Abstract
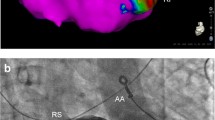
Objective: To evaluate the safety and clinical efficacy of segmental radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein (PV) ostia for patients with refractory paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) under multi-slice spiral computed tomography (MSCT) guidance before the procedure. Methods: A series of 58 consecutive patients with refractory paroxysmal AF were enrolled to undergo segmental radiofrequency ablation of PV ostia. The 36 male and 22 female patients with mean age of (57.4±9.5) (32:_79) years and no obvious organic heart disease. Before ablation, patients received MSCT to generate 3-dimentional image of the left atrium (LA) and proximal PVs. Patients then underwent segmental radiofrequency ablation of PV ostia using PV circular mapping catheter manipulated several times to ensure complete isolation between PVs and LA. Results: No complications occurred during the procedure. One patient developed delayed cardiac tamponade, which was drained percutaneously. The mean follow-up time was (17.1±9.3) months. Forty-one patients (95%) experienced improved quality of life one month after the procedure. Thirty-six patients (83%) showed stable sinus rhythm, while 10 patients (23%) required additional anti-arrhythmic drugs. AF returned≥1 time in 6 (14%) patients who underwent anti-arrhythmic drug therapy, but the number of episodes was less than that before the procedure. However, one patient experienced recurrent episodes of atrial flutter. Conclusion: It is safe and effective to perform segmental radiofrequency ablation of PV ostia for patients with refractory paroxysmal AF using MSCT guidance mappening.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fynn, S.P., Kalman, J.M., 2004. Pulmonary veins. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol., 27(11):1547–1559. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2004.00675.x.
Jongbloed, M.R., Bax, J.J., Lamb, H.J., Dirksen, M.S., Zeppenfeld, K., van der Wall, E.E., de Roos, A., Schalij, M.J., 2005. Multislice computed tomography versus intracardiac echocardiography to evaluate the pulmonary veins before radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a head-to-head comparison. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 45(3):343–350. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.10.040.
Lacomis, J.M., Wigginton, W., Fuhrman, C., Schwartzman, D., Armfield, D.R., Pealer, K.M., 2003. Multi-detector row CT of the left atrium and pulmonary veins before radio-frequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Radiographics, 23:S35–S48.
Oral, H., Scharf, C., Chugh, A., Hall, B., Cheung, P., Good, E., Veeraceddy, S., Pelosi, F., Morady, F., 2003. Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 108:2355–2360. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000095796.45180.88.
Pappone, C., Rosanio, S., Oreto, G., Tocchi, M., Gugliotta, F., Vicedomini, G., Salvati, A., Dicandia, C., Mazzone, P., Santinelli, V., et al., 2000. Circumferential radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein ostia. Circulation, 102:2619–2628.
Pappone, C., Oreto, G., Rosanio, S., Vicedomini, G., Tocchi, M., Gugliotta, F., Salvati, A., Dicandia, C., Calabro, M.P., Mazzone, P., 2001. Atrial electroanatomic remodelling after circumferential radiofrequency pulmonary vein ablation. Circulation, 104:2539–2544.
Tritto, M., de Ponti, R., Salerno-Uriarte, J.A., Spadacini, G., Marazzi, R., Moretti, P., Lanzotti, M., 2004. Adenosine restores atrio-venous conduction after apparently successful ostial isolation of the pulmonary veins. Eur. Heart J., 25(23):2155–2163. doi:10.1016/j.ehj.2004.08.023.
Wood, M.A., Wittkamp, M., Henry, D., Martin, R., Nixon, J.V., Shepard, R.K., Ellenbogen, K.A., 2004. A comparison of pulmonary vein ostial anatomy by computerized tomography, echocardiography, and venography in patients with atrial fibrillation having radiofrequency catheter ablation. Am. J. Cardiol., 93(1):49–53. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.09.011.
Yang, Y.Z., Liu, S.W., Gao, L.J., Lin, Z.H., 2003. Methodology of atrium-pulmonary vein electrical isolation by radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Chin. J. Cardiac. Arrhyth., 7:315–319 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Cy., Wang, Ja., He, H. et al. Segmental radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein ostia for patients with refractory paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using multi-slice spiral computed tomography guidance. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. B 6, 1153–1156 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B1153
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B1153