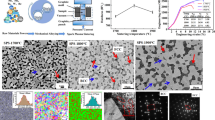
Abstract
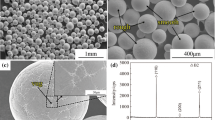
The Mo25Nb25Ta25W25 refractory high-entropy alloy, which was prepared by mechanical alloying utilizing pure elemental powder and spark plasma sintering (SPS), was explored in this work to determine the effects of sintering temperature on phases, microstructure, and mechanical characteristics. The alloyed powder with single BCC structure was fabricated after 30 h of ball-milling process and then was sintered under the SPS conditions of 1700 °C, 1800 °C, 1900 °C, along with the pressure of 50 MPa as well as the dwell time of 20 min. The findings demonstrated that the alloys consisted of BCC matrix phase and Ta and Nb-enriched FCC carbide precipitation phase. And the alloy sintered at 1800 °C possessed a compressive strength of 2571 MPa and fracture strain of 14.51%, which were mostly caused by grain refinement strengthening and particle strengthening. Additionally, the fracture mechanism of alloy was intergranular brittle fracture.
Graphical abstract
The BSE image and EDS results of local area and the TEM results indicated that two phases and their crystal structure after sintering were clearly identify as well as which phase the elements inclined to segregate in the sintered alloy.
The stress–strain curve and nano-indentation results indicated that the carbide particles with high hardness provided contribution to the high strength of the alloy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 299–303, 6 (2004)
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, A.J.B. Vincent, Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 213–218, 375–377 (2004)
J.H. Yan, M.J. Li, K.L. Li, J.W. Qiu, Y.J. Guo, Effects of Cr content on microstructure and mechanical properties of WMoNbTiCr high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perf. 2125–2133, 329 (2020)
J.B. Seol, J.W. Bae, Z.M. Li, J.C. Han, J.G. Kim, D. Raabe, H.S. Kim, Boron doped ultrastrong and ductile high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 366–376, 151 (2018)
F. Müller, B. Gorr, H.J. Christ, J. Müller, B. Butz, H. Chen, A. Kauffmann, M. Heilmaier, On the oxidation mechanism of refractory high entropy alloys. Corrosion Sci. 108161, 159 (2019)
P.K. Huang, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, S.K. Chen, Multi-principal-element alloys with improved oxidation and wear resistance for thermal spray coating. Adv. Eng. Mater. 74–78, 6 (2004)
A. Poulia, E. Georgatis, A. Lekatou, A.E. Karantzalis, Microstructure and wear behavior of a refractory high entropy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 50–63, 57 (2016)
T. Fujieda, H. Shiratori, K. Kuwabara, M. Hirotaa, T. Katoac, K. Yamanakab, Y. Koizumib, A. Chibab, S. Watanabe, CoCrFeNiTi-based high-entropy alloy with superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance achieved by a combination of additive manufacturing using selective electron beam melting and solution treatment. Mater. Lett. 148–151, 189 (2017)
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, D.B. Miracle, C.P. Chuang, P.K. Liaw, Refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 1758–1765, 18 (2010)
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, J.M. Scott, D.B. Miracle, Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 698–706, 19 (2011)
A.V. Kuznetsov, D.G. Shaysultanov, N.D. Stepanov et al., Tensile properties of an AlCrCuNiFeCo high-entropy alloy in as-cast and wrought conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 107–118, 533 (2012)
V.T. Nguyen, M. Qian, Z. Shi, T. Song, L. Huang, J. Zou, Compositional design of strong and ductile (tensile) Ti–Zr–Nb–Ta medium entropy alloys (MEAs) using the atomic mismatch approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 762–772, 742 (2019)
Z.Q. Fu, W.Q. Chen, S.C. Fang, D.Y. Zhang, H.Q. Xiao, D.Z. Zhu, Alloying behavior and deformation twinning in a CoNiFeCrAl0.6Ti0.4 high entropy alloy processed by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys. Compd. 316–323, 553 (2013)
