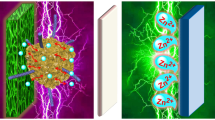
Abstract
We previously demonstrated that electrode architectures comprising nanoscale birnessite-like MnOx affixed to three-dimensional carbon nanofoam (CNF) scaffolds offer performance advantages when used as cathodes in rechargeable zinc-ion cells. To discern chemical and physical changes at the Mn0x@CNF electrode upon deep charge/discharge in aqueous Zn2+-containing electrolytes, we deploy electroanalytical methods and ex situ characterization by microscopy, elemental analysis, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, x-ray diffraction, and x-ray pair distribution function analyses. Our findings verify that redox processes at the MnOx are accompanied by reversible precipitation/dissolution of crystalline zinc hydroxide sulfate (Zn4(0H)6(S04)·xH20), mediated by the more uniformly reactive electrode structure inherent to the CNF scaffold.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Xu, B. Li, H. Du, and F. Kang: Energetic zinc ion chemistry: the rechargeable zinc ion battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 933–935 (2012).
R.K. Guduru and J.C. Icaza: A brief review on multivalent intercalation batteries with aqueous electrolytes. Nanomaterials 6, 1–19 (2016).
M. Song, H. Tan, D. Chao, and H.J. Fan: Recent advances in Zn-ion batteries. Adv. Fund. Mater. 28, 1802564 (2018).
D. Kundu, B.D. Adams, V. Duffort, S. Hosseini Vajargah, and L.F. Nazar: A high-capacity and long-life aqueous rechargeable zinc battery using a metal oxide intercalation cathode. Nat. Energy 1, 16119 (2016).
V. Soundharrajan, B. Sambandam, S. Kim, M.H. Alfaruqi, D. Yunianto Putro, J. Jo, S. Kim, V. Mathew, Y.-K. Sun, and J. Kim: Na2V6016·3H20 barnesite nanorod: an open door to display a stable and high energy for aqueous rechargeable Zn-ion batteries as cathodes. Nano Lett. 18, 2402–2410 (2018).
D. Kundu, S. Hosseini Vajargah, L. Wan, B. Adams, D. Prendergast, and L.F. Nazar: Aqueous vs. nonaqueous Zn-ion batteries: consequences of the desolvation penalty at the interface. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 881–892 (2018).
C. Wei, C. Xu, B. Li, H. Du, and F. Kang: Preparation and characterization of manganese dioxides with nano-sized tunnel structures for zinc ion storage. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 73, 1487–1491 (2012).
B. Lee, C.S. Yoon, H.R. Lee, K.Y. Chung, B.W. Cho, and S.H. Oh: Electrochemically-induced reversible transition from the tunneled to layered polymorphs of manganese dioxide. Sci. Rep. 4, 6066 (2014).
M.H. Alfaruqi, J. Gim, S. Kim, J. Song, D.T. Pham, J. Jo, Z. Xiu, V. Mathew, and J. Kim: A layered δ-Mn02 nanoflake cathode with high zinc-storage capacities for eco-friendly battery applications. Electrochem. Commun. 60, 121–125 (2015).
M.H. Alfaruqi, V. Mathew, J. Gim, S. Kim, J. Song, J.P. Baboo, S.H. Choi, and J. Kim: Electrochemically induced structural transformation in a ψ-Mn02 cathode of a high capacity zinc-ion battery system. Chem. Mater. 27, 3609–3620 (2015).
B. Lee, H.R. Lee, H. Kim, K.Y. Chung, B.W. Cho, and S.H. Oh: Elucidating the intercalation mechanism of zinc ions into α-Mn02 for rechargeable zinc batteries. Chem. Commun. 51, 9265–9268 (2015).
M.H. Alfaruqi, J. Gim, S. Kim, J. Song, J. Jo, S. Kim, V. Mathew, and J. Kim: Enhanced reversible divalent zinc storage in a structurally stable α-Mn02 nanorod electrode. J. Power Sources 288, 320–327 (2015).
