sequencing batch reactor treating soybean-processing wastewater. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(8):2818–2828. [doi:10.1021/es048950y]
Tarlera, S., Jangid, K., Ivester, A.H., Whitman, W.B. Williams, M.A., 2008. Microbial community succession and bacterial diversity in soils during 77 000 years of ecosystem development. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 64(1):129–140. [doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00444.x]
Wang, J.F., 2006. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Removal of Aerobic Granules and Granules Membrane Bioreactor. PhD Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China (in Chinese).
Wang, S.G., Liu, X.W., Gong, W.X., Gao, B.Y., Zhang, D.H., Yu, H.Q., 2007. Aerobic granulation with brewery wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresource Technology, 98(11):2142–2147. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.08.018]
Xiao, F., Yang, S.F., Li, X.Y., 2008. Physical and hydrodynamic properties of aerobic granules produced in sequencing batch reactors. Separation and Purification Technology, 63(3):634–641. [doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2008.07.002]
Zhang, B., Sun, B.S., Ji, M., Zhao, Z.G., 2008. Analysis and succession of microbial community structure in a membrane bioreactor. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 28(11): 2192–2199 (in Chinese).
Zhang, B., Sun, B.S., Ji, M., Liu, H.N., Liu, X.H., 2010. Quantification and comparison of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in MBRs treating various types of wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 101(9):3054–3059. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.048]
Zhang, J.J., Li, X.Y., Oh, S.E., Logan, B.E., 2004. Physical and hydrodynamic properties of flocs produced during biological hydrogen production. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 88(7):854–860. [doi:10.1002/bit.20297]
Zhang, L.L., Chen, J.M., Fang, F., 2008. Biodegradation of methyl t-butyl ether by aerobic granules under a cosubstrate condition. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 78(3):543–550. [doi:10.1007/s00253-007-1321-1]
Zhuang, W.Q., Tay, J.H., Yi, S., Tay, S.T., 2005. Microbial adaptation to biodegradation of tert-butyl alcohol in a sequencing batch reactor. Journal of Biotechnology, 118(1):45–53. [doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.02.014]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Water Pollution Control and Management Project of China (No. 2009ZX07314-002), the Tianjin Science and Technology Development Program (No. 06YFGZSH06700), and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Tianjin Binhai New Area, China (No. 2010-Bk130067)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Yj., Ji, M., Li, Gy. et al. Microbial and hydrodynamic properties of aerobic granules in a sequencing batch reactor treating landfill leachate. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 13, 219–229 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1100153
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1100153
Key words
- Aerobic granules
- Microbial community
- Polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE)
- Landfill leachate