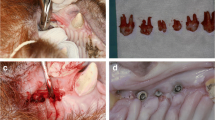
Abstract
The effect of Al2O3 with respect to TiO2 as abrasive for the osseointegration of dental implants has been questioned. The aim has been to clarify the advantages or disadvantages of mechanical and biological response. The implants studied were as-received with acid etching and sandblasted with TiO2 and with Al2O3 with posterior acid etching. Roughness, microhardness, residual stresses and fatigue were determined. In vivo tests were realized in minipigs. The percentage of bone index contact (BIC) after 2 and 6 weeks of implantation was determined histometric evaluation. Results showed that the roughness of the Al2O3 treated implants was 2.54 respect to 0.80 μm for TiO2, microhardness were 370 and 241 HVN and compressive residual stresses of − 2450 and − 78.3 MPa, respectively. These compressive stresses justify the higher fatigue strength of the Al2O3 sandblasted samples. BIC values after 6 weeks were 63% compared to 38% for TiO2.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
T. Albrektsson, P.I. BrånemarkI, H.A. Hansson, J. Lindström, Osseointegrated titanium implants: requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop. 52, 155–170 (1981). https://doi.org/10.3109/17453678108991776
A. Bagno, C. Di Bello, Surface treatments and roughness properties of Ti-based biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15, 935–949 (2004)
L. Le Guéhennec, A. Soueidan, P. Layrolle, Y. Amouriq, Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 23, 844–854 (2007)
C. Aparicio, D. Rodriguez, F.J. Gil, Variation of roughness and adhesion strength of deposited apatite layers on titanium dental implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 31(2), 320–324 (2011)
Y.S. Al Jabbari, S. Zinelis, G. Eliades, Effect of sandblasting conditions on alumina retention in representative dental alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 31, 249–255 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4012/dmj.2011-210
T. Nordin, J. Graf, A. Frykholm, L. Helldén, Early functional loading of sand-blasted and acid-etched (SLA) Straumann implants following immediate placement in maxillary extraction sockets. Clinical and radiographic result. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 18, 441–451 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01387.x
D. Buser, R.K. Schenk, S. Steinemann, Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 25, 889–902 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820250708
R.G.T. Geesink, K. de Groot, C.P.A.T. Klein, Chemical implant fixation using hydroxyl-apatite coatings. Clin. Orthop. 225, 147–170 (1987)
G. Giavaresi, M. Fini, A. Cigada, R. Chiesa, R. Rondelli, L. Rimondini, P. Torricelli, N. Aldini, R. Giardino, Mechanical and histomorphometric evaluations of titanium implants with different surface treatments inserted in sheep cortical bone. Biomaterials 24, 1583–1594 (2003)
H. Schliephake, D. Scharnweber, Chemical and biological functionalization of titanium for dental implants. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 2404–2414 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1039/b715355b
R. Fraioli, F. Rechenmacher, S. Neubauer, J.M. Manero, F.J. Gil, H. Kessler, C. Mas-Moruno, Mimicking bone extracellular matrix: integrin-binding peptidomimetics enhance osteoblast-like cells adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation on titanium. Colloids Surf. B 128, 191–200 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.12.057
B.D. Boyan, C.H. Lohmann, D.D. Dean, V.L. Sylvia, D.L. Cochran, Z. Schwartz, Mechanisms involved in osteoblast response to implant surface morphology. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 31, 357–371 (2001)
G. Giavaresi, M. Fini, A. Cigada, Histomorphometric and microhardness assessments of sheep cortical bone surrounding titanium implants with different surface treatments. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 67A, 112–120 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.10044
C. Aparicio, D. Rodriguez, F.J. Gil, Variation of roughness and adhesion strength of deposited apatite layers on titanium dental implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 31, 320–324 (2011)
A. Fukuda, M. Takemoto, T. Saito, S. Fujibayashi, M. Neo, D.K. Pattanayak, K. Sasaki, N. Nishida, T. Kokubo, T. Nakamura, Osteoinduction of porous Ti implants with a channel structure fabricated by selective laser melting. Acta Biomater. 7, 2327–2336 (2011)
