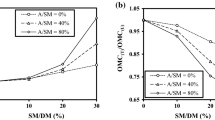
Abstract
This study investigates the influence of nano clay on the rheological properties of alkali-activated cement pastes having different GGBFS/FA ratios. The thixotropic index, structural build-up, dynamic yield stress and heat evolution of fresh AAC pastes with addition of nano clay are studied. Test results showed that nano clay had a strong influence on the thixotropy/structural build-up and dynamic yield stress of AAC pastes depending on the GGBFS/FA ratio of the mixture. It was found that the pastes with lower GGBFS/FA ratio exhibited higher thixotropic index, but lower dynamic yield stress in the presence of nano clay. This study reveals the importance of GGBFS/FA ratio in the presence of nano clay for obtaining AAC mixtures with low dynamic yield stress for a better flowability and high thixotropy/structural build-up for stability.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duxson P, Fernández-Jiménez A, Provis JL, Lukey GC, Palomo A, Van Deventer JSJ (2007) Geopolymer technology: the current state of the art. J Mater Sci 42(9):2917–2933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0637-z
Chi MC, Chang JJ, Huang R (2012) Strength and drying shrinkage of alkali-activated slag paste and mortar. Adv Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/579732
Criado M, Aperador W, Sobrados I (2016) Microstructural and mechanical properties of alkali activated Colombian raw materials. Materials (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9030158
Fernández-Jiménez A, Palomo A, Pastor JY, Martín A (2008) New cementitious materials based on alkali-activated fly ash: performance at high temperatures. J Am Ceram Soc 91(10):3308–3314. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02625.x
Komljenović M, Baščarević Z, Marjanović N, Nikolić V (2013) External sulfate attack on alkali-activated slag. Constr Build Mater 49:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.08.013
N. Roussel, “Understanding the Rheology of Concrete,” Woodhead Publ. Ltd., 2011.
Flatt RJ (2004) Towards a prediction of superplasticized concrete rheology. Mater Struct Constr 37(269):289–300. https://doi.org/10.1617/14088
Roussel N, Lemaître A, Flatt RJ, Coussot P (2010) Steady state flow of cement suspensions: a micromechanical state of the art. Cem Concr Res 40(1):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.08.026
Flatt RJ (2004) Dispersion forces in cement suspensions. Cem Concr Res 34(3):399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.08.019
Flatt RJ, Bowen P (2003) Electrostatic repulsion between particles in cement suspensions: Domain of validity of linearized Poisson-Boltzmann equation for nonideal electrolytes. Cem Concr Res 33(6):781–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(02)01059-1
Roussel N, Ovarlez G, Garraul S, Brumaud C (2012) The origins of thixotropy of fresh cement pastes. Cem Concr Res 42:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.09.004
Yuan Q, Zhou D, Khayat KH, Feys D, Shi C (2016) On the measurement of evolution of structural build-up of cement paste with time by static yield stress test vs. small amplitude oscillatory shear test. Cem Concr Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2017.05.014
Reiter T, Wangler NR, Flatt RJ (2017) The role of early age structural build-up in digital fabrication with concrete. Cem Concr Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2018.05.011
Kawashima S, Kim JH, Corr DJ, Shah SP (2012) Study of the mechanisms underlying the fresh-state response of cementitious materials modified with nanoclays. Constr Build Mater 36:749–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.06.057
Qian Y, Kawashima S (2016) Use of creep recovery protocol to measure static yield stress and structural rebuilding of fresh cement pastes. Cem Concr Res 90:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2016.09.005
Qian Y, Ma S, Kawashima S, De Schutter G (2019) Rheological characterization of the viscoelastic solid-like properties of fresh cement pastes with nanoclay addition. Theor Appl Fract Mech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102262
Tregger NA, Pakula ME, Shah SP (2010) Influence of clays on the rheology of cement pastes. Cem Concr Res 40:384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.11.001
Qian Y, De Schutter G (2018) Enhancing thixotropy of fresh cement pastes with nanoclay in presence of polycarboxylate ether superplasticizer (PCE). Cem Concr Res 111(June):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2018.06.013
Kawashima S, Hou P, Corr DJ, Shah SP (2013) Modification of cement-based materials with nanoparticles. Cem Concr Compos 36:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2012.06.012
Kazemian A, Yuan X, Cochran E, Khoshnevis B (2017) Cementitious materials for construction-scale 3D printing: laboratory testing of fresh printing mixture. Constr Build Mater 145:639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.015
Kim JH, Beacraft M, Shah SP (2010) Effect of mineral admixtures on formwork pressure of self-consolidating concrete. Cem Concr Compos 32(9):665–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2010.07.018
Amin Moeini M, Hosseinpoor M, Yahia A (2020) Effectiveness of the rheometric methods to evaluate the build-up of cementitious mortars used for 3D printing. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119551
Panda B, Unluer C, Jen M (2019) Extrusion and rheology characterization of geopolymer nanocomposites used in 3D printing. Compos Part B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107290
Ren Q, Jiang Z, Li H, Zhu X, Chen Q (2019) Fresh and hardened properties of self-compacting concrete using silicon carbide waste as a viscosity-modifying agent. Constr Build Mater 200:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.163
Panda B, Ruan S, Unluer C, Jen M (2019) Improving the 3D printability of high volume fly ash mixtures via the use of nano attapulgite clay. Compos Part B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.11.109
Panda B, Ruan S, Unluer C, Tan MJ (2020) Investigation of the properties of alkali-activated slag mixes involving the use of nanoclay and nucleation seeds for 3D printing. Compos Part B Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107826
