Abstract
The magnetic material with carbon nanodots as magnetofluorescent multi-agents was an effective way to determine cellular information in clinical diagnosis systems. However, exploring hyaluronic acid (HA) on magnetofluorescent is limited in combining with CuFe2O4. The present study reports a new design contrast agent as a hybrid carbon nanodots (CNDs–CuFe2O4–HA) by combining the fluorescence carbon nanodots (CNDs) and copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles capsulated with HA. The as-prepared nanohybrid confirmed the unique properties through some important analytical techniques. The photoluminescence data showed an average diameter of the nanohybrid of about 104 nm and exhibited blue emission (λem = 420 nm). The hybrid also showed the superparamagnetic behavior and saturated magnetization (Ms) value of 0.63 emug−1, which increased the positive contrast on T1-weight relaxation of MRI as well as its specific targeting to the tumor assessed by confocal microscopy. The effective nanohybrid particles also described remarkable fluorescence and non-toxicity features that are useful for clinical diagnosis information.
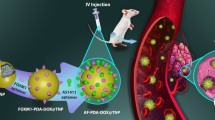
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article (and its supplementary information files).
References
A. Avasthi, C. Caro, E. Pozo‑Torres, M.P. Leal, M.L. García‑Martín, Magnetic nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Surf.-Modified Nanobiomater. Electrochem. Biomed. Appl. 49 (2020).
B. Issa, I.M. Obaidat, Magnetic nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 378, 40 (2019)
A. Farooq, S. Sabah, S. Dhou, N. Alsawaftah, G. Husseini, Exogenous contrast agents in photoacoustic imaging: an in vivo review for tumor imaging. Nanomaterials 12(3), 393 (2022)
A.B. Dias, C. O’Brien, J.-M. Correas, S. Ghai, Multiparametric ultrasound and micro-ultrasound in prostate cancer: a comprehensive review. Br. J. Radiol. 95(1131), 20210633 (2022)
W. Zhang, L. Liu, H. Chen, K. Hu, I. Delahunty, S. Gao, J. Xie, Surface impact on nanoparticle-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Theranostics 8(9), 2521 (2018)
J. Pellico, C.M. Ellis, J.J. Davis, Nanoparticle-based paramagnetic contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Contrast Med. Mol. Imaging. (2019)
V.P. Grover, J.M. Tognarelli, M.M. Crossey, I.J. Cox, S.D. Taylor-Robinson, M.J. McPhail, Magnetic resonance imaging: principles and techniques: lessons for clinicians. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 5(3), 246 (2015)
Y. Huang, L. Li, D. Zhang, L. Gan, P. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Q. Zhang, M. Hua, C. Jia, Gadolinium-doped carbon quantum dots loaded magnetite nanoparticles as a bimodal nanoprobe for both fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Resonan. Imaging 68, 113 (2020)
D. Kim, K.S. Hong, J. Song, The present status of cell tracking methods in animal models using magnetic resonance imaging technology. Mol. Cells. 23(2) (2007)
H.B. Na, I.C. Song, T. Hyeon, Inorganic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents. Adv. Mater. 21(21), 2133 (2009)
N. Boda, G. Boda, K.C.B. Naidu, M. Srinivas, K.M. Batoo, D. Ravinder, A.P. Reddy, Effect of rare earth elements on low temperature magnetic properties of Ni and Co-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 473, 228 (2019)
D.H.K. Reddy, Y.-S. Yun, Spinel ferrite magnetic adsorbents: alternative future materials for water purification? Coord. Chem. Rev. 315, 90 (2016)
S.M. Rathod, A.R. Chavan, S.S. Jadhav, K.M. Batoo, M. Hadi, E.H. Raslan, Ag+ ion substituted CuFe2O4 nanoparticles: analysis of structural and magnetic behavior. Chem. Phys. Lett. 765, 138308 (2021)
