Abstract
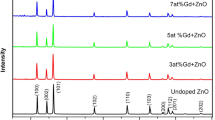
In this study, we have evaluated the biological activity of gadolinium-incorporated zinc oxide (Gd-ZnO) nanostructures prepared via a hydrothermal synthesis route. Various characterization techniques, such as powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), Ultraviolet–Visible (UV–Vis), Dynamic light scattering (DLS), and scanning electron microscope (SEM) are employed to examine the physicochemical characterization of the Gd-ZnO nanostructures. Powder XRD analysis confirmed the wurtzite hexagonal crystal structure. The FTIR bands indicated the characteristic functional groups of Gd and Zn–O, confirming the formation of Gd-ZnO. Furthermore, the antibacterial activity against gram-negative E. coli and gram-positive S. aureus and anticancer activity against A549 cancer cells have been conducted.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
L. Zhou et al., Functional DNA-based hydrogel intelligent materials for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 8(10), 1991–2009 (2020)
S. Abeer, Future medicine: Nanomedicine. JIMSA 25(3), 187–192 (2012)
J. Barman et al., The role of nanotechnology based wearable electronic textiles in biomedical and healthcare applications. Mater. Today Commun. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104055
E. Omanović-Mikličanin, M. Maksimović, V. Vujović, The future of healthcare: Nanomedicine and internet of nano things. Folia Medica FacultatisMedicinae Universitatis Saraeviensis 50(1), 23–28 (2015)
S. Kai, S. Xiaomeng, W. Zhao, F. Ai, A. Umar, S. Baskoutas, Functional inorganic nanomaterials for optical cancer theranostics. Chem. Eng. J. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.150067
K. Khan et al., Recent development in graphdiyne and its derivative materials for novel biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 9(46), 9461–9484 (2021)
A. Mansour, M. Romani, A.B. Acharya, B. Rahman, E. Verron, Z. Badran, Drug delivery systems in regenerative medicine: An updated review. Pharmaceutics (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020695
P.Q. Nguyen et al., Engineered living materials: Prospects and challenges for using biological systems to direct the assembly of smart materials. Adv. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704847
Q. Sun et al., Rational design of cancer nanomedicine: Nanoproperty integration and synchronization. Adv. Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201606628
V.K. Varadan, L. Chen, J. Xie, Nanomedicine: Design and applications of magnetic nanomaterials, nanosensors and nanosystems (Wiley, Hoboken, 2008)
S. Sagadevan, S. Imteyaz, B. Murugan, J. Anita Lett, N. Sridewi, G.K. Weldegebrieal, Is. Fatimah, W.C. Oh, A comprehensive review on green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their diverse biomedical applications. Green Process. Synth. 11(1), 44–63 (2022)
A. Fatima, M.W. Ahmad, A.K.A. Al Saidi, A. Choudhury, Y. Chang, G.H. Lee, Recent advances in Gadolinium based contrast agents for bioimaging applications. Nanomaterials (Basel) 11(9), 2449 (2021)
M. Joglekar, B.G. Trewyn, Polymer-based stimuli-responsive nanosystems for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. J.. J. 8(8), 931–945 (2013)
H.J. Kwon et al., Large-scale synthesis and medical applications of uniform-sized metal oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 30(42), 1704290 (2018)
M. Murar, L. Albertazzi, S. Pujals, Advanced optical imaging-guided nanotheranostics towards personalized cancer drug delivery. Nanomaterials 12(3), 399 (2022)
A.K. Mandal et al., Current research on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 12(17), 3066 (2022)
M. Carofiglio et al., Doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and potential use in nanomedicine. Appl. Sci. 10(15), 5194 (2020)
K. Pradeev Raj et al., Influence of Mg doping on ZnO nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic evaluation and antibacterial analysis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. Res. Lett. 13, 1–13 (2018)
S. Barui, R. Gerbaldo, N. Garino, R. Brescia, F. Laviano, V. Cauda, Facile chemical synthesis of doped ZnO nanocrystals exploiting oleic acid. Nanomaterials 10(6), 1150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061150
Z. Yu, C. Eich, L.J. Cruz, Recent advances in rare-earth-doped nanoparticles for NIR-II imaging and cancer theranostics. Front. Chem. 8, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00496
C. Bouzigues, T. Gacoin, A. Alexandrou, Biological applications of rare-earth based nanoparticles. ACS Nano 5, 8488–8505 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn202378b
H. Li, R. Wei, G.-H. Yan, J. Sun, C. Li, H. Wang, L. Shi, J.A. Capobianco, L. Sun, Smart self-assembled nanosystem based on water-soluble pillararene and rareearth-doped upconversion nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 4910–4920 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b14193
L. Qi, Y. Ge, T. Xia, J.Z. He, C. Shen, J. Wang, Y.J. Liu, Rare earth oxide nanoparticles promote soil microbial antibiotic resistance by selectively enriching antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Sci. NanoNano 6(2), 456–466 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en01129j
S. Radhakrishnan, S. Nagarajan, H. Belaid, C. Farha, I. Iatsunskyi, E. Coy, L. Soussan, V. Huon, J. Bares, K. Belkacemi, C. Teyssier, S. Balme, P. Miele, D. Cornu, N. Kalkura, V. Cavaill`es, M. Bechelany, Fabrication of 3D printed antimicrobial polycaprolactone scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 118, 111525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111525
Y. Liu, K. Ai, Q. Yuan, L. Lu, Fluorescence-enhanced gadolinium-doped zinc oxide quantum dots for magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging. Biomaterials 32, 1185–1192 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.022
M. Isik, N.M. Gasanly, Gd-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Synthesis, structural and thermoluminescence properties. J. Lumin.Lumin. 207, 220–222 (2019)
J.L. Mejía-Méndez, D.E. Navarro-López, A. Sanchez-Martinez, O. Ceballos-Sanchez, L.E. Garcia-Amezquita, N. Tiwari, E.R. López-Mena, Lanthanide-Doped ZnO nanoparticles: Unraveling their role in cytotoxicity, antioxidant capacity, and nanotoxicology. Antioxidants 13(2), 213 (2024)
K.P. Shinde et al., Study of effect of planetary ball milling on ZnO nanopowder synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Alloy. Compd. 617, 404–407 (2014)
K.P. Raj, K. Sadayandi, Effect of temperature on structural, optical and photoluminescence studies on ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the standard co-precipitation method. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 487, 1–7 (2016)
Acknowledgments
The author A. Subashini thank the Management, Principal, and Faculty members of Velammal Institute of Technology, Chennai-601 204, India, for their constant encouragement and support throughout this work.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Subashini: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation and original draft preparation. Suresh Sagadevan: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Visualization, Validation, Reviewing, and Editing. Is Fatimah: Formal analysis, Data curation, Visualization, and Validation. J. Anita Lett: Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Visualization, Validation. Maghimaa Mathanmohun: Data curation, Visualization, and Validation. Faruq Mohammad: Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Visualization, Validation. Mohammed A. Al-Anber: Formal analysis, Data curation, and Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Subashini, A., Sagadevan, S., Fatimah, I. et al. Evaluation of biological activity for gadolinium-incorporated zinc oxide nanostructures via hydrothermal method. MRS Advances (2024). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-024-00863-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-024-00863-8