Abstract
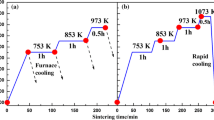
Thorium dioxide (thoria, ThO2) is used in refractory applications and as nuclear fuel. Its melting temperature, the highest of any binary oxide, makes it a difficult system to process. Here we report on the effects of flash sintering on the densification of thoria. We found 95% of theoretical density is obtained at ~950 °C (~30% of the melting temperature) with an electric field of 800 V/cm. Variation in power density had a minimal effect on the densification. Scanning electron microscopy images show the effects of flash sintering on grain size as a function of electric field.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Ronchi and J.P. Hiernaut: Experimental measurement of pre-melting and melting of thorium dioxide. J. Alloys Compd. 240, 179–;185 (1996).
S. Peterson, R.E. Adams, and D.A. Douglas: Properties of thorium, its alloys, and its compounds. In Utilization of Thorium in Power Reactors, International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Technical reports series No. 52 (IAEA, Vien.a. Austria, 1966), pp. 292–;312.
L.B. Amgaonkar, M.V. Rathod, A.P. Pardey, and S.P. Khandait: Thorium as a nuclear fuel. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Technol. AGNIPANKH-15, 48 (2015).
J.M. Pope and K.C. Radford: Physical properties of some thoria powders and their influence on sinterability. J. Nucl. Mater. 52, 241–;254 (1974).
A. Baena, T. Cardinaels, J. Vleugels, K. Binnemans, and M. Verwerft: Activated sintering of ThO2 with Al2O3 under reducing and oxidizin conditions. J. Nucl. Mater. 470, 34–;43 (2016).
K. Ananthasivan, S. Balakrishnan, S. Anthonysamy, R. Divakar, E. Mohandas, and V. Ganesan: Synthesis and sintering of nanocrystalline thoria doped with CaO and MgO derived through oxalate-deagglomeration. J. Nucl. Mater. 434, 223–;229 (2013).
V. Chandramouli, S. Anthonysamy, P.R. Vasudeva Rao, R. Divakar, and D. Sundararaman: PVA aided microwave synthesis: a novel route for the production of nanocrystalline thoria powder. J. Nucl. Mater. 231, 213–;220 (1996).
P. Balakrishna, B.P. Varma, T.S. Krishnan, T.R.R. Mohan, and P. Ramakrishnan: Thorium-oxide—calcination, compaction and sintering. J. Nucl. Mater. 160, 88–;94 (1988).
P. Balakrishna, B.P. Varma, T.S. Krishnan, T.R.R. Mohan, and P. Ramakrishnan: Low-temperature sintering of thoria. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 7, 657–;660 (1988).
K. Ananthasivan, S. Anthonysamy, C. Sudha, A.L.E. Terrance, and P.R.V. Rao: Thoria doped with cations of group VB-synthesis and sintering. J. Nucl. Mater. 300, 217–;229 (2002).
H. Muta, Y. Murakami, M. Uno, K. Kurosaki, and S. Yamanaka: Thermophysical properties of Th1-xUxO2 pellets prepared by spark plasma sintering technique. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 50, 181–;187 (2013).
V. Tyrpekl, M. Cologna, D. Robba, and J. Somers: Sintering behaviour of nanocrystalline ThO2 powder using spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 767–;772 (2016).
A.M. Raftery, J.G. Pereira da Silva, D.D. Byler, D.A. Andersson, B.P. Uberuaga, C.R. Stanek, and K.J. McClellan: Onset conditions for flash sintering of UO2. J. Nucl. Mater. 493, 264–;270 (2017).
M. Cologna, B. Rashkova, and R. Raj: Flash sintering of nanograin zirconia in < 5 s at 850 °C. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 3556–;3559 (2010).
J.S.C. Francis, M. Cologna, and R. Raj: Particle size effects in flash sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 3129–;3136 (2012).
M. Cologna, J.S.C. Francis, and R. Raj: Field assisted and flash sintering of alumina and its relationship to conductivity and MgO-doping. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 2827–;2837 (2011).