D.O. Moskovskikh, S. Vorotilo, A.S. Sedegov, K.V. Kuskov, K.V. Bardasova, Ph.V. Kiryukhantsev-korneev, M. Zhukovskyi, A.S. Mukasyan, High-entropy (HfTaTiNbZr)C and (HfTaTiNbMo)C carbides fabricated through reactive high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 19008–19014, 46 (2020)
D.A. Porter, K.E. Easterling, Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 2nd edn. (Chapman & Hall, London, 1992)
Y.L. Chen, Y.H. Hu, C.A. Hsieh, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Competition between elements during mechanical alloying in an octonary multi-principal-element alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 768–775, 481 (2009)
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, J. Shi, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, Q.J. Zhang, Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiCuAl high-entropy solid solution synthesized by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. L31–L34, 485 (2009)
T. Ungar, Microstructural parameters from X-ray diffraction peak broadening. Scripta. Mater. 777–781, 51 (2004)
Q. Liu, G.F. Wang, X.C. Sui, Y.K. Liu, X. Li, J.L. Yang, Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-fine grained MoNbTaTiV refractory high-entropy alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2600–2607, 35 (2019)
O.N. Senkov, J.M. Scott, S.V. Senkova, D.B. Miracle, C.F. Woodward, Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 6043–6048, 509 (2011)
X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 233–238, 132 (2012)
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, C.T. Liu, Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 213, 109 (2011)
O.N. Senkov, S.L. Semiatin, Microstructure and properties of a refractory high-entropy alloy after cold working. J. Alloys Compd. 1110–1123, 649 (2015)
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1–184, 46 (2001)
A. Roh, D. Kim, S. Nam, D.I. Kim, H.Y. Kim, K.A. Lee, H. Choi, J.H. Kim, NbMoTaW refractory high entropy alloy composites strengthened by in-situ metal-non-metal compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 153423, 822 (2020)
S.R. Shatynski, The thermochemistry of transition metal carbides. Oxid. Metals 105–118, 13 (1979)
N.N. Guo, L. Wang, L.S. Luo, X.Z. Li, R.R. Chen, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ MC-carbide particulates-reinforced refractory high-entropy Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi matrix alloy composite. Intermetallics 74–77, 69 (2016)
S. Lv, Y. Zu, G. Chen, X. Fu, W. Zhou, An ultra-high strength CrMoNbWTi-C high entropy alloy co-strengthened by dispersed refractory IM and UHTC phases. J. Alloys Compd. 788, 1256–1264 (2019)
Q.Q. Wei, Q. Shen, J. Zhang, Y. Zhang, G.Q. Luo, L.M. Zhang, Microstructure evolution, mechanical properties and strengthening mechanism of refractory high-entropy alloy matrix composites with addition of TaC. J. Alloy. Compd. 1168–1175, 777 (2019)
Q.Q. Wei, G.Q. Luo, J. Zhang, S.J. Jiang, P.G. Chen, Q. Shen, L.M. Zhang, Designing high entropy alloy-ceramic eutectic composites of MoNbRe0.5TaW(TiC)x with high compressive strength. J. Alloy. Compd. 152846, 818 (2020)
M.A. Omar, I. Subuki, Sintering Characteristics of Injection Moulded 316 L Component Using Palm-Based Biopolymer Binder (INTECH Open Access Publisher, London, 2012)
C.J. Tong, M.R. Chen, J.W. Yeh, S.J. Lin, P.H. Lee, T.T. Shun, S.Y. Chang, Mechanical performance of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy system with multi-principal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1263–1271, 36 (2005)
W.R. Wang, W.L. Wang, S.C. Wang, Y.C. Tsai, C.H. Lai, J.W. Yeh, Effects of Al addition on the microstructure and mechanical property of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 44–51, 26 (2012)
H. Conrad, J. Narayan, On the grain size softening in nanocrystalline materials. Scripta Mater. 1025–1030, 42 (2000)