H. Pan, Y. Shao, P. Yan, Y. Cheng, K.S. Han, Z. Nie, C. Wang, J. Yang, X. Li, P. Bhattacharya, K.T. Mueller, and J. Liu: Reversible aqueous zinc/manganese oxide energy storage from conversion reactions. Nat. Energy 1, 16039 (2016).
B. Lee, H.R. Seo, H.R. Lee, C.S. Yoon, J.H. Kim, K.Y. Chung, B.W. Cho, and S.H. Oh: Critical role of pH evolution of electrolyte in the reaction mechanism for rechargeable zinc batteries. ChemSusChem. 9, 2948–2956 (2016).
W. Sun, F. Wang, S. Hou, C. Yang, X. Fan, Z. Ma, T. Gao, F. Han, R. Hu, M. Zhu, and C. Wang: Zn/Mn02 battery chemistry with H+ and Zn2+ coin-sertion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 9775–9778 (2017).
J.S. Ko, M.B. Sassin, J.F. Parker, D.R. Rolison, and J.W. Long: Combining battery-like and pseudocapacitive charge storage in 3D MnOx@carbon electrode architectures for zinc-ion cells. Sustainable Energy Fuels 2, 626–636 (2018).
J.C. Lytle, J.M. Wallace, M.B. Sassin, A.J. Barrow, J.W. Long, J.L. Dysart, C.H. Renninger, M.P. Saunders, N.L. Brandell, and D.R. Rolison: The right kind of interior for multifunctional electrode architectures: carbon nano-foam papers with aperiodic submicrometre pore networks interconnected in 3D. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 1913–1925 (2011).
M.B. Sassin, C.P. Hoag, B.T. Willis, N.W. Kucko, D.R. Rolison, and J.W. Long: Designing high-performance electrochemical energy-storage nanoarchitectures to balance rate and capacity. Nanoscale 5, 1649–1657 (2013).
A.E. Fischer, K.A. Pettigrew, D.R. Rolison, R.M. Stroud, and J.W. Long: Incorporation of homogeneous, nanoscale Mn02 within ultraporous carbon structures via self-limiting electroless deposition: implications for electrochemical capacitors. Nano Lett. 7, 281–286 (2007).
A.E. Fischer, M.P. Saunders, K.A. Pettigrew, D.R. Rolison, and J.W. Long: Electroless deposition of nanoscale MnO2 on ultraporous carbon nano-architectures: correlation of evolving pore-solid structure and electrochemical performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 155, A246–A252 (2008).
P.J. Chupas, X. Qui, J.C. Hanson, P.L. Lee, C.P. Grey, and S.J. Billinge: Rapid-acquisition pair distribution function (RA-PDF) analysis. J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 1342–1347 (2003).
A.P. Hammersley: FIT2D: a multi-purpose data reduction, analysis and visualization program. J. Appl. Cryst. 49, 646–652 (2016).
C.L. Farrow, P. Juhas, J.W. Liu, D. Bryndin, E.S. Bozln, J. Bloch, T. Profen, and S.J. Billinge: PDFfit2 and PDFgui: Computer programs for studying nanostructure in crystals. J. Phys. Condens. Matter., 19, 335219 (2007).
J.S. Ko, M.B. Sassin, D.R. Rolison, and J.W. Long: Deconvolving double-layer, pseudocapacitance, and battery-like charge-storage mechanisms in nanoscale LiMn204 at 3D carbon architectures. Electrochim. Acta 275, 225–235 (2018).
M.D. Donakowski, J.M. Wallace, M.B. Sassin, K.W. Chapman, J.F. Parker, J.W. Long, and D.R. Rolison: Crystal engineering in 3D: converting nanoscale lamellar manganese oxide to cubic spinel while affixed to a carbon architecture. CrystEngComm 18, 6035–6048 (2016).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the U.S. Office of Naval Research. J.S.K. is an NRL-NRC Postdoctoral Associate (2016-2018). This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. The authors would like to thank Dr. Olaf Borkiewicz of Argonne National Laboratory for data acquisition, integration, and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary material
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, J.S., Donakowski, M.D., Sassin, M.B. et al. Deciphering charge-storage mechanisms in 3D MnOx@carbon electrode nanoarchitectures for rechargeable zinc-ion cells. MRS Communications 9, 99–106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.3