Abstract
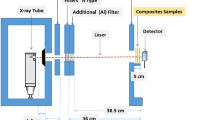
This study focuses on synthesizing and characterizing Mg-doped SnO2 nanoparticles as a safe substitute for lead-based X-ray shielding aprons. Various molar weight percentages of Mg dopant were utilized during synthesis, and the resulting samples were analyzed using multiple techniques, such as X-ray diffraction, UV–visible, Photoluminescence, Raman spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission and scanning electron microscopes. The nanoparticles were then combined with a nano-epoxy polymer composite and coated onto rexine cloth through drop casting. To assess the X-ray shielding performance, the percentage of attenuation, attenuation coefficient, and half-value layer studies were conducted. Comparative analysis with traditional lead oxide (PbO) aprons revealed that the 3% Mg-doped SnO2 nanocomposite aprons exhibited superior X-ray attenuation properties. In summary, this study highlights the potential of Mg-doped SnO2 nanoparticles as an effective, hydrophobic, and lightweight alternative to commercial aprons that are made of toxic, hydrophilic, and heavy lead-based materials.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
L. Chang, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Fang, W. Luan, X. Yang, W. Zhang, Preparation and characterization of tungsten/epoxy composites for γ-rays radiation shielding. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 356, 88–93 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2015.04.062
N.Z.N. Azman, N.F.L. Musa, N.N.A.N.A. Razak, R.M. Ramli, I.S. Mustafa, A.A. Rahman, N.Z. Yahaya, Effect of Bi2O3 particle sizes and addition of starch into Bi2O3–PVA composites for x-ray shielding. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 122, 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0329-8
H.H. Aygün, M.H. Alma, Bismuth (III) oxide/polyethylene terephthalate nanocomposite fiber coated polyester spunbonds for ionizing radiation protection. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 1–8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03880-0
S.J. Hyun, K.J. Kim, T.A. Jahng, H.J. Kim, Efficiency of lead aprons in blocking radiation − how protective are they? Heliyon (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00117
A.M.A. Mostafa, S.A.M. Issa, M.I. Sayyed, Gamma ray shielding properties of PbO-B2O3-P2O5 doped with WO3. J. Alloys Compd. 708, 294–300 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.303
K.T. Varughese, V. Harish, N. Nagaiah, T. Niranjana Prabhu, Preparation and characterization of lead monoxide filled unsaturated polyester based polymer composites for gamma radiation shielding applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci.Polym. Sci. 112, 1503–1508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29633
K. Yue, W. Luo, X. Dong, C. Wang, G. Wu, M. Jiang, Y. Zha, A new lead-free radiation shielding material for radiotherapy. Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 133, 256–260 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncp053
A.K. Singh, R.K. Singh, B. Sharma, A.K. Tyagi, Characterization and biocompatibility studies of lead free X-ray shielding polymer composite for healthcare application. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 138, 9–15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2017.04.016
S. Sambhudevan, B. Shankar, A. Saritha, K. Joseph, J. Philip, T. Saravanan, Development of X-ray protective garments from rare earth-modified natural rubber composites. J. Elastomers Plast. 49, 527–544 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244316676866
Y. Kim, S. Park, Y. Seo, Enhanced X-ray shielding ability of polymer-nonleaded metal composites by multilayer structuring. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 5968–5973 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00425
A. Aghaz, R. Faghihi, S.M.J. Mortazavi, A. Haghparast, S. Mehdizadeh, S. Sina, Radiation attenuation properties of shields containing micro and Nano WO3 in diagnostic X-ray energy range. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 14, 127–131 (2016). https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.ijrr.14.2.127
S. Nambiar, E.K. Osei, J.T.W. Yeow, Polymer nanocomposite-based shielding against diagnostic X-rays. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 127, 4939–4946 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.37980
E.W. Taylor, Organics, polymers and nanotechnology for radiation hardening and shielding applications. Nanophotonics Macrophotonics Sp. Environ. 6713, 671307 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.729156
