Abstract
An unreported rhenium-based calcium aluminum sodalite (CARe sodalite) has been synthesized by a traditional solid-state method. The rhenium is located in the sodalite β-cage and can be reduced under 5% H2 forming gas without breaking the cage framework. Preliminary characterizations of the structural, optical, and magnetic properties are reported.
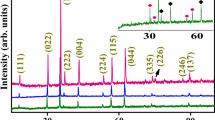
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available on request from the authors.
References
D.W. Breck, Zeolite Molecular Sieves: Structure, Chemistry, and Use (Wiley, New York, 1973)
A.R. West, Solid State Chemistry and Its Applications, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 2022)
T. Weller M, Where zeolites and oxides merge: semi-condensed tetrahedral frameworks. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 5, 4227–4240 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1039/B003800H
J. Li, A. Corma, J. Yu, Synthesis of new zeolite structures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 7112–7127 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CS00023H
W. Depmeier, The sodalite family: a simple but versatile framework structure. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 57, 203–240 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2005.57.7
M.E. Brenchley, M.T. Weller, Synthesis and structure of sulfide aluminate sodalites. J. Mater. Chem. 2, 1003–1005 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1039/JM9920201003
M.E. Brenchley, M.T. Weller, Structures of strontium selenite and strontium selenide aluminate sodalites and the relationship of framework structure to vibrational spectra in aluminate sodalites. Chem. Mater. 5, 970–973 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm00031a015
S. van Smaalen, R. Dinnebier, H. Katzke, W. Depmeier, Structural characterization of the high-temperature phase transitions in Ca8[Al12O24](MoO4)2 aluminate sodalite using x-ray powder diffraction. J. Solid State Chem. 129, 130–143 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1996.7251
W. Depmeier, Structure of cubic aluminate sodalite Ca8[Al12O24](WO4)2 in comparison with its orthorhombic phase and with cubic Sr8[Al12O24](CrO4)2. Acta Cryst. B 44, 201–207 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108768187011959
S. Lee, H. Xu, H. Xu, R. Jacobs, D. Morgan, Valleyite: a new magnetic mineral with the sodalite-type structure. Am. Miner. 104, 1238–1245 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2019-6856
B.K. Singh, M.A. Hafeez, H. Kim, S. Hong, J. Kang, W. Um, Inorganic waste forms for efficient immobilization of radionuclides. ACS EST Eng. 1, 1149–1170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.1c00184
A. Merchant, S. Batzner, S.S. Schoenholz, M. Aykol, G. Cheon, E.D. Cubuk, Scaling deep learning for materials discovery. Nature 624, 80–85 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06735-9
L.T. Glasby, E.H. Whaites, P.Z. Moghadam, Machine learning and digital manufacturing approaches for solid-state materials development. In: AI-Guided Design and Property Prediction for Zeolites and Nanoporous Materials. Wiley, pp 377–409 (2023)
R.P. Xian, V. Stimper, M. Zacharias, M. Dendzik, S. Dong, S. Beaulieu, B. Schölkopf, M. Wolf, L. Rettig, C. Carbogno, S. Bauer, R. Ernstorfer, A machine learning route between band mapping and band structure. Nat. Comput. Sci. 3, 101–114 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43588-022-00382-2
J.M. Gregoire, L. Zhou, J.A. Haber, Combinatorial synthesis for AI-driven materials discovery. Nat Synth 2, 493–504 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-023-00251-4
D. Ni, Z. Hu, G. Cheng, X. Gui, W.-Z. Yu, C.-J. Jia, X. Wang, J. Herrero-Martín, N. Yao, L.-H. Tjeng, R.J. Cava, Magnetic frustration in a zeolite. Chem. Mater. 33, 9725–9731 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c03500
S.M. Antao, I. Hassan, J.B. Parise, Chromate aluminate sodalite, Ca8[Al12O24](CrO4)2: phase transitions and high-temperature structural evolution of the cubic phase. Can. Mineral. 42, 1047–1056 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2113/gscanmin.42.4.1047
I. Hassan, Structural modulations in a pseudo-cubic aluminate sodalite, Ca8[Al12O24](CrO4)2. Z. Kristallogr. 211, 228–233 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.1996.211.4.228
M.T. Greiner, T.C.R. Rocha, B. Johnson, A. Klyushin, A. Knop-Gericke, R. Schlögl, The oxidation of rhenium and identification of rhenium oxides during catalytic partial oxidation of ethylene: an in-situ XPS study. Z. Phys. Chem. 228, 521–541 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2014-0002
I. Hassan, Direct observation of phase transitions in aluminate sodalite, Ca8[Al12O24](CrO4)2. Am. Miner. 81, 1375–1379 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1996-11-1210
I. Hassan, Aluminate socialite, Ca8[Al12O24](CrO4)2, with tetragonal and orthorhombic superstructures. Eur. J. Mineral. 8, 477–486 (1996)
R. Melzer, W. Depmeier, A structural study of aluminate sodalite Ca8[Al12O24](CrO4)2 (CACr). Cryst. Res. Technol. 31, 459–467 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.2170310409
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi B 15, 627–637 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.19660150224
J. Tauc, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater. Res. Bull. 3, 37–46 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(68)90023-8
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Gordon and betty Moore Foundation grant number GBMF-9066. The authors acknowledge the use of Princeton’s Imaging and Analysis Center, which is partially supported by the Princeton Center for Complex Materials, a National Science Foundation (NSF)-MRSEC program (DMR-2011750).
Funding
This study was funded by Gordon and betty Moore Foundation Grant Number GBMF-9066 and National Science Foundation (NSF)-MRSEC program (DMR-2011750).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Danrui Ni contributed toward conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, visualization, and writing—original draft; Guangming Cheng contributed toward validation, investigation, formal analysis, visualization, and writing—reviewing and editing; Lun Jin contributed toward validation, investigation, and formal analysis; Chen Yang contributed toward validation and investigation; Nan Yao contributed toward resource, supervision, and project funding acquisition; Robert J. Cava* contributed toward conceptualization, resource, supervision, project funding acquisition, administration, and writing- reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, D., Cheng, G., Jin, L. et al. A calcium aluminum rhenium sodalite with reducible rhenium in the sodalite cage. MRS Communications (2024). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-024-00550-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-024-00550-7