S. Kim, S.L. Kang, and I. Chen: Electro-sintering of yttria-stabilized cubic zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1398–;1406 (2013).
W. Rheinheimer, M. Fülling, and M.J. Hoffmann: Grain growth in weak electric fields in strontium titanate: grain growth acceleration by defect redistribution. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 2773–;2780 (2016).
W. Qin, H. Majidi, J. Yun, and K. van Benthem: Electrode effects on microstructure formation during FLASH sintering of yttrium-stabilized zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2253–;2259 (2016).
J.G. Pereira da Silva, H.A. Al-Qureshi, F. Keil, and R. Janssen: A dynamic bifurcation criterion for thermal runaway during the flash sintering of ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 1261–;1267 (2016).
R.I. Todd, E. Zapata-Solvas, R.S. Bonilla, T. Sneddon, and P.R. Wilshaw: Electrical characteristics of flash sintering: thermal runaway of Joule heating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 1865–;1877 (2015).
Y. Dong and I. Chen: Predicting the onset of flash sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 2333–;2335 (2015).
Y. Dong and I.W. Chen: Onset criterion for flash sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 3624–;3627 (2015).
S.K. Jha, J.M. Lebrun, and R. Raj: Phase transformation in the alumina-;titania system during flash sintering experiments. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 733–;739 (2016).
J.A. Downs and V.M. Sglavo: Electric field assisted sintering of cubic zirconia at 390 degrees C. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1342–;1344 (2013).
A.L.G. Prette, M. Cologna, V. Sglavo, and R. Raj: Flash-sintering of Co2MnO4 spinel for solid oxide fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 196, 2061–;2065 (2011).
R.W.G. Wyckoff: Crystal Structures (John Wiley, New York, 1963).
H.S. Maiti and E.C. Subbarao: Electrical-conduction in CaO-doped thoria electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 123, 1713–;1718 (1976).
W.E. Danforth and F.H. Morgan: Electrical resistance of thoria. Phys. Rev. 79, 142–;144 (1950).
M. Iqbal and E.H. Baker: Conductivity measurements on thoria and thoria—yttria solid solutions at high oxygen pressures. High Temp. Press. 5, 265–;271 (1973).
A. Hammou and C. Deportes: Electrical conductivity and defect structure in thorium-dioxide at high-temperature: study of ionic and electronic conductivities. J. Chime Phys. Phys.-Chim. Biol. 71, 1071–;1080 (1974).
M. Aizenshtein, T.Y. Shvareva, and A. Navrotsky: Thermochemistry of lanthana- and yttria-dope thorial. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 4142–;4147 (2010).
P.L. Chen and I.W. Chen: Role of defect interaction in boundary mobility and cation diffusivity of CeO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77, 2289–;2297 (1994).
P.L. Chen and I.W. Chen: Grain boundary mobility in Y2O3: defect mechanism and dopant effects. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1801–;1809 (1996).
P.L. Chen and I.W. Chen: Grain growth in CeO2: dopant effects, defect mechanism, and solute drag. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1793–;1800 (1996).
Y. Dong, H. Wang, and I.W. Chen: Electrical and hydrogen reduction enhances kinetics in doped zirconia and ceria I. Grain growth study. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 876–;886 (2017).
M. Biesuz and V.M. Sglavo: Flash sintering of alumina: effect of different operating conditions on densification. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 2535–;2542 (2016).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Roger Russell and Toby Tung for their help with the experimental setup, the Clemson University Electron Microscopy Laboratory for allowing us to utilize their SEMs, and Brian Powell for his assistance in acquiring the electron images. In addition, we acknowledge NSF support for the REU on Advanced Materials for Environmental Sustainability under grant EEC 1156762 which funded one ofthe authors (S. A.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Materials
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.70.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Straka, W., Amoah, S. & Schwartz, J. Densification of thoria through flash sintering. MRS Communications 7, 677–682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.70
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.70