Abstract
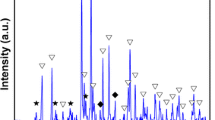
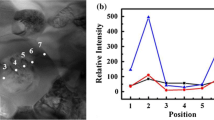
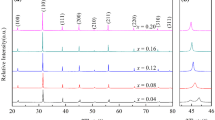
0.5wt%MnO2-doped (1 − x)BaTiO3–xBiCoO3 ceramics short as (1 − x)BT–xBC–M sintered in air and reducing atmosphere via solid-state process were investigated. The X-ray diffraction results showed that solid solubility in (1 − x)BT–xBC ceramics sintered in the air was higher than that in reducing atmosphere. (1 − x)BT–xBC–M ceramics sintered in air transformed from tetragonal to pseudo-cubic phase when x ≥ 0.1. The scanning electron microscopy results indicated that the average grain size increased with the BC component increasing; however, opposite phenomena occurred in samples sintered in the reducing atmosphere. The dielectric temperature curves of samples sintered in reducing atmosphere were flatted with excellent insulation resistivity of an order of magnitude of 1013 Ω·cm, while anomalous dielectric constant and dielectric loss of samples sintered in the air with deteriorated insulation resistivity of an order of magnitude of 107 Ω·cm. The anti-reduction mechanism of (1 − x)BT–xBC–M system was explained by the “electron–hole” trapping effect and formation of defect dipoles \(\left[ {{\text{Mn}}_{{{\text{Ti}}}} ^{{\prime \prime }} - V_{{\text{O}}}^{{ \cdot \cdot }} } \right]\) and \(\left[ {2{\text{Co}}_{{{\text{Ti}}}} ^{\prime } - V_{{\text{O}}}^{{ \cdot \cdot }} } \right]\).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Pan, C. Randall, A brief introduction to ceramic capacitors. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 26(3), 44 (2010)
R. Zuo, N. Zhang, L. Li, Interfacial:reaction of Ag/Pd metals with Pb-based relaxor ferroelectrics including additives. Ceram. Int. 27, 85 (2001)
H. Gong, X. Wang, L. Li, Interfacial diffusionbehavior inNi-BaTiO3 MLCCs with ultra-thin active layers. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 417 (2014)
H. Saito, H. Chazono, H. Kishi, X7R multilayer ceramic capacitors with nickel electrodes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 2307 (1991)
Y. Sakabe, T. Reynolds, Base-metal electrode capacitors. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 81, 24 (2002)
G.H. Haertling, Ferroelectric ceramics: history and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 797 (1999)
D. Wang, Z. Fan, S. Zhang, Ultrahigh piezoelectricity in lead-free piezoceramics by synergistic design. Nano Energy 76, 104944 (2020)
S. Wang, S. Zhang, X. Zhou, Effect of sintering atmospheres on the microstructure and dielectric properties of Yb/Mg co-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. Mater. Lett. 59, 2457 (2005)
Y. Tsur, T.D. Dunbar, C.A. Randall, Crystal and defect chemistry of rare earth cations in BaTiO3. J. Electroceram. 7, 25 (2001)
L. Chen, H. Fan, S. Zhang, Investigation of MnO2-doped (Ba, Ca)TiO3 lead-free ceramics for high power piezoelectric applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 3568 (2017)
B.M. Teresa, V. Massimo, B. Vincenzo, Incorporation of Er3+ into BaTiO3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 1569 (2010)
G. Jonker, E. Havinga, The influence of foreign ions on the crystal lattice of barium titanate. Mater. Res. Bull. 17, 345 (1982)
H. Kishi, N. Kohzu, T. Okuda, Effect of occupational sites of rare-earth elements on the microstructure in BaTiO3. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 5452 (1999)
H.M. Chan, M.R. Harmer, D.M. Smyth, Compensating defects in highly donor-doped BaTiO3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 69, 507 (1986)
J. Bernard, D. Houivet, J. El Fallah, J.M. Haussonne, MgTiO3 for Cubase metal muItiIayer ceramic capacitors. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 1877 (2004)
D. Hennings, H. Schreinemacher, Ca-acceptors in dielectric ceramics sintered in reducive atmospheres. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 15, 795 (1995)
Y. Han, J. Appleby, D. Smyth, Calcium as acceptor impurity in BaTiO3. J. Am Ceram. Soc. 70, 96 (1987)
Z. Sheng, X. Wang, Effect of MnO2 on the electrical and dielectric properties of Y-doped Ba0.95Ca0.05Ti0.85Zr0.15O3 ceramics in reducing atmosphere. Ceram. Int. 40, 13833 (2014)
X. Cheng, X. Li, Z. Zhao, Influence of reoxidation time on electrical properties of Y2O3-doped BaTiO3 ceramics sintered in a reducing atmosphere. J. Mater. Sci. 274, 012124 (2017)
