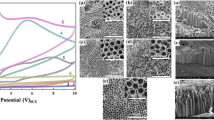
Abstract
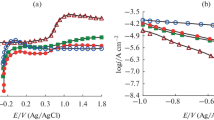
Titanium was anodically oxidized in aqueous electrolyte containing dissolved 1 M Na2SO4 and 0.5 wt% NaF. This oxidation was performed for 0.5 and 1 h at 20 and 30 V in unstirred and magnetic pellet stirred baths. Irrespective of the stirring conditions, amorphous, nanotubular oxide was formed at 20 V. Compared to the unstirred condition, the tubular length was increased upon stirring at 20 V. However, flat, anatase layers were produced at 30 V in both stirring conditions. The nanotube network was formed probably in first 5 min and disturbed later, so that the oxidation proceeds laterally and perpendicular to the longitudinal tubular axis. Among the oxides tested, the oxide films obtained by oxidation for 0.5 h at 20 and 30 V under stirring condition (M20, 0.5 and M30, 0.5) have higher impedance and lower corrosion current density in simulated body fluid (SBF). The SBF represents the actual conditions of fluid inside the body.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
H. Ishizawa, M. Ogino, Formation and characterization of anodic titanium oxide films containing Ca and P. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29, 65–72 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820290110
M. Shirkhanzadeh, Electrochemical preparation of protective oxide coatings on titanium surgical alloys. J. Mater. Sci.—Mater. Med. 3, 322–325 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705362
M. Long, H.J. Rack, Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—a materials science perspective. Biomaterials 19(18), 1621–1639 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(97)00146-4
S. Oh, S. Jin, Titanium oxide nanotubes with controlled morphology for enhanced bone growth. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 26(8), 1301–1306 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2005.08.014
H. Tsuchiya, J.M. Macak, A. Ghicov, L. Taveira, P. Schmuki, Self-organized porous TiO2 and ZrO2 produced by anodization. Corros. Sci. 47(12), 3324–3335 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.05.041
S. Yoriya, M. Paulose, O.K. Varghese, G.K. Mor, C.A. Grimes, Fabrication of vertically oriented TiO2 nanotube arrays using dimethyl sulfoxide electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(37), 13770–13776 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp074655z
S. Oh, C. Daraio, L.-H. Chen, T.R. Pisanic, R.R. Finones, S. Jin, Significantly accelerated osteoblast cell growth on aligned TiO2 nanotubes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. PART A 78, 97–103 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.30722
V.S. Saji, H.C. Choe, W.A. Brantley, Nanotubular oxide layer formation on Ti–13Nb–13Zr alloy as a function of applied potential. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 3975–3982 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3542-4
A. Simchi, E. Tamjid, F. Pishbin, A.R. Boccaccini, Recent progress in inorganic and composite coatings with bactericidal capability for orthopaedic applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 7(1), 22–39 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2010.10.005
V.S. Saji, H.C. Choe, Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of nanotubular Ti–13Nb–13Zr alloy in Ringer’s solution. Corros. Sci. 51(8), 1658–1663 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2009.04.013
R. Narayanan, J.-Y. Ha, T.-Y. Kwon, K.-H. Kim, Structure and Properties of self-organized TiO2 nanotubes from stirred baths. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 39, 493–499 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9153-7
R. Narayanan, T.-Y. Kwon, K.-H. Kim, Anodic TiO2 from stirred Na2SO4/NaF electrolytes: effect of applied voltage and stirring. Mater. Lett. 63(23), 2003–2006 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.06.036
L.V. Taveira, J.M. Macák, H. Tsuchiya, L.F.P. Dick, P. Schmuki, Initiation and growth of self-organized TiO2 nanotubes anodically formed in NH4F/(NH4)2SO4 electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152(10), B405–B410 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2008980
H. Uzal, A. Döner, Corrosion behavior of titanium dioxide nanotubes in alkaline solution. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 56, 311–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S207020512002029X
F.A.A. Al-Saady, S.A. Rushdi, A.H. Abbar, Improvement the corrosion behavior of titanium by nanotubular oxide in a simulated saliva solution. IOP Conf. Series Mater. Sci. Eng. 870, 012060 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/870/1/012060