S. Ferraris, S. Spriano, G. Pan, A. Venturello, C.L. Bianchi, R. Chiesa et al., Surface modification of Ti-6Al-4V alloy for biomineralization and specific biological response: part I, inorganic modification. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 22, 533–545 (2011)
S. Ferraris, F. Truffa Giachet, M. Miola, E. Bertone, A. Varesano, C. Vineis, Nanogrooves and keratin nanofibers on titanium surfaces aimed at driving gingival fibroblasts alignment and proliferation without increasing bacterial adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. 76, 1–12 (2017)
H. Deppe, C. Wolff, F. Bauer, R. Ruthenberg, A. Sculean, T. Mücke, Dental implant surfaces after insertion in bone: an in vitro study in four commercial implant systems. Clin. Oral. Invest. 22, 1593–1600 (2017)
C. Massaro, P. Rotolo, F. de Ricardis, E. Milella, A. Napoli, M. Wieland, Comparative investigation of the surface properties of commercial titanium dental implants. Part I: chemical composition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 13, 535–548 (2002)
F.J. Gil, E. Espinar, J.M. Llamas, P. Sevilla, Fatigue life of bioactive titanium dental implants treated by means of Grit Blasting and Thermo-Chemical treatment. Clin. Impl. Dent. Rel. Res. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2012.00468.x
L. Pazos, P. Corengia, H. Svoboda, Effect of surface treatments on the fatigue life of titanium for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 3, 416–424 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2010.03.006
P. Schupbach, R. Glauser, S. Bauer, Al2O3 particles on titanium dental implant systems following sandblasting and acid-etching process. Int J Biomater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6318429
H.J. Rønold, S.P. Lyngstadaas, J.E. Ellingsen, A study on the effect of dual blasting with TiO2 on titanium implant surfaces on functional attachment in bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 67, 524–530 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.10580
D. Buser, Titanium for dental applications (II): implants with roughened surfaces, in Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications. ed. by D.M. Brunette, P. Tengvall, M. Textor, P. Thomsen (Berlin, Springer, 2001), pp. 875–888
C.H. Han, C.B. Johansson, A. Wennerberg, T. Albrektsson, Quantitative and qualitative investigations of surface enlarged titanium and titanium alloy implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 9, 1–10 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.1998.090101.x
C. Aparicio, E. Engel, F.J. Gil, J.A. Planell, Human-osteoblast proliferation and differentiation on grit-blasted and bioactive titanium for dental applications. J. Mater. Sci. 13, 1105–1111 (2002)
K. Anselme, Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials 21, 667–681 (2000)
J.Y. Martin, Z. Schwartz, T.W. Hummert, Effect of titanium surface roughness on proliferation, differentiation, and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells (MG63). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29, 389–401 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820290314
B.D. Boyan, T.W. Hummert, D.D. Dean, Z. Schwartz, Role of material surfaces in regulating bone and cartilage cell response. Biomaterials 17, 137–146 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(96)85758-9
F.J. Gil, E. Espinar, J.M. Llamas, P. Sevilla, Fatigue life of bioactive titanium dental implants treated by means of grit-blasting and thermo-chemical treatment. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 16, 273–281 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2012.00468.x
F.J. Gil, J.A. Planell, A. Padrós, C. Aparicio, The effect of sand blasting and heat treatment on the fatigue behavior of titanium for dental implant applications. Dent. Mater. 23, 486–491 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2006.03.003
K.H. Lau, A. Yoo, S.P. Wang, Aluminum stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro by a mechanism that is the different from fluorine. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 105, 93–105 (1991)
A. Wenneberg, T. Albrektsson, J. Lausmaa, Torque and histomorphometric evaluation of c.p. titanium screws blasted with 25 and 75 mm sized particles of Al2O3. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 30, 251–260 (1996)
A. Piatelli, L. Manzon, A. Scarano, M. Paolantonio, M. Piatelli, Histologic and morphologic analysis of the bone response to machined and sandblasted titanium implants: an experimental study in rabbit. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac Implants 13, 805–810 (1998)
