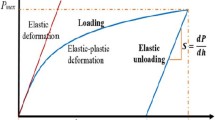
Abstract
A microhardness tester equipped with a Vickers indenter allows the determination of mechanical properties of a large variety of materials by analyzing load–displacement curves. In present work, a new model to compute the coefficient of proportionality K (named K-factor) between P and h relating to the pile-up have been developed. It was proved that indenter tip defect must be absolutely considered for an accurate determination of the contact area reducing an overestimation of mechanical properties and better fitting the loading curve. The proposed model is validated on a large variety of materials, i.e. carbides, nitrides and oxides showing sink-in phenomenon and steel, stainless steel, brass, bronze and copper having pile-up deformation mode. The model is compared with previous developed ones for sink-in and pile-up that can be easily applied but ignoring deformation mode and discarding the indenter defects will lead to not quite right no phenomenologically representative mechanical properties.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.-V. Hainsworth, H.-W. Chandler, T.-F. Page, Analysis of nanoindentation load–displacement loading curves. J. Mater. Res. 11, 8 (1996)
Loubet, J.-L., Georges, J.-M. and Meille, J.: In Microindentation Techniques in Materials Science and Engineering, edited by Blau, P. J., and Lawn, B. R.: American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia. Pp. 72–89 (1986).
K. Zeng, D. Rowcliffe, Analysis of penetration curves produced by sharp indentations on ceramic materials. Philos. Mag. A 74, 1107–1116 (1996)
Y.-T. Cheng, C.-M. Cheng, Relationships between hardness, elastic modulus, and the work of indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 614 (1998)
Y. Sun, Y. Zheng, T. Bell, J. Smith, Indenter tip radius and load frame compliance calibration using nanoindentation loading curves. Philos. Mag. Lett. 79(9), 649–658 (1999)
J. Malzbender, G. de With, J. den Toonder, The P–h2 relationship in indentation. J. Mater. Res. 15(5), 1209–1212 (2000)
W.-C. Oliver, G.-M. Pharr, An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7(6), 1564–1583 (1992)
J.-L. Loubet, M. Bauer, S. Tonckbec, B. Gauthier-Manuel, Nanoindentation with a Surface Force Apparatus, Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behaviour of Materials Having Ultra-Fine Microstructures (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1993)
M. YetnaN’Jock, D. Chicot, J.-M. Ndjaka, J. Lesage, X. Decoopman, F. Roudet, A. Mejias, A criterion to identify sinking-in and piling-up in indentation of materials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 90, 145–150 (2015)
W.-C. Oliver, G.-M. Phar, Measurement of harness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advanced in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mat. Res. 19(1), 3–20 (2004)
D. Chicot, P. De Baets, M.-H. Staia, E.-S. Puchi-Cabrera, G. Louis, Y. Perez Delgado, J. Vleugels, Influence of tip defect and indenter shape on the mechanical properties determination by indentation of a TiB2–60%B4C ceramic composite. Int. J. Refrac. Metals Hard Mater. 38, 102–110 (2013)
J. Gong, H. Miao, Z. Peng, On the contact area for nanoindentation tests with Berkovich indenter: case study on soda-lime glass. Mater. Lett. 58, 1349–1353 (2004)
M. Troyon, L. Huang, Correction factor for contact area in nanoindentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 20, 610–617 (2005)
D. Chicot, M. Yetna Njock, E.-S. Puchi-Cabrera, A. Iost, M.-H. Staia, G. Louis, G. Bouscarrat, R. Aumaitre, A contact area function for Berkovich nanoindentation: Case study on TiHfCN thin film. Thin Solid Films 558, 259–266 (2014)
Guillonneau, G.: Nouvelles techniques de nanoindentation pour des conditions expérimentales difficiles: très faibles enfoncements, surfaces rugueuses, température. Autre. Ecole Centrale de Lyon (2012).
G. Hochstetter, A. Jimenez, J.-L. Loubet, Strain-rate effects on hardness of glassy polymers in the nanoscale range. Comparison between quasi-static and continuous stiffness measurements. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B. 38, 681–692 (1999)
S. Bec, A. Tonck, J.-M. Georges, E. Georges, J.-L. Loubet, Improvements in the indentation method with a surface force apparatus. Philos. Mag. A 74, 1061 (1996)
J.-E. Field, R.-H. Telling, The Young Modulus and Poisson Ratio of Diamond, Research Note (Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge, 1999)
G.-D. Quinn, P.-L. Patel, I. Lloyd, Effect of loading rate upon conventional ceramic microindentation hardness. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 107, 299–306 (2002)
A.-C. Fischer-Cripps, Critical review of analysis and interpretation of nano-indentation test data. Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 4153–4165 (2006)
D. Chicot, F. Roudet, A. Zaoui, G. Louis, V. Lepingle, Influence of visco-elasto-plastic properties of magnetite on the elastic modulus: multicyclic indentation and theoretical studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 119(1–2), 75–81 (2010)
W.-D. Nix, H. Gao, Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: A law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46(3), 411–425 (1998)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the General Directorate of Scientific Research and Technological Development of Algeria (DGRSDT: Under the authority of the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research in charge of scientific research).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript has been compiled with contributions from all authors. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habibi, S., Chicot, D., Mejias, A. et al. The P–h2 relationship on load–displacement curve considering pile-up deformation mode in instrumented indentation. Journal of Materials Research 36, 3074–3085 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00286-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00286-3