F. Safaei, S.N. Khorasani, H. Rahnama, R.E. Neisiany, M.S. Koochaki, Single microcapsules containing epoxy healing agent used for development in the fabrication of cost efficient self-healing epoxy coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 114, 40–46 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2017.09.019
S.A. Haddadi, S. Hu, S. Ghaderi, A. Ghanbari, M. Ahmadipour, S.Y. Pung, S. Li, M. Feilizadeh, M. Arjmand, Amino-functionalized mxene nanosheets doped with Ce(III) as potent nanocontainers toward self-healing epoxy nanocomposite coating for corrosion protection of mild steel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 42074–42093 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c13055
X. Liu, H. Zhang, J. Wang, Z. Wang, S. Wang, Preparation of epoxy microcapsule based self-healing coatings and their behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 206, 4976–4980 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.05.133
B.M. Abunahel, R.M. Ramli, K.M. Quffa, N.Z.N. Azman, Effect of nanofibrous porosity on the X-ray attenuation properties of electrospun n-Bi2O3/epoxy–polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofiber mats. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1975-9
Y. Dong, S.Q. Chang, H.X. Zhang, C. Ren, B. Kang, M.Z. Dai, Y.D. Dai, Effects of WO3 particle size in WO3/Epoxy resin radiation shielding material. Chin. Phys. Lett. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/29/10/108102
F.I. El-Agawany, O.L. Tashlykov, K.A. Mahmoud, Y.S. Rammah, The radiation-shielding properties of ternary SiO2–SnO–SnF2 glasses: simulation and theoretical study. Ceram. Int. 46, 23369–23378 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.042
A.S. Abouhaswa, Y.S. Rammah, S.E. Ibrahim, A.A. El-Hamalawy, Structural, optical, and electrical characterization of borate glasses doped with SnO2. J. Non Cryst. Solids 494, 59–65 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2018.04.051
K. Suzuki, G. Tricot, B. Revel, A. Saitoh, Properties and structure of SnO−SiO2 and SnO−SnF2−SiO2 glasses. J. Non Cryst. SolidsCryst. Solids. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119706
Y.S. Rammah, M.I. Sayyed, A.S. Abohaswa, H.O. Tekin, FTIR, electronic polarizability and shielding parameters of B2O3 glasses doped with SnO2. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2069-4
P.S. Shajira, M.J. Bushiri, B.B. Nair, V.G. Prabhu, Energy band structure investigation of blue and green light emitting Mg doped SnO2 nanostructures synthesized by combustion method. J. Lumin. 145, 425–429 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.07.073
N. Mazumder, A. Bharati, S. Saha, D. Sen, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Effect of Mg doping on the electrical properties of SnO 2 nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 975–982 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2011.12.022
H. Yang, H. Fan, J. Duan, Effect of Mg doping on SnO2 energy band and power conversion efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2101/1/012066
S. Li, R. Yan, M. Cai, W. Jiang, M. Zhang, X. Li, Enhanced antibiotic degradation performance of Cd0.5Zn0.5S/Bi2MoO6 S-scheme photocatalyst by carbon dot modification. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 164, 59–67 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMST.2023.05.009
S. Li, M. Cai, C. Wang, Y. Liu, Ta3N5/CdS core-shell s-scheme heterojunction nanofibers for efficient photocatalytic removal of antibiotic tetracycline and Cr(VI): performance and mechanism insights. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5, 994–1007 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/S42765-022-00253-5/METRICS
S. Li, C. Wang, K. Dong, P. Zhang, X. Chen, X. Li, MIL-101(Fe)/BiOBr S-scheme photocatalyst for promoting photocatalytic abatement of Cr(VI) and enrofloxacin antibiotic: performance and mechanism. Chin. J. Catal. 51, 101–112 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64479-1
S. Li, M. Cai, Y. Liu, C. Wang, K. Lv, X. Chen, S-Scheme photocatalyst TaON/Bi2WO6 nanofibers with oxygen vacancies for efficient abatement of antibiotics and Cr(VI): intermediate eco-toxicity analysis and mechanistic insights. Chin. J. Catal. 43, 2652–2664 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64106-8
R.K. Mishra, P.P. Sahay, Zn-doped and undoped SnO 2 nanoparticles: a comparative structural, optical and LPG sensing properties study. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 4112–4118 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.08.051
P.P. Sahay, R.K. Mishra, S.N. Pandey, S. Jha, M. Shamsuddin, Structural, dielectric and photoluminescence properties of co-precipitated Zn-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 479–486 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2012.09.010