I.C. Turu, N. Cansever, Anodization of Ti6Al4V in water-ethylene glycol solution containing NH4F and its corrosion behavior in ringer’s solution. Int. J. of Electrochem. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.20964/2022.06.33
Z. Peng, J. Ni, Surface properties and bioactivity of TiO2 nanotube array prepared by two-step anodic oxidation for biomedical applications. Royal Soc. Open Sci. 6(181948), 1–15 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.181948
J.M. Macak, H. Tsuchiya, L. Taveira, S. Aldabergerova, P. Schmuki, Smooth anodic TiO2 nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44(45), 7463–7465 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200502781
S.K. Mohapatra, K.S. Raja, M. Misra, V.K. Mahajan, M. Ahmadian, Synthesis of self-organized mixed oxide nanotubes by sonoelectrochemical anodization of Ti–8Mn alloy. Electrochim. Acta. 53(2), 590–597 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.04.123
C.-S. Chien, Y.-C. Hung, T.-F. Hong, C.-C. Wu, T.-Y. Kuo, T.-M. Lee, T.-Y. Liao, H.-C. Lin, C.-H. Chuang, Preparation and characterization of porous bioceramic layers on pure titanium surfaces obtained by micro-arc oxidation process. Appl. Phys. A. 123(204), 1–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0765-0
M. Tamaddon, S. Samizadeh, L. Wang, G. Blunn, C. Liu, Intrinsic osteoinductivity of porous titanium scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. 5093063, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5093063
R.P. Nogueira, J. Deuzimar Uchoa, F. Hilario, G.F. Santana-Melo, L.M.R. de Vasconcellos, F.R. Marciano, V. Roche, A. Moreira Jorge Jr., A.O. Lobo, Characterization of optimized TiO2 nanotubes morphology for medical implants: biological activity and corrosion resistance. Int. J. Nanomed. 16, 667–682 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S285805
R.M. Souto, M.M. Laz, R.L. Reis, Degradation characteristics of hydroxyapatite coatings on orthopaedic TiAlV in simulated physiological media investigated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biomaterials 24(23), 4213–4221 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00362-4
R. Venugopalan, J.J. Weimer, M.A. George, L.C. Lucas, The effect of nitrogen diffusion hardening on the surface chemistry and scratch resistance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Biomaterials 21(16), 1669–1677 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00049-1
S.L. de Assis, S. Wolynec, I. Costa, Corrosion characterization of titanium alloys by electrochemical techniques. Electrochim. Acta. 51(8–9), 1815–1819 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.02.121
F. Richter, C-A. Schiller, N. Wagner, Current interrupt technique—Measuring low impedances at high frequencies. Electrochem. Appl. 1 (2002)
C. Jaeggi, P. Kern, J. Michler, T. Zehnder, H. Siegenthaler, Anodic thin films on titanium used as masks for surface micropatterning of biomedical devices. Surf. Coat. Technol. 200(5–6), 1913–1919 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.08.021
A. Döner, Compparison of corrosion behaviors of bare Ti and TiO2. Emerg. Sci. J. 3(4), 235–240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.28991/esj-2019-01185
L. Mohan, C. Anandan, N. Rajendran, Effect of plasma nitriding on structure and biocompatibility of self-organised TiO2 nanotubes on Ti–6Al–7Nb. RSC Adv. 5, 41763–41771 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA05818J
C. Liu, Y. Wang, M. Wang, W. Huang, P.K. Chu, Electrochemical stability of TiO2 nanotubes with different diameters in artificial saliva. Surf. Coat. Technol. 206(1), 63–67 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.06.038
A.A. Al-Swayih, Electrochemical behavior of self-ordered titania nanotubes prepared by anodization as a promising material for biomedical applications. J. Am. Sci. 10(10), 165–173 (2014). https://doi.org/10.7537/marsjas101014.25
A.R. Rafieerad, A.R. Bushroa, E. Zalnezhad, M. Sarraf, W.J. Basirun, S. Baradaran, B. Nasiri-Tabrizi, Microstructural development and corrosion behavior of self-organized TiO2 nanotubes coated on Ti–6Al–7Nb. Ceram. Int. 41(9), 10844–10855 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.05.025
K.M. Deen, A. Farooq, M.A. Raza, W. Haider, Effect of electrolyte composition on TiO2 nanotubular structure formation and its electrochemical evaluation. Electrochim. Acta. 117, 329–335 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.11.108
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Narayanan, R., Panigrahi, M. & Tae-Yub, K. Electrochemical behavior of anodic nano-structured titania synthesized from stirred and unstirred electrolytes. Journal of Materials Research 38, 3160–3171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01040-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01040-7