N.L. Okamoto, K. Yuge, K. Tanaka, H. Inui, E.P. George, Atomic displacement in the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy-a scaling factor to predict solid solution strengthening. AIP Adv. 125008, 6 (2016)
L. Li, Q.H. Fang, J. Li, B. Liu, Y. Liu, P.K. Liaw, Lattice-distortion dependent yield strength in high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 139323, 784 (2020)
Z.P. Wang, Q.H. Fang, J. Li, B. Liu, Y. Liu, Effect of lattice distortion on solid solution strengthening of BCC high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 349–354, 34 (2018)
P. Wang, Y. Wu, J.B. Liu, H.T. Wang, Impacts of atomic scale lattice distortion on dislocation activity in high-entropy alloys. Extre. Mech. Lett. 38–42, 17 (2017)
Y. Long, H. Zhang, T. Wang, X. Huang, Y. Li, J. Wu, H. Chen, High-strength Ti–6Al–4V with ultrafine-grained structure fabricated by high energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 408–414, 585 (2013)
R.L. Fleischer, The flow stress of body-centered cubic metals: inherent lattice hardening or solution hardening. Acta Metall. 1513–1519, 15 (1967)
F.R.N. Nabarro, The theory of solution hardening. Philos. Mag. 613–622, 35 (1977)
B. Kang, J. Lee, H.J. Ryu, S.H. Hong, Ultra-high strength WNbMoTaV high-entropy alloys with fine grain structure fabricated by powder metallurgical process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 616–624, 712 (2018)
J.Y. Pan, T. Dai, T. Lu, X.Y. Ni, J.W. Dai, M. Li, Microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and Ti8Nb23Mo23Ta23W23 high entropy alloys prepared by MA and SPS. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 362–366, 738 (2018)
K.M. Youssef, A.J. Zaddach, C.N. Niu, D.L. Irving, C.C. Koch, A novel low-density, high-hardness, high-entropy alloy with close-packed single-phase nanocrystalline structures. Mater. Res. Lett. 95–99, 3 (2014)
B. Gwalani, R.M. Pohan, J. Lee, B. Lee, R. Banerjee, H.J. Ryu, S.H. Hong, High-entropy alloy strengthened by in situ formation of entropy-stabilized nano-dispersoids. Sci. Rep. 14085, 8 (2018)
Z. Zhang, D.L. Chen, Consideration of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites: a model for predicting their yield strength. Script. Mater. 1321–1326, 54 (2006)
Z. Zhang, D.L. Chen, Contribution of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 148–152, 483 (2008)
N. Ramakrishnan, An analytical study on strengthening of particulate reinforced metal matrix composites. Acta Mater. 69–77, 44 (1996)
N. Hansen, The effect of grain size and strain on the tensile flow stress of aluminium at room temperature. Acta Metall. 863–869, 25 (1977)
M. Taya, R.J. Arsenault, Metal Matrix Composites-Thermomechanical Behaviour (Pergamon Press, New York, 1989)
L. Hu, M.J. Lin, B. Wei, Hypercooling limit and physical properties of liquid MoNbReTaW refractory high-entropy alloy. Philos. Magn. Lett. 312–319, 101 (2021)
M.B. Bever, Encyclopedia of Materials Science and Engineering (Pergamon Press, New York, 1986)
K. Nakamura, M. Yashima, Crystal structure of NaCl-type transition metal monocarbides MC (M=V, Ti, Nb, Ta, Hf, Zr), a neutron powder diffraction study. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 69–72, 148 (2008)
Q. Zhang, D.L. Chen, A model for predicting the particle size dependence of the low cycle fatigue life in discontinuously reinforced MMCs. Scripta Mater. 863–867, 51 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by Scientific and Technological Plan of Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (Grant No. Z191100002719009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhao, X., Zhang, S. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of MoNbTaW refractory high-entropy alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering. Journal of Materials Research 38, 484–496 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00833-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00833-6