C.Y. Guo, J.P. Matinlinna, J.K.H. Tsoi, A.T.H. Tang, Residual contaminations of silicon-based glass, alumina an aluminum grits on a Titanium surface after sandblasting. SILICON 11, 2313–2320 (2019)
A. Canabarro, M.G. Diniz, L. Paciornik, E.M. Sampaio, M.M. Beloti, A.L. Rosa, R.G. Fischer, High concentration of residual aluminum oxide on titanium surface inhibits extracellular matrix mineralization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 87A, 588–597 (2008)
A. Piattelli, M. Degidi, M. Paolantonio, C. Mangano, A. Scarano, Residual aluminum oxide on the surface of titanium implants has no effect on osseointegration. Biomaterials 24(22), 4081–4089 (2003)
H.J. Ronold, J.E. Ellingsen, Effect of micro-roughness produced by TiO2 blasting-tensiles testing of bone attachment by using coin-shaped implants. Biomaterials 23, 4211–4219 (2002)
S.A. Gehrke, M.P. Ramírez-Fernandez, J.M. Granero Marín, M. Barbosa Salles, M. Del Fabbro, J.L. Calvo Guirado, A comparative evaluation between aluminium and titanium dioxide microparticles for blasting the surface titanium dental implants: an experimental study in rabbits. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 29(7), 802–807 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12973.H
G.B. Valverde, R. Jimbo, H.S. Teixeira, E.A. Bonfante, M.N. Janal, P.G. Coelho, Evaluation of Surface roughness as a function of múltiple blasting processing variables. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 24(2), 238–242 (2013)
G.R.M. Matos, Surface roughness of dental implant and osseointegration. J. Maxillofac. Oral. Surg. 20, 1–4 (2021)
G. Marenzi, G. Spagnuolo, J.C. Sammartino, R. Gasparro, A. Rebaudi, M. Salerno, Micro-scale surface pattering of titanium dental implants by anodization in the presence of modifying salts. Materials 30, 1753 (2019)
E. Velasco-Ortega, I. Ortiz-García, A. Jiménez-Guerra, L. Monsalve-Guil, F. Munoz-Guzon, R.A. Perez, F.J. Gil, Comparison between sandblasted acid-etched and oxidized titanium dental implants: In vivo study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 3267 (2019)
D. Labonte, A.K. Lenz, M.L. Oyen, On the relationship between indentation hardness and modulus, and the damage resistance of biological materials. Acta Biomater. 57, 373–383 (2017)
B. Yin, J.L. Guo, J.Z. Wang, S. Li, Y.K. Liu, Y.Z. Zhang, Bone material properties of human phalanges using vickers indentation. Orthop. Surg. 11, 487–492 (2019)
J. Samuel, D. Sinha, J.C.G. Zhao, X. Wang, Water residing in small ultrastructural spaces plays a critical role in the mechanical behavior of bone. Bone 59, 199–206 (2014)
E. Velasco, L. Monsalve-Guil, A. Jimenez, I. Ortiz, J. Moreno-Muñoz, E. Nuñez-Marquez, M. Pegueroles, R. Perez, F.J. Gil, Importance of the roughness and residual stresses of dental implants on fatigue and osseointegration behavior. In vivo study in rabbits. J. Oral Inv. 42, 469–476 (2016)
F. Rupp, L. Liang, J. Geis-Gerstorfer, L. Scheideler, F. Huttig, Surface characteristics of dental implants: a review. Dent. Mater. 34, 40–57 (2018)
E. Velasco-Ortega, A. Flichy-Fernández, M. Punset, A. Jiménez-Guerra, J.M. Manero, F.J. Gil, Fracture and fatigue of titanium narrow dental implants: new trends in order to improve the mechanical response. Materials 12(22), 3728 (2019)
R.A. Pérez, J. Gargallo, P. Altuna, M. Herrero-Climent, F.J. Gil, Fatigue of narrow dental implants: influence of the hardening method. Materials 13, 1429 (2020)
Funding
This research was funded by Spanish Government and European Union FEDER by the concession of the grant RTI2018-098075-B-C22, the Spanish Government by the Ramón y Cajal Program (RYC2018-025977-I) and the research group Generalitat de Catalunya 2017SGR708.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FJG, RAP and YO worked in the materials science aspects (roughness, microhardness, fatigue tests) and CH, JLG and DT-L in the clinical aspects (in vivo tests).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not any conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical Commission of the Faculty of Veterinary Sciences of the University of Cordoba (Spain). Reference SSA-SI-MD-ps 450/19640.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gil, F.J., Pérez, R.A., Olmos, J. et al. The effect of using Al2O3 and TiO2 in sandblasting of titanium dental implants. Journal of Materials Research 37, 2604–2613 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00534-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00534-0