Abstract
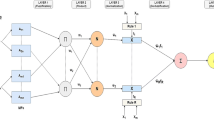
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) process, at present is still an experience process, wherein selected parameters are often far from the optimum, and at the same time selecting optimization parameters is costly and time consuming. In this paper, artificial neural network (ANN) and genetic algorithm (GA) are used together to establish the parameter optimization model. An ANN model which adapts Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm has been set up to represent the relationship between material removal rate (MRR) and input parameters, and GA is used to optimize parameters, so that optimization results are obtained. The model is shown to be effective, and MRR is improved using optimized machining parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, F.G., Yang, D.Y., 2004. The study of high effciency and intelligent optimization system in EDM sinking process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 149(1–3):83–87. [doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2003.10.059]
Das, S., Klotz, M., Klocke, F., 2003. EDM simulation: finite element-based calculation of deformation, microstructure and residual stresses. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 142(2):434–451. [doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00624-1]
Ho, K.H., Newman, S.T., 2003. State of the art electrical discharge machining (EDM). International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 43(13):1287–1300. [doi:10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00162-7]
Kuriakose, S., Shunmugam, M.S., 2005. Multi-objective optimization of wire-electro discharge machining process by non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 170(1–2):133–141. [doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.04.105]
Li, X.L., Yin, G.F., Lin, C.Y., 2004. Tool wear prediction in electrical discharge milling machining based on evolutionary neural network. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 40(3):61–64 (in Chinese).
Mandal, D., Pal, S.K., Saha, P., 2007. Modeling of electrical discharge machining process using back propagation neural network and multi-objective optimization using non-dominating sorting genetic algorithm-II. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 186(1–3):154–162. [doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.12.030]
Rao, S.S., 1991. Optimization Theory and Applications. Wiley Eastern Limited, New Delhi.
Tsai, K.M., Wang, P.J., 2001. Predictions on surface finish in electrical discharge machining based upon neural network models. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 41:1385–1403.
Yang, X.D., 2002. Genetic algorithms based optimization model for EDM parameters. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 34(4):450–454 (in Chinese).
Yang, X.D., Zhao, W.S., 2005. The artificial neural network technology for EDM process forecasting based on web. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 37(8):1029–1031 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 50575128 and 50775128), and the Outstanding Young Scientist Foundation of Shandong Province (No. 2005BS05004), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Zhang, Qh., Su, Sp. et al. Parameter optimization model in electrical discharge machining process. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 9, 104–108 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071242
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A071242
Key words
- Electrical discharge machining (EDM)
- Genetic algorithm (GA)
- Artificial neural network (ANN)
- Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm