Abstract
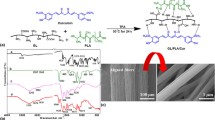
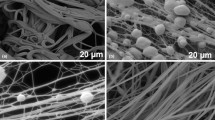
In this study, based on the collection process, three-dimensional aligned fiber scaffolds from gelatin and zein protein were manufactured using Forcespinning®. The homogeneous blending of gelatin:zein (1:4) showed improved tensile and good hydrophobic properties (water contact angle of 115 °C). Cell viability, adhesion, proliferation, and drug release were measured. The cell viability was studied with human fibroblasts and a low cytotoxic effect was observed. Berberine drug release was measured and sustained release rate was observed over 15 days. The morphologic features, prolonged drug release, and cytotoxicity results suggest that these fibers could be appropriate for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.G. Flemming, C.J. Murphy, G.A. Abrams, S.L. Goodman, and P.F. Nealey: Effects of synthetic micro- and nano-structured surfaces on cell behavior. Biomaterials 20, 573 (1999).
C.Y. Tay, S.A. Irvine, F.Y.C. Boey, L.P. Tan, and S. Venkatraman: Micro-/nano-engineered cellular responses for soft tissue engineering and biomedical applications. Small 7, 1361 (2011).
H.N. Kim, A. Jiao, N.S. Hwang, M.S. Kim, D.H. Kang, D.H. Kim, and K.Y. Suh: Nanotopography-guided tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 65, 536 (2013).
X. Xin, M. Hussain, and J.J. Mao: Continuing differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and induced chondrogenic and osteogenic lineages in electrospun PLGA nanofiber scaffold. Biomaterials 28, 316 (2007).
H. Yoshimoto, Y.M. Shin, H. Terai, and J.P. Vacanti: A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 24, 2077 (2003).
R.J. Wade, E.J. Bassin, C.B. Rodell, and J.A. Burdick: Protease-degradable electrospun fibrous hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 6, 6639 (2015).
Y.J. Tan, X. Tan, W.Y. Yeong, and S.B. Tor: Additive manufacturing of patient-customizable scaffolds for tubular tissues using the melt-drawing method. Materials 9, 893 (2016).
L. Wang, M.W. Chang, Z. Ahmad, H. Zheng, and J.S. Li: Mass and controlled fabrication of aligned PVP fibers for matrix type antibiotic drug delivery systems. Chem. Eng. J. 307, 661 (2017).
J. Kazantseva, R. Ivanov, M. Gasik, T. Neuman, and I. Hussainova: Graphene-augmented nanofiber scaffolds demonstrate new features in cells behaviour. Sci. Rep. 6, 30150 (2016).
Z. Fereshteh, M. Fathi, A. Bagri, and A.R. Boccaccini: Preparation and characterization of aligned porous PCL/zein scaffolds as drug delivery systems via improved unidirectional freeze-drying method. Mater. Sci. Eng. 68, 613 (2016).
Y.W. Moon, I.J. Choi, Y.H. Koh, and H.E. Kim: Porous alumina ceramic scaffolds with biomimetic macro/micro-porous structure using three-dimensional (3-D) ceramic/camphene-based extrusion. Ceram. Int. 41, 12371 (2015).
H. Bai, F. Walsh, B. Gludovatz, B. Delattre, C. Huang, Y. Chen, A.P. Tomsia, and R.O. Ritchie: Bioinspired hydroxyapatite/poly(methyl methacrylate) composite with a nacre-mimetic architecture by a bidirectional freezing method. Adv. Mater. 28, 50 (2016).
S. Das, M. Sharma, D. Saharia, K.K. Sarma, M.G. Sarma, B.B. Borthakur, and U. Bora: Data in support of in vivo studies of silk based gold nano-composite conduits for functional peripheral nerve regeneration. Data Breif 4, 315 (2015).
J.K. Wise, A.L. Yarin, C.M. Megaridis, and M. Cho: Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on oriented nanofibrous scaffolds: engineering the superficial zone of articular cartilage. Tissue Eng. Part A 15, 913 (2009).
V. Chaurey, F. Block, Y.H. Su, P.C. Chiang, E. Botchwey, C.F. Chou, and N.S. Swami: Nanofiber size-dependent sensitivity of fibroblast directionality to the methodology for scaffold alignment. Acta Biomater. 8, 3982 (2012).
J.I. Kim, T.I. Hwang, L.E. Aguilar, C.H. Park, and C.S.A. Kim: Controlled design of aligned and random nanofibers for 3D bi-functionalized nerve conduits fabricated via a novel electrospinning set-up. Sci. Rep. 6, 23761 (2016).
C.Y. Wang, K.H. Zhang, C.Y. Fan, X.M. Mo, H.J. Ruan, and F.F. Li: Aligned natural-synthetic polyblend nanofibers for peripheral nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 7, 634 (2011).
S.H. Park, M.S. Kim, B. Lee, J.H. Park, H.J. Lee, N.K. Lee, N.L. Jeon, and K.Y. Suh: Creation of a hybrid scaffold with dual configuration of aligned and random electrospun fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 2826 (2016).
J. Feng, D. Zhang, M. Zhu, and C. Gao: Poly(L-lactide) melt spun fiber-aligned scaffolds coated with collagen or chitosan for guiding the directional migration of osteoblasts in vitro. J. Mater. Chem. B 5, 5176 (2017).
A. Fernandez, S. Torres-Giner, and J.M. Lagaron: Novel route to stabilization of bioactive antioxidants by encapsulation in electrospun fibers of zein prolamine. Food Hydrocoll. 23, 1427 (2009).
N. Mamidi, H.M. Leija, J. Villela, L. Isenhart, E.V. Barrera, and A. Elías: Fabrication of gelatin-poly(epichlorohydrin-co-ethylene oxide) fiber scaffolds by Forcespinning® for tissue engineering and drug release. MRS Commun. 7, 913 (2017).
S.Ö. Gönen, M. Erol, and S. Küçükbayrak: Evaluation of the factors influencing the resultant diameter of the electrospun gelatin/sodium alginate nanofibers via Box-Behnken design. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 58, 709 (2016).
E. Corradini, P.S. Curti, A.B. Meniqueti, A.F. Martins, A.F. Rubira, and E.C. Muniz: Recent advances in food-packing, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of zein and zein-based materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 22438 (2014).
R. Paliwal and S. Palakurthi: Zein in controlled drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 189, 108 (2014).
K. Sarkar, C. Gomez, S. Zambrano, M. Ramirez, E. De Hoyos, H. Vasquez, and K. Lozano: Electrospinning to Forcespinning™. Mater. Today 13, 12 (2010).
C. Guo, L. Zhou, and J. Lv: Effects of expandable graphite and modified ammonium polyphosphate on the flame-retardant and mechanical properties of wood flour-polypropylene composites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 21, 449 (2013).
W. Kong, Y. Zhao, X. Xiao, C. Jin, Y. Liu, and Z. Li: Comparison of anti-bacterial activity of four kinds of alkaloids in Rhizoma coptidis based on microcalorimetry. Chin. J. Chem. 27, 1186 (2009).
H.H. Yu, K.J. Kim, J.D. Cha, H.K. Kim, Y.E. Lee, N.Y. Choi, and Y.O. You: Antimicrobial activity of berberine alone and in combination with ampicillin or oxacillin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Food 8, 254 (2005).
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologίa de Mexico (CONACyT; Project Number 242269) for financial support. The authors thank Dr. Karina Del Angel for water contact angle.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamidi, N., Romo, I.L., Leija Gutiérrez, H.M. et al. Development of forcespun fiber-aligned scaffolds from gelatin-zein composites for potential use in tissue engineering and drug release. MRS Communications 8, 885–892 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.89
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.89