Abstract
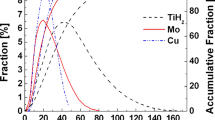
Novel three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical macro- to nano-porous titanium (Ti) and TiMo alloys with sufficient compressive strength (CS) were prepared using NaCl spacer and dealloying methods. The dealloying process was implemented by the heat treatment of TiCu and TiMoCu master alloys in Mg powders. The 3D-hierarchical porous structures were composed of large pores having a mean size of 400 μm with interconnected micro-pores in the size of 10–30 μm, where the pore walls possessed numerous nano-pores with a size range of 10–50 nm. The CS and elastic modulus values were 72.4 MPa and 2.67 GPa as well as 92.62 MPa and 3.36 GPa for Ti and TiMo, respectively. The hierarchical porous structure is beneficial for the fast nucleation of bone-like apatite after immersion in simulated body fluid (SBF). In addition, TiMo samples after NaOH and heat treatments provide better apatite formation after soaking in SBF for a week, in comparison with the samples without treatment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Nakajima: Fabrication, properties and application of porous metals with directional pores. Prog. Mater. Sci. 52, 1091 (2007).
Z.J. Wally, W. van Grunsven, F. Claeyssens, R. Goodall, and G.C. Reilly: Porous titanium for dental implant applications. Metals 5, 1902 (2015).
N.F. Gao and Y. Miyamoto: Joining of Ti3SiC2 with Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Res. 17, 52 (2002).
M. Takemoto, S. Fujibayashi, M. Neo, J. Suzuki, T. Kokubo, and T. Nakamura: Mechanical properties and osteoconductivity of porous bioactive titanium. Biomaterials 26, 6014 (2005).
M. Borowski, A. Traverse, and J.P. Dallas: Structural characterization of Ti implanted AIN. J. Mater. Res. 10, 3136 (1995).
K. Wang: The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 213, 134 (1996).
K.E. Tanner: Titanium in medicine. J. Eng. Med. 216, 215 (2002).
R. Van Noort: Titanium: The implant material of today. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 3801 (1987).
L.M.R. De Vasconcellos, D. De Oliveira Leite, F.O. Nascimento, L.G.O. De Vasconcellos, M.L. De Alencastro Graça, Y.R. Carvalho, and C.A.A. Cairo: Porous titanium for biomedical applications: An experimental study on rabbits. Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 15, 407 (2010).
A. Yamamoto, R. Honma, and M. Sumita: Cytotoxicity evaluation of 43 metal salts using murine fibroblasts and osteoblastic cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 39, 331 (1998).
Y. He, Y. Zhang, Y. Jiang, and R. Zhou: Fabrication and characterization of superelastic Ti-Nb alloy enhanced with antimicrobial Cu via spark plasma sintering for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. 32, 2510 (2017).
E. Luong-Van, I. Rodriguez, H.Y. Low, N. Elmouelhi, B. Lowenhaupt, S. Natarajan, C.T. Lim, R. Prajapati, M. Vyakarnam, and K. Cooper: Review: Micro- and nanostructured surface engineering for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. 28, 165 (2013).
S. Radzi, G. Cowin, M. Robinson, J. Pratap, A. Volp, M.A. Schuetz, and B. Schmutz: Metal artifacts from titanium and steel screws in CT, 1.5 T and 3 T MR images of the tibial Pilon: A quantitative assessment in 3D. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 4, 163 (2014).
Y.T. Sul, C.B. Johansson, S. Petronis, A. Krozer, Y. Jeong, A. Wennerberg, and T. Albrektsson: Characteristics of the surface oxides on turned and electrochemically oxidized pure titanium implants up to dielectric breakdown: The oxide thickness, micropore configurations, surface roughness, crystal structure and chemical composition. Biomaterials 23, 491 (2002).
Y. Chen, B. Feng, Y. Zhu, J. Weng, J. Wang, and X. Lu: Preparation and characterization of a novel porous titanium scaffold with 3D hierarchical porous structures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 22, 839 (2011).
S. Arabnejad, B. Johnston, M. Tanzer, and D. Pasini: Fully porous 3D printed titanium femoral stem to reduce stress-shielding following total hip arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Res. 35, 1774 (2017).
R.A. Ayers, S.J. Simske, T.A. Bateman, A. Petkus, R.L.C. Sachdeva, and V.E. Gyunter: Effect of nitinol implant porosity on cranial bone ingrowth and apposition after 6 weeks. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 45, 42 (1999).
S. Kujala, J. Ryhänen, A. Danilov, and J. Tuukkanen: Effect of porosity on the osteointegration and bone ingrowth of a weight-bearing nickel-titanium bone graft substitute. Biomaterials 24, 4691 (2003).
H.E. Götz, M. Müller, A. Emmel, U. Holzwarth, R.G. Erben, and R. Stangl: Effect of surface finish on the osseointegration of laser-treated titanium alloy implants. Biomaterials 25, 4057 (2004).
Y.C.K. Chen-Wiegart, T. Wada, N. Butakov, X. Xiao, F. De Carlo, H. Kato, J. Wang, D.C. Dunand, and E. Maire: 3D morphological evolution of porous titanium by x-ray micro- and nano-tomography. J. Mater. Res. 28, 2444 (2013).