K.M. Batoo, D. Salah, G. Kumar, A. Kumar, M. Singh, M. Abd El-Sadek, F.A. Mir, A. Imran, D.A. Jameel, Hyperfine interaction and tuning of magnetic anisotropy of Cu doped CoFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 411, 91 (2016)
G.H. Im, S.M. Kim, D.-G. Lee, W.J. Lee, J.H. Lee, I.S. Lee, Fe3O4/MnO hybrid nanocrystals as a dual contrast agent for both T1-and T2-weighted liver MRI. Biomaterials 34(8), 2069 (2013)
S. Chapman, M. Dobrovolskaia, K. Farahani, A. Goodwin, A. Joshi, H. Lee, T. Meade, M. Pomper, K. Ptak, J. Rao, Nanoparticles for cancer imaging: the good, the bad, and the promise. Nano today. 8(5), 454 (2013)
O. Veiseh, C. Sun, C. Fang, N. Bhattarai, J. Gunn, F. Kievit, K. Du, B. Pullar, D. Lee, R.G. Ellenbogen, Specific targeting of brain tumors with an optical/magnetic resonance imaging nanoprobe across the blood-brain barrier. Cancer Res. 69(15), 6200 (2009)
N. Pothayee, S. Balasubramaniam, N. Pothayee, N. Jain, N. Hu, Y. Lin, R.M. Davis, N. Sriranganathan, A.P. Koretsky, J. Riffle, Magnetic nanoclusters with hydrophilic spacing for dual drug delivery and sensitive magnetic resonance imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 1(8), 1142 (2013)
X. Shi, T.P. Thomas, L.A. Myc, A. Kotlyar, J.R. Baker Jr., Synthesis, characterization, and intracellular uptake of carboxyl-terminated poly (amidoamine) dendrimer-stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9(42), 5712 (2007)
A. Kumar, B. Sahoo, A. Montpetit, S. Behera, R.F. Lockey, S.S. Mohapatra, Development of hyaluronic acid–Fe2O3 hybrid magnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of peptides. Nanomedicine 3(2), 132 (2007)
M.A. Dobrovolskaia, S.E. McNeil, Immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2(8), 469 (2007)
D. Lachowicz, A. Szpak, K.E. Malek-Zietek, M. Kepczynski, R.N. Muller, S. Laurent, M. Nowakowska, S. Zapotoczny, Biocompatible and fluorescent superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with superior magnetic properties coated with charged polysaccharide derivatives. Colloids Surf. B 150, 402 (2017)
M.Z. Fahmi, D.L.N. Wibowo, S.C.W. Sakti, H.V. Lee, Human serum albumin capsulated hydrophobic carbon nanodots as staining agent on HeLa tumor cell. Mater. Chem. Phys. 239, 122266 (2020)
W. Wang, Y. Ni, Z. Xu, One-step uniformly hybrid carbon quantum dots with high-reactive TiO2 for photocatalytic application. J. Alloys Compds. 622, 303 (2015)
S.N. Baker, G.A. Baker, Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49(38), 6726 (2010)
Y.Y. Aung, A.N. Kristanti, S.Q. Khairunisa, N. Nasronudin, M.Z. Fahmi, Inactivation of HIV-1 infection through integrative blocking with amino phenylboronic acid attributed carbon dots. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. (2020)
M.Z. Fahmi, A. Haris, A.J. Permana, D.L.N. Wibowo, B. Purwanto, Y.L. Nikmah, A. Idris, Bamboo leaf-based carbon dots for efficient tumor imaging and therapy. RSC Adv. 8(67), 38376 (2018)
A.J. Permana, A. Haris, H. Setyawati, M.Z. Fahmi, Partial oxidative synthesis of fluorescent carbon derived from local bamboo leaves. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 52(6), 1101 (2017)
Y. Kwee, A.N. Kristanti, N.S. Aminah, M.Z. Fahmi, Design of catechin-based carbon nanodots as facile staining agents of tumor cells. Indonesian J. Chem. 20(6), 1332 (2020)
G. Supriyanto, N.K. Rukman, A.K. Nisa, M. Jannatin, B. Piere, A. Abdullah, M.Z. Fahmi, H.S. Kusuma, Graphene oxide from indonesian biomass: synthesis and characterization. BioResources 13(3), 4832 (2018)
P. Sreenath, S. Mandal, S. Singh, H. Panigrahi, P. Das, A.K. Bhowmick, K.D. Kumar, Unique approach to debundle carbon nanotubes in polymer matrix using carbon dots for enhanced properties. Eur. Polym. J. 123, 109454 (2020)
