Abstract
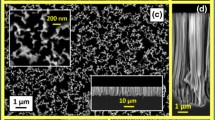
In the current studies a miniature silicon wafer fuel cell (FC) using L-ascorbic acid as fuel was developed. The cell employs L-ascorbic acid and air as reactants and a thin polymer electrolyte as a separator. Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) silicon etching was employed to fabricate high aspect-ratio columns on the silicon substrate to increase the surface area. A thin platinum layer deposited directly on the silicon surface by the sputtering was used as the catalyst layer for L-ascorbic acid electro-oxidation. Cyclic voltammetry shows that the oxidation of L-ascorbic acid on the sputtered platinum layer is irreversible and that the onset potentials for the oxidation of L-ascorbic acid are from 0.27 V to 0.35 V versus an Ag/AgCl reference electrode. It is found that at the room temperature, with 1 mol/L L-ascorbic acid/PBS (phosphate buffered solution) solution pumped to the anode at 1 ml/min flow rate and air spontaneously diffusing to the cathode as the oxidant, the maximum output power density of the cell was 1.95 mW/cm2 at a current density of 10 mA/cm2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan, S., Nguyen, N., Xia, Z., Wu, Z., 2005. Development of a polymeric micro fuel cell containing laser-micromachined flow channels. Journal Micromechanics Microengineering, 15(1):231–236. [doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/1/032]
Fujiwara, N., Yasuda, K., Ioroi, T., Siroma, Z., Miyazaki, Y., Kobayashi, T., 2003. Direct polymer electrolyte fuel cells using L-ascorbic acid as a fuel. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 6(12):A257–A259. [doi:10.1149/1.1621287]
Kelley, S.C., Deluga, G.A., Smyrl, W.H., 2002. Miniature fuel cells fabricated on silicon substrates. AIChE Journal, 48(5):1071–1082. [doi:10.1002/aic.690480516]
Lu, G.Q., Wang, C.Y., Yen, T.J., Zhang, X., 2004. Development and characterization of a silicon-based micro direct methanol fuel cell. Electrochimica Acta, 49(5):821–828. [doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2003.09.036]
Mano, N., Mao, F., Heller, A., 2004. A miniature membrane-less biofuel cell operating at +0.60 V under physiological conditions. Chembiochem, 5:1703–1705.
Ruiz, J.J., Aldaz, A., Dominguez, M., 1977. Mechanism of L-ascorbic acid oxidation and dehydro-L-ascorbic acid reduction on a mercury electrode. Canadian Journal Chemistry, 56:2799–2806. [doi:10.1139/v77-389]
Seo, Y.H., Cho, Y.H., 1997. A Miniature Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Using Platinum Sputtered Microcolumn Electrodes with Limited Amount of Fuel. Proc. 16th IEEE Int. Conf. Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Kyoto, Japan, p.375–378.
Seo, Y.H., Cho, Y.H., 1998. MEMS-based Direct Methanol Fuel Cells and their Stacks Using a Common Electrolyte Sandwiched by Reinforced Microcolumn Electrodes. Proc. 17th IEEE Int. Conf. Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Maastricht, The Netherlands, p.65–68.
Yen, T.J., Fang, N., Zhang, X., Lu, G.Q., Wang, C.Y., 2003. A micro methanol fuel cell operating at near room temperature. Applied Physics Letters, 83(19):4056–4058. [doi:10.1063/1.1625429]
Yu, J., Cheng, P., Ma, Z., Yi, B., 2003a. Fabrication of a miniature silicon wafer fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 124(1):40–46. [doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00618-9]
Yu, J., Cheng, P., Ma, Z., Yi, B., 2003b. Fabrication of a Miniature twin-fuel-cell on silicon wafer. Electrochimica Acta, 48(11):1537–1541. [doi:10.1016/S0013-4686(03)00034-3]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30670535) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-07-0752), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Xiao, Zy., Ying, Yb. et al. Development of a miniature silicon wafer fuel cell using L-ascorbic acid as fuel. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 9, 955–960 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0720049
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0720049