Abstract
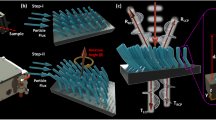
Plasmonic waveguides can transport light while still confining it beyond the diffraction limit. Recently, crossing plasmonic waveguides have been suggested for the implementation of higher-density optical networks. However, suppressing undesirable scattering at their crossing point is still a challenging task because waveguides in these structures are physically connected. Here, we present an experimental demonstration of surface plasmon propagation on an overcrossing metallic waveguide fabricated by a pick-and-place method. By spatially separating the waveguides, the undesirable interaction at the interconnection can be suppressed. Our approach could be a powerful platform to achieve high-density integration of optical waveguides.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Takahara and T. Kobayashi: Low-dimensional optical waves and nano-optical circuits. Opt. Photonics News 15, 54–59 (2004).
M.L. Brongersma, J.A. Schuller, J. White, Y.C. Jun, S.I. Bozhevolnyi, T. Sondergaard, and R. Zia: Nanoplasmonics: components, devices, and circuits. In Plasmonic Nanoguides and Circuits, edited by S. I. Bozhevolnyi (Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore, 2009), 405–438.
W.L. Barnes, A. Dereux, and T.W. Ebbesen: Surface plasmon subwave-length optics. Nature 424, 824–830 (2003).
M.L. Brongersma and V.M. Shalaev: The case for plasmonics. Science 328, 440–441 (2010).
M. Miyata and J. Takahara: Excitation control of long-range surface plas-mons by two incident beams. Opt. Express 20, 9493–9500 (2012).
J. Takahara, S. Yamagishi, H. Taki, A. Morimoto, and T. Kobayashi: Guiding of a one-dimensional optical beam with nanometer diameter. Opt. Lett. 22, 475–477 (1997).
P. Berini: Plasmon-polariton modes guided by a metal film of finite width. Opt. Lett. 24, 1011–1013 (1999).
G. Veronis and S. Fan: Guided subwavelength plasmonic mode supported by a slot in a thin metal film. Opt. Lett. 30, 3359–3361 (2005).
D.F.P. Pile and D.K. Gramotnev: Channel plasmon-polariton in a triangular groove on a metal surface. Opt. Lett. 29, 1069–1071 (2004).
S. Xiao and N.A. Mortensen: Resonant-tunnelling-assisted crossing for subwavelength plasmonic slot waveguides. Opt. Express 16, 14997–15005 (2008).
Y. Li, C. Xu, C. Zeng, W. Wang, J. Yang, H. Yu, and X. Jiang: Hybrid plasmonic waveguide crossing based on the multimode interference effect. Opt. Commun. 335, 86–89 (2015).
M. Ota, M. Fukuhara, A. Sumimura, M. Ito, T. Aihara, Y. Ishii, and M. Fukuda: Dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polariton crossing waveguides using multimode interference. Opt. Lett. 40, 2269–2272 (2015).
C. Manolatou, S.G. Johnson, S. Fan, P.R. Villeneuve, H.A. Haus, and J.D. Joannopoulos: High-density integrated optics. J. Lightw. Technol. 17, 1682–1692 (1999).
T. Fukazawa, T. Hirano, F. Ohno, and T. Baba: Low loss intersection of Si photonic wire waveguides. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43, 646–647 (2004).
N.C. Lindquist, T.W. Johnson, D.J. Norris, and S.-H. Oh: Monolithic integration of continuously tunable plasmonic nanostructures. Nano Lett. 11, 3526–3530 (2011).
M. Miyata, A. Holsteen, Y. Nagasaki, M.L. Brongersma, and J. Takahara: Gap plasmon resonance in a suspended plasmonic nanowire coupled to a metallic substrate. Nano Lett. 15, 5609–5616 (2015).
J. Wen, P. Banzer, A. Kriesch, D. Ploss, B. Schmauss, and U. Peschel: Experimental cross-polarization detection of coupling far-field light to highly confined plasmonic gap modes via nanoantennas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 101109 (2011).
P.B. Johnson and R.W. Christy: Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 6, 4370–4379 (1972).
E.D. Palik: Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids. Academic Press, New York (1998).
W.L. Barnes: Surface plasmon-polariton length scales: a route to subwavelength optics. J. Opt. A, Pure Appl. Opt. 8, S87–S93 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research B (no. 25286007) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan (MEXT). M. M. is supported by Research Fellowships of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) for Young Scientists. Y. N. is supported by Interactive Materials Science Cadet Program of Osaka University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagasaki, Y., Miyata, M., Higuchi, M. et al. Surface plasmon propagation on overcrossing metallic waveguides fabricated by a pick-and-place method. MRS Communications 5, 587–591 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2015.80
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2015.80