D. Liu, L. Yang, Z. Chen, G. Zou, H. Hou, J. Hu, X. Ji, Ultra-stable Sb confined into N-doped carbon fibers anodes for high-performance potassium-ion batteries. Sci. Bull. (2020)
J. Shen, Y. Zhu, X. Yang, C. Li, Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 48(31), 3686 (2012)
A. Vibhute, O. Nille, G. Kolekar, S. Rohiwal, S. Patil, S. Lee, A.P. Tiwari, Fluorescent carbon quantum dots functionalized by poly l-lysine: efficient material for antibacterial, bioimaging and antiangiogenesis applications. J. Fluoresc. 32(5), 1789 (2022)
A. Wibrianto, S.Q. Khairunisa, S.C. Sakti, Y.L. Ni’Mah, B. Purwanto, M.Z. Fahmi, Comparison of the effects of synthesis methods of B, N, S, and P-doped carbon dots with high photoluminescence properties on HeLa tumor cells. RSC Adv. 11(2), 1098 (2021)
M.Z. Fahmi, R.A. Prasetya, M.F. Dzikri, S.C.W. Sakti, B. Yuliarto, MnFe2O4 nanoparticles/cellulose acetate composite nanofiber for controllable release of naproxen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 123055 (2020)
W. Cheng, J. Nie, L. Xu, C. Liang, Y. Peng, G. Liu, T. Wang, L. Mei, L. Huang, X. Zeng, pH-sensitive delivery vehicle based on folic acid-conjugated polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(22), 18462 (2017)
G. Tripodo, A. Trapani, M.L. Torre, G. Giammona, G. Trapani, D. Mandracchia, Hyaluronic acid and its derivatives in drug delivery and imaging: recent advances and challenges. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 97, 400 (2015)
Y. Gokce, B. Cengiz, N. Yildiz, A. Calimli, Z. Aktas, Ultrasonication of chitosan nanoparticle suspension: Influence on particle size. Colloids Surf. A 462, 75 (2014)
P. Nigam, S. Waghmode, M. Louis, S. Wangnoo, P. Chavan, D. Sarkar, Graphene quantum dots conjugated albumin nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging of pancreatic cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2(21), 3190 (2014)
Z. Shen, Y. Li, K. Kohama, B. Oneill, J. Bi, Improved drug targeting of cancer cells by utilizing actively targetable folic acid-conjugated albumin nanospheres. Pharmacol. Res. 63(1), 51 (2011)
Y. He, Y. Zhong, Y. Su, Y. Lu, Z. Jiang, F. Peng, T. Xu, S. Su, Q. Huang, C. Fan, Water-dispersed near-infrared-emitting quantum dots of ultrasmall sizes for in vitro and in vivo imaging. Angew. Chem. 123(25), 5813 (2011)
S.M. Fotukian, A. Barati, M. Soleymani, A.M. Alizadeh, Solvothermal synthesis of CuFe2O4 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles with high heating efficiency for magnetic hyperthermia application. J. Alloys Compds. 816, 152548 (2020)
Q. Wang, X. Huang, Y. Long, X. Wang, H. Zhang, R. Zhu, L. Liang, P. Teng, H. Zheng, Hollow luminescent carbon dots for drug delivery. Carbon 59, 192 (2013)
M. Fahmi, W. Sukmayani, S.Q. Khairunisa, A. Witaningrum, D. Indriati, M. Matondang, J.-Y. Chang, T. Kotaki, M. Kameoka, Design of boronic acid-attributed carbon dots on inhibits HIV-1 entry. RSC Adv. 6(95), 92996 (2016)
R. Justin, K. Tao, S. Román, D. Chen, Y. Xu, X. Geng, I.M. Ross, R.T. Grant, A. Pearson, G. Zhou, Photoluminescent and superparamagnetic reduced graphene oxide–iron oxide quantum dots for dual-modality imaging, drug delivery and photothermal therapy. Carbon 97, 54 (2016)
T.P. Armedya, M.F. Dzikri, S.C.W. Sakti, A. Abdulloh, Y. Raharjo, S. Wafiroh, M.Z. Fahmi, Kinetical release study of copper ferrite nanoparticle incorporated on PCL/collagen nanofiber for naproxen delivery. Bionanoscience 9(2), 274 (2019)
M. Tuerhong, X. Yang, Y. Xue-bo, Review on carbon dots and their applications. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 45(1), 139 (2017)