M. Sabarilakshmi, K. Janaki, Effect of Mg concentration on structural, optical and humidity sensing performance of SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by one step facile route. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 8101–8107 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6516-3
K. Venkateswarlu, M. Sandhyarani, T.A. Nellaippan, N. Rameshbabu, Estimation of crystallite size, lattice strain and dislocation density of nanocrystalline carbonate substituted hydroxyapatite by X-ray peak variance analysis, procedia. Mater. Sci. 5, 212–221 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.260
E.T. Seid, F.B. Dejene, Z.N. Urgessa, J.R. Botha, Refluxed sol–gel synthesized ZnO nanopowder with variable zinc precursor concentrations. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2148-6
G. Kalpana, J. Varuna, P. Sanjeevi, M. Elango, Influence of Mg concentration on structural, morphological and optical properties of nanoceria. Ceram. Int. 44, 11820–11827 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.03.269
T. Thilagavathi, D. Venugopal, R. Marnadu, J. Chandrasekaran, T. Alshahrani, M. Shkir, An investigation on microstructural, morphological, optical, photoluminescence and photocatalytic activity of WO3 for photocatalysis applications: an effect of annealing. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 1217–1230 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01731-2
M. Kumar, A. Kumar, A.C. Abhyankar, Occurrence of non-equilibrium orthorhombic SnO2 phase and its effect in preferentially grown SnO2 nanowires for CO detection. RSC Adv. 5, 35704–35708 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra15539d
G. Singh, S.B. Shrivastava, D. Jain, S. Pandya, T. Shripathi, V. Ganesan, Effect of indium dop ing on zinc oxide films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis technique. Bull. Mater. Sci. 33, 581–587 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0089-6
S. Asaithambi, P. Sakthivel, M. Karuppaiah, Y. Hayakawa, A. Loganathan, G. Ravi, Improved photocatalytic performance of nanostructured SnO2 via addition of alkaline earth metals (Ba2+, Ca2+ and Mg2+) under visible light irradiation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 1–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3441-8
N. Mazumder, D. Sen, S. Saha, U.K. Ghorai, N.S. Das, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Enhanced ultraviolet emission from Mg doped SnO2 nanocrystals at room temperature and its modulation upon H2 annealing. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 6454–6461 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4000329
S.A. Saleh, A.A. Ibrahim, S.H. Mohamed, Structural and optical properties of nanostructured Fe-doped SnO2. Acta. Phys. Pol. A. 129, 1220–1225 (2016). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.129.1220
A. Diéguez, A. Romano-Rodríguez, A. Vilà, J.R. Morante, The complete Raman spectrum of nanometric SnO2 particles. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 1550–1557 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1385573
M.B. Sahana, C. Sudakar, A. Dixit, J.S. Thakur, R. Naik, V.M. Naik, Quantum confinement effects and band gap engineering of SnO 2 nanocrystals in a MgO matrix. Acta Mater. 60, 1072–1078 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.11.012
S.H. Sun, G.W. Meng, G.X. Zhang, T. Gao, B.Y. Geng, L.D. Zhang, J. Zuo, Raman scattering study of rutile SnO2 nanobelts synthesized by thermal evaporation of Sn powders. Chem. Phys. Lett. 376, 103–107 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(03)00965-5
Y. Liu, Y. Jiao, Z. Zhang, F. Qu, A. Umar, X. Wu, Hierarchical SnO2 nanostructures made of intermingled ultrathin nanosheets for environmental remediation, smart gas sensor, and supercapacitor applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 2174–2184 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am405301v
X. Wang, X. Wang, Q. Di, H. Zhao, B. Liang, J. Yang, Mutual effects of fluorine dopant and oxygen vacancies on structural and luminescence characteristics of F doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Materials (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121398
N. Bhakta, P.K. Chakrabarti, XRD analysis, Raman, AC conductivity and dielectric properties of Co and Mn co-doped SnO 2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2370-2
J. Singh, V. Verma, R. Kumar, R. Kumar, Influence of Mg 2+ -substitution on the optical band gap energy of Cr 2–x Mg 2–x O 3 nanoparticles. Results Phys. 13, 102106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.02.042