K. Schwarz and M. Epple: Hierarchically structured polyglycolide–a biomaterial mimicking natural bone. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 19, 613 (1998).
S. Thelen, F. Barthelat, and L.C. Brinson: Mechanics considerations for microporous titanium as an orthopedic implant material. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 69, 601 (2004).
T. Song, M. Yan, and M. Qian: The enabling role of dealloying in the creation of specific hierarchical porous metal structures—A review. Corros. Sci. 134, 78 (2018).
M.H. Sun, S.Z. Huang, L.H. Chen, Y. Li, X.Y. Yang, Z.Y. Yuan, and B.L. Su: Applications of hierarchically structured porous materials from energy storage and conversion, catalysis, photocatalysis, adsorption, separation, and sensing to biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 3479 (2016).
T. Wada, K. Yubuta, A. Inoue, and H. Kato: Dealloying by metallic melt. Mater. Lett. 65, 1076 (2011).
C. Xu, J. Su, X. Xu, P. Liu, H. Zhao, F. Tian, and Y. Ding: Low temperature CO oxidation over unsupported nanoporous gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 42 (2007).
J. Liu, G. Jiang, Y. Liu, J. Di, Y. Wang, Z. Zhao, Q. Sun, C. Xu, J. Gao, A. Duan, J. Liu, Y. Wei, Y. Zhao, and L. Jiang: Hierarchical macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 zeolite hollow fibers with highly efficient catalytic cracking capability. Sci. Rep. 4, 1 (2014).
X.Y. Yang, Y. Li, A. Lemaire, J.G. Yu, and B.L. Su: Hierarchically structured functional materials: Synthesis strategies for multimodal porous networks. Pure Appl. Chem. 81, 2265 (2009).
F. Zhang, L. Wang, P. Li, S. Liu, P. Zhao, G. Dai, and S. He: Preparation of nano to submicro-porous TiMo foams by spark plasma sintering. Adv. Eng. Mater. 19, 1 (2017).
F. Zhang, P. Li, J. Yu, L. Wang, F. Saba, G. Dai, and S. He: Fabrication, formation mechanism and properties of three-dimensional nanoporous titanium dealloyed in metallic powders. J. Mater. Res. 32, 1528 (2017).
F. Zhang, E. Otterstein, and E. Burkel: Spark plasma sintering, microstructures, and mechanical properties of macroporous titanium foams. Adv. Eng. Mater. 12, 863 (2010).
A. Takeuchi, and A. Inoue: Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 46, 2817 (2005).
B. Li and X. Lu: Influence of Ti powder characteristics on the mechanical properties of porous Ti using space holder technique. Acta Metall. Sin. 27, 338 (2014).
M. Hashimoto, S. Kitaoka, S. Muto, K. Tatsumi, and Y. Obata: The microstructure of scale formed by oxynitriding of Ti and exhibiting significant apatite-forming ability. J. Mater. Res. 31, 1004 (2016).
X. Fan, J. Chen, J.P. Zou, Q. Wan, Z.C. Zhou, and J.M. Ruan: Bone-like apatite formation on HA/316L stainless steel composite surface in simulated body fluid. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 19, 347 (2009).
J. Liu, J. Ruan, L. Chang, H. Yang, and W. Ruan: Porous Nb-Ti-Ta alloy scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Fabrication, mechanical properties and in vitro/vivo biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 78, 503 (2017).
X.J. Wang, Y.C. Li, J.G. Lin, P.D. Hodgson, and C.E. Wen: Apatite-inducing ability of titanium oxide layer on titanium surface: The effect of surface energy. J. Mater. Res. 23, 1682 (2008).
R. Rohanizadeh, M. Al-Sadeq, and R.Z. LeGeros: Preparation of different forms of titanium oxide on titanium surface: Effects on apatite deposition. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 71, 343 (2004).
G. Faúndez, M. Troncoso, P. Navarrete, and G. Figueroa: Antimicrobial activity of copper surfaces against suspensions of Salmonella enterica and Campylobacter jejuni. BMC Microbiol. 4, 1 (2004).
V.M. Villapún, L.G. Dover, A. Cross, and S. González: Antibacterial metallic touch surfaces. Materials 9, 1 (2016).
Y.N. Slavin, J. Asnis, U.O. Häfeli, and H. Bach: Metal nanoparticles: Understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 15, 1 (2017).
D.M. Rivera-Chacon, M. Alvarado-Velez, C.Y. Acevedo-Morantes, S.P. Singh, E. Gultepe, D. Nagesha, S. Sridhar, and J.E. Ramirez-Vick: Fibronectin and vitronectin promote human fetal osteoblast cell attachment and proliferation on nanoporous titanium surfaces. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 9, 1092 (2013).
Y. Quan, F. Zhang, H. Rebl, B. Nebe, O. Keßler, and E. Burkel: Ti6Al4 V foams fabricated by spark plasma sintering with post-heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 565, 118 (2013).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1737103), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20161419), Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars at State Education Ministry (No. 2015-1098), and Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Advanced Metallic Materials (No. BM2007204) at Southeast University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saba, F., Garmroudi-Nezhad, E., Zhang, F. et al. Fabrication, mechanical property and in vitro bioactivity of hierarchical macro-/micro-/nano-porous titanium and titanium molybdenum alloys. Journal of Materials Research 35, 2597–2609 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.123
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.123