Abstract
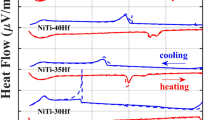
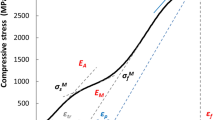
In this study, Vickers indentation was used to investigate the two-way shape-memory effect (TWSME) in an austenitic Ti-50.9 at.% Ni alloy, exposed to different heat treatments. Three aging treatments were used to manipulate the size of Ti3Ni4 precipitates. All samples were Vickers indented, and the indent depth was investigated as function of thermal cycling. The TWSME was found only in the material aged at 400 °C, which contained coherent precipitates. Thermal cycling shows stable TWSME, however, heating well above the austenite finish temperature lead to permanent austenitic protrusions. The results indicate that stabilized martensite plays a critical role in creating TWSME surfaces.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Shaw and S. Kyriakides: Thermomechanical aspects of NiTi. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 43, 1243–1281 (1995).
K. Otsuka and X. Ren: Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 50, 511–678 (2005).
Y.J. Zhang, Y.T. Cheng, and D.S. Grummon: Shape memory surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 041912 (2006).
Y.J. Zhang, Y.T. Cheng, and D.S. Grummon: Understanding indentation-induced two-way shape memory effect. J. Mater. Res. 22, 2851–2855 (2007).
X.L. Fei, Y.J. Zhang, D.S. Grummon, and Y.T. Cheng: Indentation-induced two-way shape memory surfaces. J. Mater. Res. 24, 823–830 (2009).
E. Qin, N.J. Peter, M. Frensemeier, C.P. Frick, E. Arzt, and A.S. Schneider: Vickers indentation induced one-way and two-way shape memory effect in austenitic NiTi. Adv. Eng. Mater. 16, 72–79 (2014).
K. Gall, H. Sehitoglu, Y.I. Chumlyakov, I.V. Kireeva, and H.J. Maier: The influence of aging on critical transformation stress levels and martensite start temperatures in NiTi: part II—discussion of experimental results. J. Eng. Mater. 121, 28–37 (1999).
K. Gall, H. Sehitoglu, Y.I. Chumlyakov, I.V. Kireeva, and H.J. Maier: The influence of aging on critical transformation stress levels and martensite start temperatures in NiTi: part I—aged microstructure and micro-mechanical modeling. J. Eng. Mater. 121, 19–27 (1999).
Y.N. Liu, H. Yang, and A. Voigt: Thermal analysis of the effect of aging on the transformation behaviour of Ti-50.9 at. % Ni. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 360, 350–355 (2003).
J. Khalil-Allafi, A. Dlouhy, and G. Eggeler: Ni4Ti3-precipitation during aging of NiTi shape memory alloys and its influence on martensitic phase transformations. Acta Mater. 50, 4255–4274 (2002).
C.P. Frick, A.M. Ortega, J. Tyber, A.E.M. Maksound, H.J. Maier, Y.N. Liu, and K. Gall: Thermal processing of polycrystalline NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 405, 34–49 (2005).
W.Y. Ni, Y.T. Cheng, and D.S. Grummon: Recovery of microindents in a nickel-titanium shape-memory alloy: a “self-healing” effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3310–3312 (2002).
G.A. Shaw, D.S. Stone, A.D. Johnson, A.B. Ellis, and W.C. Crone: Shape memory effect in nanoindentation of nickel-titanium thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 257–259 (2003).
K. Otsuka and C.M. Wayman: Shape Memory Materials (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1998).
H.C. Lin, S.K. Wu, T.S. Chou, and H.P. Kao: The effects of cold-rolling on the martensitic-transformation of an equiatomic tini alloy. Acta Metall. Mater. 39, 2069–2080 (1991).
Y.N. Liu and D. Favier: Stabilisation of martensite due to shear deformation via variant reorientation in polycrystalline NiTi. Acta Mater. 48, 3489–3499 (2000).
A.S. Mahmud, H. Yang, S. Tee, G. Rio, and Y. Liu: Effect of annealing on deformation-induced martensite stabilisation of NiTi. Intermetallics 16, 209–214 (2008).
G. Laplanche, J. Pfetzing-Micklich, and G. Eggeler: Orientation dependence of stress-induced martensite formation during nanoindentation in NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 68, 19–31 (2014).
J. Pfetzing, A. Schaefer, C. Somsen, and M.F.-X. Wagner: Nanoindentation of pseudoelastic NiTi shape memory alloys: thermomechanical and micro-structural aspects. Int. J. Mater. Res. 100, 936–942 (2009).
C. Ye and G.J. Cheng: Scalable patterning on shape memory alloy by laser shock assisted direct imprinting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 10042–10046 (2012).
Acknowledgments
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program (FP/2007-2013)/ERC Grant Agreement no. 340929. CPF gratefully acknowledges support of this work from the National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER award (grant no. DMR-1255603), as well as the University of Wyoming International Travel Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frensemeier, M., Arzt, E., Qin, E. et al. Indentation-induced two-way shape-memory effect in aged Ti−50.9 at.% Ni. MRS Communications 5, 77–82 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2014.37
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2014.37