S. Li, C. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, M. Cai, W. Zhao, X. Duan, S-scheme MIL-101(Fe) octahedrons modified Bi2WO6 microspheres for photocatalytic decontamination of Cr(VI) and tetracycline hydrochloride: synergistic insights, reaction pathways, and toxicity analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 455, 140943 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2022.140943
C. Wang, R. Yan, M. Cai, Y. Liu, S. Li, A novel organic/inorganic S-scheme heterostructure of TCPP/Bi12O17Cl2 for boosting photodegradation of tetracycline hydrochloride: kinetic, degradation mechanism, and toxic assessment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 610, 155346 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2022.155346
S. Li, M. Cai, Y. Liu, C. Wang, R. Yan, X. Chen, Constructing Cd0.5Zn0.5S/Bi2WO6 S-scheme heterojunction for boosted photocatalytic antibiotic oxidation and Cr(VI) reduction. Adv. Powder Mater. 2, 100073 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APMATE.2022.100073
M. Cai, Y. Liu, K. Dong, X. Chen, S. Li, Floatable S-scheme Bi2WO6/C3N4/carbon fiber cloth composite photocatalyst for efficient water decontamination, Chinese. J. Catal. 52, 239–251 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64496-1
M. Rouchdi, E. Salmani, A. El Hat, C. Nassiri, N. Hassanain, A. Mzerd, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Mg doped SnO2 thin films: experimental and Ab-initio study. Opt. Quantum Electron. 49, 1–13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-0990-y
M. Karmaoui, A.B. Jorge, P.F. McMillan, A.E. Aliev, R.C. Pullar, J.A. Labrincha, D.M. Tobaldi, One-step synthesis, structure, and band gap properties of SnO2 nanoparticles made by a low temperature nonaqueous sol-gel technique. ACS Omega 3, 13227–13238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02122
J. Liqiang, Q. Yichun, W. Baiqi, L. Shudan, J. Baojiang, Y. Libin, F. Wei, F. Honggang, S. Jiazhong, Review of photoluminescence performance of nano-sized semiconductor materials and its relationships with photocatalytic activity. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, 1773–1787 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2005.11.007
R. Mani, K. Vivekanandan, K. Vallalperuman, Synthesis of pure and cobalt (Co) doped SnO2 nanoparticles and its structural, optical and photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 4396–4402 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6067-z
D. Madhan, M. Sangeetha, P. Rajkumar, Visible light photocatalytic activity of pure and palladium (Pd) doped SnO2 nanoparticles by a one step facile route. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 14453–14459 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7307-6
B. Venugopal, B. Nandan, A. Ayyachamy, V. Balaji, S. Amirthapandian, B.K. Panigrahi, T. Paramasivam, Influence of manganese ions in the band gap of tin oxide nanoparticles: structure, microstructure and optical studies. RSC Adv. 4, 6141–6150 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra46378h
R. Bargougui, K. Omri, A. Mhemdi, S. Ammar, Synthesis and characterization of SnO2 nanoparticles: effect of hydrolysis rate on the optical properties. Adv. Mater. Lett. 6, 816–819 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2015.5844
N. Shanmugam, T. Sathya, G. Viruthagiri, C. Kalyanasundaram, R. Gobi, S. Ragupathy, Photocatalytic degradation of brilliant green using undoped and Zn doped SnO 2 nanoparticles under sunlight irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 360, 283–290 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.11.008
R. Zulfiqar, Y. Khan, Z. Yuan, J. Iqbal, W. Yang, Z. Wang, J. Ye, Lu, Variation of structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 4625–4636 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6101-1
K. Ravichandran, K. Thirumurugan, N. Jabena Begum, S. Snega, Investigation of p-type SnO2: Zn films deposited using a simplified spray pyrolysis technique. Superlattices Microstruct. Microstruct. 60, 327–335 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2013.05.006
R.N. Mariammal, K. Ramachandran, B. Renganathan, D. Sastikumar, On the enhancement of ethanol sensing by CuO modified SnO 2 nanoparticles using fiber-optic sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 169, 199–207 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.04.067
M.H. McKetty, The AAPM/RSNA physics tutorial for residents: x-ray attenuation. Radiographics 18, 151–163 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.18.1.9460114
M.Z. Botelho, R. Künzel, E. Okuno, R.S. Levenhagen, T. Basegio, C.P. Bergmann, X-ray transmission through nanostructured and microstructured CuO materials. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 69, 527–530 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2010.11.002
