Abstract
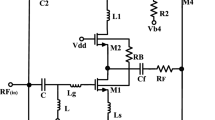
Noise and linearity performances are critical characteristics for radio frequency integrated circuits (RFICs), especially for low noise amplifiers (LNAs). In this paper, a detailed analysis of noise and linearity for the cascode architecture, a widely used circuit structure in LNA designs, is presented. The noise and the linearity improvement techniques for cascode structures are also developed and have been proven by computer simulating experiments. Theoretical analysis and simulation results showed that, for cascode structure LNAs, the first metallic oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) dominates the noise performance of the LNA, while the second MOSFET contributes more to the linearity. A conclusion is thus obtained that the first and second MOSFET of the LNA can be designed to optimize the noise performance and the linearity performance separately, without trade-offs. The 1.9GHz Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) LNA simulation results are also given as an application of the developed theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Floyd, B. A., Mehta, J., Camero, C. and Kenneth, K. O., 1999. A 900 MHz, 0.8 μm CMOS Low Noise Amplifier with 1.2 dB Noise Figure. IEEE 1999 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Diego, CA, p. 661–664
Jin, W., Liu, W., Hai, C., Chan, Philip, C. H. and Hu, C., 2001. Noise modeling and characterization for 1.5V 1.8GHz SOI low-noise amplifier.IEEE Transaction on Electron Devices,48(4): 803–809.
Lee, T. H., 1998. The Design of CMOS Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits. Cambridge University Press.
Park, P. and Kim, C. S., 2001. Linearity, Noise Optimization for Two Stage RF CMOS LNA. Proc. Of IEEE,2: 756–758.
Shaeffer, D. K. and Lee, T. H., 1997. 1.5 V, 1.5GHz CMOS low noise amplifier.Solid-State Circuits, IEEE Journal,32: 745–759.
Tinella, C., Fournier, J. M. and Haidar, J., 2001. Noise Contribution in A Fully Integrated 1V, 2.5GHz LNA in CMOS-SOI Technology. The 8th IEEE International Conference on, Electronics Circuits and Systems, 3: 1611–1614.
Van der Ziel, A., 1986. Noise in Solid State Devices and Circuits. Wiley, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Huang, Dq. Noise and linearity optimization methods for a 1.9GHz low noise amplifier. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 4, 281–286 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0281
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0281