Abstract
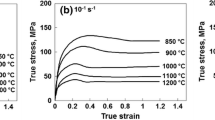
The warm-hot deformation behavior of 20CrMnTi steel was studied with hot compression tests at temperature range of 1123∼1273 K and strain rate of 0.1∼20 s−1. The activation energy for warm-hot deformation is 426.064 KJ/mol. The influences of Zener-Hollomon parameter, strain and grain size imposing on the flow stress were analyzed in the temperature range of warm-hot forging. Creep theory and methematical theory of statistics were used to obtain mathematical models of flow stress. The research and results provide scientific basis for controlling microstructure of forging process through Zener-Hollomon parameter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho, S.H., Kang, K.B., Jonas, J.J., 2001. Mathematical modeling of the recrystallization kinetics of Nb microalloyed steels. ISIJ International, 41(7):766–773.
Elwazri, A.M., Wanjara, P., Yue, S., 2003. Dynamic recrystallization of austenite in microalloyed high carbon steels. Materials Science and Engineering A, 339(1–2):209–215. [doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00164-8]
Hirschvogel, M., Dommelen, H., 1992. Some applications of cold and warm forging. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 35(3–4):343–356. [doi:10.1016/0924-0136(92)90326-N]
Hodgson, P.D., 1996. Microstructure modelling for property prediction and control. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 60(1–4):27–33. [doi:10.1016/0924-0136(96)02304-7]
Jonas, J.J., Sellars, C., Tegart, M., 1969. Strength and stucture under hot working conditions. Int. Metallurgical Reviews, 14:1–24.
Lange, K., 1997. Modern metal forming technology for industrial production. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 71(1):2–13. [doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00113-1]
Poliak, E.I., Jonas, J.J., 2003. Critical strain for dynamic recrystallization in variable strain rate hot deformation. ISIJ International, 43(5):692–700.
Sakai, T., 1995. Dynamic recrystallization microstructures under hot working conditions. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 53(1–2):349–361. [doi:10.1016/0924-0136(95)01992-N]
Serajzadeh, S., Mirbagheri, S.M.H., Taheri, A.K., Zebarjad, S.M., 2004. Modelling of metal flow during hot forging with regard to microstructural aspects. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 44(14):1537–1545. [doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.04.015]
Sheljaskov, S., 1994. Current level of development of warm forging technology. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 46(1–2):3–18. [doi:10.1016/0924-0136(94)90099-X]
Shivpuri, R., Babu, S., Kini, S., Pauskar, P., Deshpande, A., 1994. Recent advances in cold and warm forging process modeling techniques: selected examples. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 46(1–2):253–274. [doi:10.1016/0924-0136(94)90114-7]
Siegert, K., Kammerer, M., Keppler-Ott, T., Ringhand, D., 1997. Recent developments on high precision forging of aluminum and steel. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 71(1):91–99. [doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00153-2]
Venugopal, S., Mannan, S.L., Rodriguez, P., 2002. Optimum design of a hot extrusion process for AISI type 304L stainless steel using a model for the evolution of microstructure. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 10(3):253–265. [doi:10.1088/0965-0393/10/3/301]
Zhang, Z.L., 1986. Warm Forging Technology. Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House, Shanghai, p.2–38 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the Shanghai Automotive Industry Science and Technology Development Fund, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Li, Zh. & Zhang, Zl. Investigation on Zener-Hollomon parameter in the warm-hot deformation behavior of 20CrMnTi. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. A 7, 1453–1460 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.A1453
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.A1453