S. Sahu, N. Sinha, S.K. Bhutia, M. Majhi, S. Mohapatra, Luminescent magnetic hollow mesoporous silica nanotheranostics for camptothecin delivery and multimodal imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2(24), 3799 (2014)
M. Sivakumar, A. Towata, K. Yasui, T. Tuziuti, T. Kozuka, Y. Iida, M.M. Maiorov, E. Blums, D. Bhattacharya, N. Sivakumar, Ultrasonic cavitation induced water in vegetable oil emulsion droplets—a simple and easy technique to synthesize manganese zinc ferrite nanocrystals with improved magnetization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 19(3), 652 (2012)
M. Xu, S. Xu, Z. Yang, M. Shu, G. He, D. Huang, L. Zhang, L. Li, D. Cui, Y. Zhang, Hydrophilic and blue fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from tartaric acid and various alkylol amines under microwave irradiation. Nanoscale 7(38), 15915 (2015)
D. Xiao, L. Xi, W. Yang, H. Fu, Z. Shuai, Y. Fang, J. Yao, Size-tunable emission from 1, 3-diphenyl-5-(2-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(22), 6740 (2003)
Y. Xu, X.-H. Jia, X.-B. Yin, X.-W. He, Y.-K. Zhang, Carbon quantum dot stabilized gadolinium nanoprobe prepared via a one-pot hydrothermal approach for magnetic resonance and fluorescence dual-modality bioimaging. Anal. Chem. 86(24), 12122 (2014)
B. De, N. Karak, A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice. Rsc Adv. 3(22), 8286 (2013)
S. Pazokifard, S. Mirabedini, M. Esfandeh, S. Farrokhpay, Fluoroalkylsilane treatment of TiO2 nanoparticles in difference pH values: characterization and mechanism. Adv. Powder Technol. 23(4), 428 (2012)
W. Gao, J. Zhang, Q. Xue, X. Yin, X. Yin, C. Li, Y. Wang, Acute and sub-acute toxicity study of graphene-based tumor cell nuclear Targeting fluorescent nanoprobe. Mol. Pharm. (2020)
M.Z. Fahmi, N.F. Sholihah, A. Wibrianto, S.C. Sakti, F. Firdaus, J.-Y. Chang, Simple and fast design of folic acid-based carbon dots as theranostic agent and its drug release aspect. Mater. Chem. Phys. 267, 124596 (2021)
C. Yu, T. Xuan, Y. Chen, Z. Zhao, X. Liu, G. Lian, H. Li, Gadolinium-doped carbon dots with high quantum yield as an effective fluorescence and magnetic resonance bimodal imaging probe. J. Alloys Compds. 688, 611 (2016)
N. Gong, H. Wang, S. Li, Y. Deng, X.A. Chen, L. Ye, W. Gu, Microwave-assisted polyol synthesis of gadolinium-doped green luminescent carbon dots as a bimodal nanoprobe. Langmuir 30(36), 10933 (2014)
M.Z. Fahmi, J.-K. Chen, C.-C. Huang, Y.-C. Ling, J.-Y. Chang, Phenylboronic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles as a platform for carbon dot conjugation and doxorubicin delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 3(27), 5532 (2015)
S.M. Sharker, S.M. Kim, J.E. Lee, J.H. Jeong, I. In, K.D. Lee, H. Lee, S.Y. Park, In situ synthesis of luminescent carbon nanoparticles toward target bioimaging. Nanoscale 7(12), 5468 (2015)
H.S.U. Usreg, A. Husein, M.Z. Fahmi, Uji Sitotosik Terhadap Sintesis Dan Karakterisasi Magnetik Nanopartikel CuFe2O4 Yang Dilingkupi Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA). Sci. J. Chem. Res. 4(1), 7 (2019)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Universitas Airlangga for research facilities and the Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education, Republic of Indonesia, for financial support under PPKI contract No. 304/UN3.14/PT/2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest in the present study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fahmi, M.Z., Wibowo, D.L.N., Aung, Yy. et al. Nanohybrid carbon nanodots-CuFe2O4 as selectively magnetofluorescent agent on tumor cells. Journal of Materials Research 38, 3416–3428 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01066-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01066-x