J. Rödel, G. Tomandl, Degradation of Mn-doped BaTiO3 ceramic under a high d.c. electric field. J. Mater. Sci. 19, 3515 (1984)
H.J. Hagemann, H. Ihrig, Valence change and phase stability of 3d-doped BaTiO3 annealed in oxygen and hydrogen. Phys. Rev. B 20, 3871 (1979)
S.H. Yoon, C.A. Randall, K.H. Hur, Difference between resistance degradation of fixedvalence acceptor (Mg) and variable valence acceptor (Mn)-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 0641011 (2010)
H. Gong, X. Wang, L. Li, Electrical and reliability characteristics of Mn-doped nano BaTiO3-based ceramics for ultrathin multilayer ceramic capacitor application. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 114119 (2012)
K. Albertsen, D. Hennings, O. Steigelmann, Donor/acceptor charge complex formation, the role of firingatmospheres. J. Electroceram. 23, 193 (1998)
R. Waser, T. Baiatu, K.H. Härdtl, Dc electrical degradation of perovskite-type titanates: I, ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. 73, 1645 (2010)
S.H. Cha, Y.H. Han, Effects of Mn doping on dielectric properties of Mg-doped BaTiO3. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 751 (2006)
S.K. Jo, S.H. Kang, Y.H. Han, Dielectric properties of Mg-and Mn-doped (Ba1−xSrx)(Ti1-yZry)O3. Met. Mater. Int. 19, 341 (2013)
J. Jeong, Y.H. Han et al., Electrical properties of acceptor doped BaTiO3. J. Electroceram. 13, 549 (2004)
D. Han, C. Wang, D. Lu, A temperature stable (Ba1–xCex)(Ti1–x/2Mgx/2)O3 lead-free ceramic for X4D capacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 821, 153480 (2020)
X. Lai, H. Hao, H. Liu, Structure and dielectric properties of MgO-coated BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 8963 (2020)
L. Wu, X. Wang, L. Li, Core-shell BaTiO3@BiScO3 particles for local graded dielectric ceramicswith enhanced temperature stability and energy storage capability. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 113 (2016)
M. Liu, H. Hao, W. Chen, Preparation and dielectric properties of X9R core–shell BaTiO3 ceramics coated by BiAlO3–BaTiO3. Ceram. Int. 42, 379 (2016)
Z. Sheng, X. Wang, L. Li, Dielectric properties and microstructures of Ta-doped BaTiO3-(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 ceramic for X9R application. J. Mater. Sci. 28, 3768 (2017)
Z. Shen, X. Wang, L. Li, Nb-doped BaTiO3-(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 ceramics with core-shell structure for high-temperature dielectric applications. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 115, 435 (2017)
H. Hao, H. Liu, S. Zhang, Fabrication, structure and property of BaTiO3-based dielectric ceramics with a multilayer core–shell structure. Scr. Mater. 67, 451 (2012)
C. Chen, H. Hao, J. Cui, The role of diffusion behavior on the formation and evolution of the core-shell structure in BaTiO3-based ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 103, 304 (2019)
L. Wang, W. Ren, W. Ma, Improved electrical properties for Mn-doped lead-free piezoelectric potassium sodium niobate ceramics. AIP. Adv. 5, 097120 (2015)
W. Liu, C. Randall, Thermally stimulated relaxation in Fe-doped SrTiO3 systems: I. single crystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 3245 (2008)
S. Yoon, C. Randall, K. Hur, Correlation between resistancedegradation and thermally stimulated depolarization current inacceptor (Mg)-doped BaTiO3 submicrometer fine-grain ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 1950 (2012)
L. Zhang, H. Hao, H. Liu, Defect structure-electrical property relationship in Mn-dopedcalcium strontium titanate dielectric ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 4638 (2017)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSFC-Guangdong Joint Funds of the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1601209), Major Program of the Natural Science Foundation of China (51790490), Foshan Xianhu Laboratory of the Advanced Energy Science and Technology Guangdong Laboratory, and Natural Science Foundation of China (51872213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Hao, H., Luo, Z. et al. Electric property, anti-reduction mechanism of (1 − x)BaTiO3–xBiCoO3–Mn ceramics. Journal of Materials Research 36, 1037–1047 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-020-00002-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-020-00002-7