Provis JL, Kilcullen A, Duxson P, Brice DG, Van Deventer JSJ (2012) Stabilization of low-modulus sodium silicate solutions by alkali substitution. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:2483–2486. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie202143j
Mostafa AM, Yahia A (2016) New approach to assess build-up of cement-based suspensions. Cem Concr Res 85:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2016.03.005
Schultz MA, Struble LJ (1993) Use of oscillatory shear to study flow behavior of fresh cement paste. Cem Concr Res 23(2):273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(93)90092-N
Yuan Q, Lu X, Khayat KH, Feys D, Shi C (2017) Small amplitude oscillatory shear technique to evaluate structural build-up of cement paste. Mater Struct Constr 50(2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-016-0978-2
Qian Y, Kawashima S (2018) Distinguishing dynamic and static yield stress of fresh cement mortars through thixotropy. Cem Concr Compos 86:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.11.019
Qian Y, Lesage K, El Cheikh K, De Schutter G (2017) Effect of polycarboxylate ether superplasticizer ( PCE ) on dynamic yield stress, thixotropy and fl occulation state of fresh cement pastes in consideration of the Critical Micelle Concentration ( CMC ). Cem Concr Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2018.02.019
Rifaai Y, Yahia A, Mostafa A, Aggoun S, Kadri EH (2019) Rheology of fly ash-based geopolymer: Effect of NaOH concentration. Constr Build Mater 223:583–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.028
Rouyer J, Poulesquen A (2015) Evidence of a Fractal Percolating Network During Geopolymerization. Am Ceram Soc. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.13480
Dai X, Aydin S, Yücel M, Lesage K, De Schutter G (2020) Influence of water to binder ratio on the rheology and structural Build-up of Alkali-Activated Slag / Fly ash mixtures. Constr Build Mater 264:120253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120253
Kashani A, Provis JL, Qiao GG, Van Deventer JSJ (2014) The interrelationship between surface chemistry and rheology in alkali activated slag paste. Constr Build Mater 65:583–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.127
Alnahhal MF, Kim T, Hajimohammadi A (2021) Distinctive rheological and temporal viscoelastic behaviour of alkali-activated fly ash/slag pastes: a comparative study with cement paste. Cem Concr. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2021.106441
Zhang Y, Jiang Z, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Ren Q, Huang T (2020) Effects of redispersible polymer powders on the structural build-up of 3D printing cement paste with and without hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120551
Dai X, Aydın S, Yardımcı MY, Lesage K, De Schutter G (2020) Effects of activator properties and GGBFS/FA ratio on the structural build-up and rheology of AAC. Cem Concr Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2020.106253
Dejaeghere I, Sonebi M, De Schutter G (2019) Influence of nano-clay on rheology, fresh properties, heat of hydration and strength of cement-based mortars. Constr Build Mater 222:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.111
Kawashima S, Chaouche M, Corr DJ, Shah SP (2013) Rate of thixotropic rebuilding of cement pastes modified with highly purified attapulgite clays. Cem Concr Res 53:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.05.019
Chang SH, Ryan MH, Gupta RK (1993) The effect of pH, ionic strength, and temperature on the rheology and stability of aqueous clay suspensions. Rheol Acta 32(3):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00434190
Neaman A, Singer A (2000) Rheological Properties of Aqueous Suspensions of Palygorskite. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64(1):427–436. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2000.641427x
Palacios M, Alonso MM, Varga C, Puertas F (2018) Influence of the alkaline solution and temperature on the rheology and reactivity of alkali-activated fly ash pastes. Cem Concr Compos. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.08.010
Puertas F, Varga C, Alonso MM (2014) Rheology of alkali-activated slag pastes. effect of the nature and concentration of the activating solution. Cem Concr Compos 53:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.07.012
Yang T, Zhu H, Zhang Z, Gao X, Zhang C, Wu Q (2018) Effect of fly ash microsphere on the rheology and microstructure of alkali-activated fly ash/slag pastes. Cem Concr Res 109(April):198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2018.04.008
Gao X, Yu QL, Brouwers HJH (2015) Reaction kinetics, gel character and strength of ambient temperature cured alkali activated slag-fly ash blends. Constr Build Mater 80:105–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.01.065
Nedeljković M, Li Z, Ye G (2018) Setting, strength, and autogenous shrinkage of alkali-activated fly ash and slag pastes: effect of slag content. Materials (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112121
Zuhua Z, Xiao Y, Huajun Z, Yue C (2009) Role of water in the synthesis of calcined kaolin-based geopolymer. Appl Clay Sci 43(2):218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2008.09.003
Acknowledgements
This paper is the result of research actions performed in the framework of the FWO-EOS project 30439691 ‘INTERdisciplinary multiscale Assessment of a new generation of Concrete with alkali- activated maTerials’ (INTERACT). The financial support by FWO-EOS is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaodi DAI: Methodology, Investigation, Writing–original draft; Qiang Ren: Investigation, Writing–review editing; Serdar AYDIN: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing–review editing; Mert Yücel YARDIMCI: Validation, Writing–review editing; Karel LESAGE: Supervision, Writing–review editing; Geert De SCHUTTER: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, X., Ren, Q., Aydın, S. et al. Enhancing thixotropy and structural build-up of alkali-activated slag/fly ash pastes with nano clay. Mater Struct 54, 163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-021-01760-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-021-01760-4