Abstract
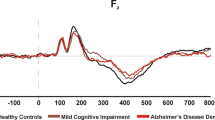
To investigate the features of electroencephalography (EEG) power and coherence at rest and during a working memory task of patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Thirty-five patients (17 males, 18 females; 52:_71 years old) and 34 sex-and age-matched controls (17 males, 17 females; 51:_63 years old) were recruited in the present study. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) of 35 patients with MCI and 34 normal controls revealed that the scores of MCI patients did not differ significantly from those of normal controls (P>0.05). Then, EEGs at rest and during working memory task with three levels of working memory load were recorded. The EEG power was computed over 10 channels: right and left frontal (F3, F4), central (C3, C4), parietal (P3, P4), temporal (T5, T6) and occipital (O1, O2); inter-hemispheric coherences were computed from five electrode pairs of F3-F4, C3-C4, P3-P4, T5-T6 and O1-O2 for delta (1.0:_3.5 Hz), theta (4.0:_7.5 Hz), alpha-1 (8.0:_10.0 Hz), alpha-2 (10.5:_13.0 Hz), beta-1 (13.5:_18.0 Hz) and beta-2 (18.5:_30.0 Hz) frequency bands. All values of the EEG power of MCI patients were found to be higher than those of normal controls at rest and during working memory tasks. Furthermore, the values of EEG power in the theta, alpha-1, alpha-2 and beta-1 bands of patients with MCI were significantly high (P<0.05) in comparison with those of normal controls. Correlation analysis indicated a significant negative correlation between the EEG powers and MMSE scores. In addition, during working memory tasks, the EEG coherences in all bands were significantly higher in the MCI group in comparison with those in the control group (P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in EEG coherences between two groups at rest. These findings comprise evidence that MCI patients have higher EEG power at rest, and higher EEG power and coherence during working conditions. It suggests that MCI may be associated with compensatory processes at rest and during working memory tasks. Moreover, failure of normal cortical connections may be exist in MCI patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association, 1994. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Ed. (DSM-IV). American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC.
Basar, E., Yordanova, J., Kolev, V., Basar-Eroglu, C., 1997. Is the alpha rhythm a control parameter for brain responses? Boil. Cybern., 76:471–480. doi:10.1007/s004220050360.
Dierks, T., Perisic, I., Frolich, L., Ihl, R., Maurer, K., 1991. Topography of the quantitative electroencephalogram in dementia of the Alzheimer type: relation to severity of dementia. Psychiatry Res., 40:181–194. doi:10.1016/0165-1781(91)90157-K.
Hogan, M.J., Swanwick, G.R.J., Kaiser, J., Rowan, M., Lawlor, B., 2003. Memory-related EEG power and coherence reduction in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Psychophysiol., 49:147–163. doi:10.1016/S0167-8760(03)00118-1.
Jelic, V., Johansson, S. E., Almkvist, O., Shigeta, M., Julin, P., Winblad, B., Wahlund, L.O., 2000. Quantitative electroencephalography in mild cognitive impairment: longitudinal changes and possible prediction of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging., 21:533–540. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(00)00153-6.
Jiang, Z.Y., 2004. Research of diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on coherence analysis of EEG signal. Chinese J. Sensor Actuator, 17(3):363–366 (in Chinese).
Jiang, Z.Y., 2005. Abnormal cortical functional connections in Alzheimer’s disease: analysis of inter-and intra-hemispheric EEG coherence. J. Zhejiang Univ. SCI, 6B(4):259–264. doi:10.1631/jzus.2005.B0259.
Kikuchi, M., Wada, Y., Takeda, T., Oe, H., Hashimoto, T., Koshino, Y., 2002. EEG harmonic responses to phonic stimulation in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease: differences in interhemispheric coherence. Clin. Neurophysiol., 113:1045–1051. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00129-3.
Klimesch, W., 1996. Memory processes, brain oscillations and EEG synchronization. Int. J. Psychophysiol., 24:61–100. doi:10.1016/S0167-8760(96)00057-8.
Petersen, R.C., Smith, G.E., Waring, S.C., Ivnik, R.J., Tangalos, E.G., Kokmen, E., 1999. Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch. Neurol., 56:303–308. doi:10.1001/archneur.56.3.303.
Pijnenburg, Y.A.L., vd Made, Y., van Cappellen van Walsum, A.M., Knol, D.L., Scheltens, P., Stem, C.J., 2004. EEG synchronization likelihood in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease during a working memory task. Clin. Neurophysiol., 115:1332–1339. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2003.12.029.
Salthouse, T.A., Babcock, R.L., 1991. Decomposing adult age difference in working memory. Developmental Psychology, 27:763–776. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.27.5.763.
Schurmann, M., Basar, E., 2001. Functional aspects of alpha oscillations in the EEG. Int. J. Psychophysiol., 39:151–158. doi:10.1016/S0167-8760(00)00138-0.
Xie, S., Xiao, J.X., Jiang, X.X., 2003. The fMRI study of the calculation tasks in normal aged volunteers. J. Peking Univ. (Health Sci.), 35:311–313 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project (No. 2004C30020) supported by the Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Zy. Study on EEG power and coherence in patients with mild cognitive impairment during working memory task. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 6, 1213–1219 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B1213
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B1213