S. Iqbal, G. Kotnala, J. Shah, S. Ahmad, Barium ferrite nanoparticles: a highly effective EMI shielding material. Mater. Res. Express. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab02a4
E. Mansouri, A. Mesbahi, R. Malekzadeh, A. Mansouri, Shielding characteristics of nanocomposites for protection against X- and gamma rays in medical applications: effect of particle size, photon energy and nano-particle concentration. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-020-00865-8
A. Mesbahi, H. Ghiasi, Shielding properties of the ordinary concrete loaded with micro- and nano-particles against neutron and gamma radiations. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 136, 27–31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2018.02.004
M. Ghaseminejad, L. Gholamzadeh, F. Ostovari, Investigation of x-ray attenuation property of modification PbO with graphene in epoxy polymer. Mater. Res. Express. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abecea
M. Dejangah, M. Ghojavand, R. Poursalehi, P.R. Gholipour, X-ray attenuation and mechanical properties of tungsten-silicone rubber nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Express. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab1a89
A.M. Reda, A.A. El-Daly, Gamma ray shielding characteristics of Sn-20Bi and Sn-20Bi-0.4Cu lead-free alloys. Prog. Nucl. Energy. Nucl. Energy. 123, 103304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2020.103304
L. Yu, P.L. Yap, A. Santos, D. Tran, D. Losic, Lightweight bismuth titanate (Bi4Ti3O12) nanoparticle-epoxy composite for advanced lead-free x-ray radiation shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 7471–7478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c01475
N.Z. Noor Azman, W.F.I. Wan Mohamed, R.M. Ramli, Synthesis and characterization of electrospun n-ZnO/n-Bi2O3/epoxy-PVA nanofiber mat for low X-ray energy shielding application. Radiat. Phys. Chem.. Phys. Chem. 195, 110102 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2022.110102
M. Dong, X. Xue, S. Liu, H. Yang, Z. Li, M.I. Sayyed, O. Agar, Using iron concentrate in Liaoning Province, China, to prepare material for X-Ray shielding. J. Clean. Prod. 210, 653–659 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.038
N. Şahin, M. Bozkurt, Y. Karabul, M. Kılıç, Z.G. Özdemir, Low cost radiation shielding material for low energy radiation applications: Epoxy/Yahyali Stone composites. Prog. Nucl. Energy. Nucl. Energy. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2021.103703
L.B.T. La, C. Leatherday, Y.K. Leong, H.P. Watts, L.C. Zhang, Green lightweight lead-free Gd2O3/epoxy nanocomposites with outstanding X-ray attenuation performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 163, 89–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.05.018
N.Z. Noor Azman, S.A. Siddiqui, M. Ionescu, I.M. Low, Synthesis and characterisation of ion-implanted epoxy composites for X-ray shielding. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms. 287, 120–123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2012.06.004
S.C. Kim, J.R. Choi, B.K. Jeon, Physical analysis of the shielding capacity for a lightweight apron designed for shielding low intensity scattering X-rays. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27721
B.M. Abunahel, I.S. Mustafa, N.Z. Noor Azman, Characteristics of X-ray attenuation in nano-sized bismuth oxide/epoxy-polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) matrix composites. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2254-5
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Vishnu Shankar Dhandapani, School of Mechatronics Engineering, Korea University of Technology and Education, Chungnam 31253, South Korea, Dr. P. Puviarasu, Ceramic Processing Lab, Department of Physics, PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore—641004, India and Dr. A. Saravanakumar, Department of Medical Physics, PSG Institute of Medical Sciences and Research for their support and facilitation during the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sanjeevi Palanisami participated in the Conceptualization and Writing of the Original draft. Varuna Jayachandran participated in the Writing and review of the manuscript. Atheek Posha participated in the Editing of the manuscript. Kalpana G participated in the Formal analysis. Elango M participated in the Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Palanisami, S., Jayachandran, V., Posha, A. et al. A systematic investigation on the potential X-ray attenuation properties of Mg-doped SnO2 epoxy nanocomposite-based aprons as an alternate for lead commercial aprons. Journal of Materials Research (2024). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-024-01314-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-024-01314-8