Abstract
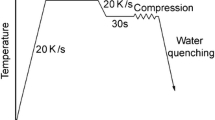
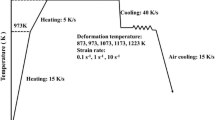
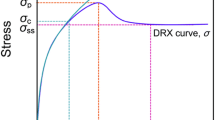
The hot flow behavior of an Nb-Ti microalloyed steel is investigated through hot compression test at various strain rates and temperatures. By the combination of dynamic recovery (DRV) and dynamic recrystallization (DRX) models, a phenomenological constitutive model is developed to derive the flow stress. The predefined activation energy of Q = 270 kJ/mol and the exponent of n = 5 are successfully set to derive critical stress at the onset of DRX and saturation stress of DRV as functions of the Zener–Hollomon parameter by the classical hyperbolic sine equation. The remaining parameters of the constitutive model are determined by fitting them to the experiments. Through substitution of a normalized strain in the DRV model and considering the interconnections between dependent parameters, a new model is developed. It is shown that, despite its fewer parameters, this model is in good agreement with the experiments. Accurate analyses of flow data along with microstructural analyses indicate that the dissolution of NbC precipitates and its consequent solid solution strengthening and retardation of DRX are responsible for the distinguished behaviors in the two temperature ranges between T < 1100 °C and T ≥ 1100 °C. Nevertheless, it is shown that a single constitutive equation can still be employed for the present steel in the whole tested temperature ranges.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamura I, Sekine H, Tanaka T (1988) Thermomechanical Processing of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels. 1st ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford pp. 1-15.
D.K. Matlock, G. Krauss, and J.G. Speer: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vol. 500-501, pp. 87-96. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.500-501.87.
C.A. Hernandez, S.F. Medina, and J. Ruiz: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44(1), pp. 155-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-6454(95)00153-4.
S. Saadatkia, H. Mirzadeh, and J.M. Cabrera: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, vol. 636, 196-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.03.104.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed., Oxford, Elsevier, 2004, pp. 415-50.
H. Mirzadeh, J.M. Cabrera, and A. Najafizadeh: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59(16), pp. 6441-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.07.008.
X. Li, L. Duan, J. Li, and X. Wu: Mater. Design, 2015, vol. 66, pp. 309-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.076.
H. Zou and J.S. Kirkaldy: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23(2), pp. 651-57. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02801182.
S.-H. Cho, K.-B. Kang, and J.J. Jonas: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41(1), pp. 63-69. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.41.63.
W.F. Hosford and R.M. Caddell: Metal Forming (Mechanics and Metallurgy), 4th ed., Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, 1993, pp. 92-93.
E. López-Chipres, I. Mejía, C. Maldonado, A. Bedolla-Jacuinde, M. El-Wahabi, and J.M. Cabrera: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 480(1-2), pp. 49-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.06.067.
C. Zhang, L. Zhang, W. Shen, C. Liu, Y. Xia, and R. Li: Mater. Design, 2016, vol. 90, pp. 804-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.036.
L.X. Kong, P.D. Hodgson, and B. Wang: J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 1999, vol. 89-90, pp. 44-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-0136(99)00015-1.
H. Mirzadeh and A. Najafizadeh: Mater. Design, 2010, vol. 31(10): 4577-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.05.052.
Y. Estrin and H. Mecking: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32(1) pp. 57-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(84)90202-5.
J.J. Jonas, X. Quelennec, L. Jiang, and É. Martin: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57(9), pp. 2748-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.02.033.
A. Fernandez, P. Uranga, B. Lopez, and J. Rodriguezibabe: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 361(1-2), pp. 367-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0921-5093(03)00562-8.
H.J. McQueen and N.D. Ryan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002,vol. 322(1-2), pp. 43-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0921-5093(01)01117-0.
J.M. Cabrera, A. Al Omar, J.M. Prado, and J.J. Jonas: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28(11), pp. 2233-44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0181-8.
J.M. Cabrera, J.J. Jonas, and J.M. Prado: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, vol. 12(7), pp. 579-85. https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1996.12.7.579.
H.J. Frost and M.F. Ashby: Deformation Mechanism Maps-The Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics, Chapter 4, 1982.
Jmatpro: The Materials Property Simulation Package, Public Release Version 6.1, Sente Software Ltd.
J. Wang, H.T. Yang, X.G. Wang, and H. Xiao: Mater. Design, 2015, vol. 65, pp. 637-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.09.072.
Z. Akbari, H. Mirzadeh, and J.M. Cabrera: Mater. Des., 2015, vol. 77, pp. 126-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.04.005.
X. Ma, C. Miao, B. Langelier, and S. Subramanian: Mater. Design, 2017, vol. 132, pp. 244-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.07.006.
P. Gong, E.J. Palmiere, and W.M. Rainforth: Mater. Charact., 2017, vol. 124, pp. 83-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2016.12.009.
S.F. Medina: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 84, pp. 202-07. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.10.056.
A.G. Kostryzhev, A. Al Shahrani, C. Zhu, J.M. Cairney, S.P. Ringer, C.R. Killmore, and E.V. Pereloma: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 607, pp. 226-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.03.140.
K. Xu, B.G. Thomas, and R. O’malley: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 42(2), pp. 524-539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0428-7.
K. Frisk and U. Borggren: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47(10), pp. 4806-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3639-8.
A. Karmakar, S. Biswas, S. Mukherjee, D. Chakrabarti, and V. Kumar: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, vol. 690, pp. 158-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.101.
M.G. Akben, B. Bacroix, and J.J. Jonas: Acta Metall., 1983, vol. 31(1), pp. 161-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(83)90076-7.
S.Q. Yuan and G.L. Liang: Mater. Lett., 2009, vol. 63(27), pp. 2324-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.07.064.
S. Vervynckt, P. Thibaux, and K. Verbeken: Met. Mater. Int., 2012, vol. 18(1), pp. 37-46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-012-0005-2.
B. Dutta and C.M. Sellars: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1986, vol. 2(2), pp. 146-53. https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1986.2.2.146.
N. Fujita, K. Ohmura, M. Kikuchi, T. Suzuki, S. Funaki, and I. Hiroshige: Scripta Mater., 1996, vol. 35(6), pp. 705-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-6462(96)00214-x.
S. Hong, K. Kang, and C. Park: Scripta mater., 2002, vol. 46(2), pp. 163-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1359-6462(01)01214-3.
A. Schmitz, J. Neutjens, J. Herman, V. Leroy, and R.E. Solvay: 40th MWSP Conf Proc., ISS, Warrendale, PA, 1998, pp. 311–21.
H.L. Wei and G.Q. Liu: Mater. Design, 2014, vol 56, pp. 437-444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.009.
F.-r. Xiao, Y.-b. Cao, G.-y. Qiao, X.-b. Zhang, and L. Bo: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2012, vol. 19(11), pp. 52-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1006-706x(13)60020-5.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge the support of Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) for this research under the Project No. 94026725. This work was supported by Slovak Foundation VEGA Grant 2/0158/16 and by Grant APVV-14-0936.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 11, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohebbi, M.S., Parsa, M.H., Rezayat, M. et al. Analysis of Flow Behavior of an Nb-Ti Microalloyed Steel During Hot Deformation. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 1604–1614 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4536-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4536-0